Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for Mitsubishi Electric FR-D720 K Series
- Page 1 INVERTER FR-D700 INSTRUCTION MANUAL (Applied) FR-D720-0.1K to 15K FR-D740-0.4K to 15K FR-D720S-0.1K to 2.2K FR-D710W-0.1K to 0.75K OUTLINE WIRING PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF THE INVERTER PARAMETERS TROUBLESHOOTING PRECAUTIONS FOR MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION SPECIFICATIONS...
- Page 2 Thank you for choosing this Mitsubishi Electric Inverter. This Instruction Manual (Applied) provides instructions for advanced use of the FR-D700 series inverters. Incorrect handling might cause an unexpected fault. Before using the inverter, always read this Instruction Manual and the Instruction Manual (Basic) [IB-0600438ENG] packed with the product carefully to use the equipment to its optimum performance.
- Page 3 The electronic thermal relay function does not guarantee protection of the motor from overheating. It is iodine, etc.) infiltrate into a Mitsubishi Electric product, the recommended to install both an external thermal and PTC product will be damaged. Halogen-based materials are thermistor for overheat protection.
-
Page 4: Table Of Contents
CONTENTS OUTLINE Product checking and parts identification ......... 2 Inverter and peripheral devices ............3 1.2.1 Peripheral devices .......................... 4 Removal and reinstallation of the cover..........5 1.3.1 Front cover ............................. 5 1.3.2 Wiring cover............................ 7 Installation of the inverter and enclosure design ......8 1.4.1 Inverter installation environment..................... - Page 5 3.1.1 Leakage currents and countermeasures ..................40 3.1.2 EMC measures ..........................42 3.1.3 Power supply harmonics....................... 44 3.1.4 Harmonic suppression guideline in Japan ..................45 Installation of power factor improving reactor........ 47 Power-OFF and magnetic contactor (MC) ........48 Inverter-driven 400V class motor ............. 49 Precautions for use of the inverter ..........
- Page 6 deceleration pattern................. 99 4.7.1 Setting of the acceleration and deceleration time (Pr. 7, Pr. 8, Pr. 20, Pr. 44, Pr. 45) ..................... 99 4.7.2 Starting frequency and start-time hold function (Pr. 13, Pr. 571) ..........101 4.7.3 Acceleration/deceleration pattern (Pr. 29) ................. 102 Selection and protection of a motor ..........
- Page 7 4.14 Energy saving operation ..............150 4.14.1 Optimum excitation control (Pr. 60) ................... 150 4.15 Motor noise, EMI measures, mechanical resonance ....151 4.15.1 PWM carrier frequency and Soft-PWM control (Pr. 72, Pr. 240, Pr. 260)........151 4.15.2 Speed smoothing control (Pr. 653) .................... 152 4.16 Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) ......
- Page 8 4.21.5 Free parameter (Pr. 888, Pr. 889) ..................... 237 4.22 Setting the parameter unit and operation panel ......238 4.22.1 RUN key rotation direction selection (Pr. 40) ................238 4.22.2 PU display language selection (Pr. 145) ................... 238 4.22.3 Operation panel frequency setting/key lock selection (Pr. 161) ..........239 4.22.4 Magnitude of frequency change setting (Pr.
- Page 9 Inspection items ................276 6.1.1 Daily inspection........................... 276 6.1.2 Periodic inspection........................276 6.1.3 Daily and periodic inspection ...................... 277 6.1.4 Display of the life of the inverter parts ..................278 6.1.5 Checking the inverter and converter modules ................279 6.1.6 Cleaning............................
- Page 10 <Abbreviation> /FR-PU07 PU ..............Operation panel and parameter unit (FR-PU04 Inverter .............Mitsubishi Electric inverter FR-D700 series D700 ............Mitsubishi Electric inverter FR-D700 series Pr..............Parameter number (Number assigned to function) PU operation ............Operation using the PU (operation panel/FR-PU04/FR-PU07) External operation ..........Operation using the control circuit signals Combined operation.........Operation using both the PU (operation panel/FR-PU04/FR-PU07) and...
- Page 11 MEMO VIII...
- Page 12 OUTLINE This chapter explains the "OUTLINE" for use of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. Product checking and parts identification ......... 2 Inverter and peripheral devices........... 3 Removal and reinstallation of the cover ........5 Installation of the inverter and enclosure design ...... 8...
-
Page 13: Product Checking And Parts Identification
Product checking and parts identification Product checking and parts identification Unpack the inverter and check the capacity plate on the front cover and the rating plate on the inverter side face to ensure that the product agrees with your order and the inverter is intact. ... -
Page 14: Inverter And Peripheral Devices
Inverter and peripheral devices Inverter and peripheral devices AC power supply Use within the permissible power supply specifications of the inverter. To ensure safety, use a molded case circuit breaker, RS-232C - RS-485 converter is Enclosure surface operation earth leakage circuit breaker or magnetic required when connecting to PC contactor to switch power ON/OFF. -
Page 15: Peripheral Devices
Inverter and peripheral devices 1.2.1 Peripheral devices Check the inverter model of the inverter you purchased. Appropriate peripheral devices must be selected according to the capacity. Refer to the following list and prepare appropriate peripheral devices. Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) Input Side Magnetic or Earth Leakage Circuit Reactor... -
Page 16: Removal And Reinstallation Of The Cover
Removal and reinstallation of the cover Removal and reinstallation of the cover 1.3.1 Front cover 3.7K or lower Removal (Example of FR-D740-1.5K) 1) Loosen the mounting screws of the front cover. (The screws cannot be removed.) 2) Remove the front cover by pulling it like the direction of arrow. Mounting screw Reinstallation (Example of FR-D740-1.5K) 1) Place the front cover in front of the inverter, and install it straight. - Page 17 Removal and reinstallation of the cover 5.5K or higher Removal (Example of FR-D740-7.5K) 1) Loosen the mounting screws of the front cover. (The screws cannot be removed.) 2) Remove the front cover by pulling it like the direction of arrow with holding the installation hook on the front cover. Installation hook Mounting screw...
-
Page 18: Wiring Cover
Removal and reinstallation of the cover 1.3.2 Wiring cover Removal and reinstallation 3.7K or lower Hold the side of the wiring cover, and pull it downward for Also pull the wiring cover downward by holding a removal. frontal part of the wiring cover. To reinstall, fit the cover to the inverter along the guides. -
Page 19: Installation Of The Inverter And Enclosure Design
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design Installation of the inverter and enclosure design When an inverter enclosure is to be designed and manufactured, heat generated by contained equipment, etc., the environment of an operating place, and others must be fully considered to determine the enclosure structure, size and equipment layout. - Page 20 Installation of the inverter and enclosure design Dust, dirt, oil mist Dust and dirt will cause such faults as poor contact of contact points, reduced insulation or reduced cooling effect due to moisture absorption of accumulated dust and dirt, and in-enclosure temperature rise due to clogged filter. In the atmosphere where conductive powder floats, dust and dirt will cause such faults as malfunction, deteriorated insulation and short circuit in a short time.
-
Page 21: Cooling System Types For Inverter Enclosure
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design 1.4.2 Cooling system types for inverter enclosure From the enclosure that contains the inverter, the heat of the inverter and other equipment (transformers, lamps, resistors, etc.) and the incoming heat such as direct sunlight must be dissipated to keep the in-enclosure temperature lower than the permissible temperatures of the in-enclosure equipment including the inverter. -
Page 22: Inverter Placement
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design 1.4.3 Inverter placement Installation of the inverter Enclosure surface mounting Remove the front cover and wiring cover to mount the inverter to the surface. (Remove the covers in the directions of the arrows.) FR-D720-0.1K to 0.75K FR-D720-1.5K to 3.7K FR-D720-5.5K to 15K... - Page 23 Installation of the inverter and enclosure design (3) Inverter mounting orientation Mount the inverter on a wall as specified. Do not mount it horizontally or any other way. (4) Above inverter Heat is blown up from inside the inverter by the small fan built in the unit. Any equipment placed above the inverter should be heat resistant.
-
Page 24: Wiring
WIRING This chapter describes the basic "WIRING" for use of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. Wiring..................... 14 Main circuit terminal specifications ..........15 Control circuit specifications ............20 Connection of stand-alone option unit ........31... -
Page 25: Terminal Connection Diagram
Wiring Wiring 2.1.1 Terminal connection diagram 1. DC reactor (FR-HEL) When connecting a DC reactor, remove the Sink logic jumper across P1 and P/+ *6 Terminal P1 is not available for Main circuit terminal Single-phase 100V power input model is not single-phase 100V power input model. -
Page 26: Main Circuit Terminal Specifications
Main circuit terminal specifications Main circuit terminal specifications 2.2.1 Specification of main circuit terminal Terminal Terminal Name Description Symbol R/L1, Connect to the commercial power supply. S/L2, AC power input Keep these terminals open when using the high power factor converter (FR-HC2) or T/L3 ... - Page 27 Main circuit terminal specifications Three-phase 400V class FR-D740-0.4K to 3.7K FR-D740-5.5K, 7.5K Jumper Jumper N/- P/+ R/L1 S/L2 T/L3 R/L1 S/L2 T/L3 P/+ PR Power supply Motor Power supply Motor FR-D740-11K, 15K P/+ PR R/L1 S/L2 T/L3 Jumper Power supply Motor Single-phase 200V class FR-D720S-0.1K to 0.75K...
-
Page 28: Cables And Wiring Length
Main circuit terminal specifications 2.2.3 Cables and wiring length Applied wire size Select the recommended cable size to ensure that a voltage drop will be 2% or less. If the wiring distance is long between the inverter and motor, a main circuit cable voltage drop will cause the motor torque to decrease especially at the output of a low frequency. - Page 29 Main circuit terminal specifications (2) Earthing (Grounding) precautions Always earth (ground) the motor and inverter. 1) Purpose of earthing (grounding) Generally, an electrical apparatus has an earth (ground) terminal, which must be connected to the ground before use. An electrical circuit is usually insulated by an insulating material and encased. However, it is impossible to manufacture an insulating material that can shut off a leakage current completely, and actually, a slight current flow into the case.
- Page 30 Main circuit terminal specifications Total wiring length The overall wiring length for connection of a single motor or multiple motors should be within the value in the table below. Cable Pr. 72 Setting 3.7K Voltage Class 0.1K 0.2K 0.4K 0.75K 1.5K 2.2K Type...
-
Page 31: Control Circuit Specifications
Control circuit specifications Control circuit specifications 2.3.1 Control circuit terminal indicates that terminal functions can be selected using Pr. 178 to Pr. 182, Pr. 190, Pr. 192, Pr. 197 (I/O terminal function selection). (Refer to page 116.) (1) Input signal Terminal Refer to Type... - Page 32 Control circuit specifications NOTE Set Pr. 267 and a voltage/current input switch correctly, then input analog signals in accordance with the settings. Applying a voltage with voltage/current input switch in "I" position (current input is selected) or a current with switch in "V"...
-
Page 33: Changing The Control Logic
Control circuit specifications 2.3.2 Changing the control logic The input signals are set to sink logic (SINK) when shipped from the factory. To change the control logic, the jumper connector above the control terminal must be moved to the other position. Change the jumper connector in the sink logic (SINK) position to source logic (SOURCE) position using tweezers, a pair of long-nose pliers etc. - Page 34 Control circuit specifications (1) Sink logic type and source logic type In sink logic, a signal switches ON when a current flows from the corresponding signal input terminal. Terminal SD is common to the contact input signals. Terminal SE is common to the open collector output signals. In source logic, a signal switches ON when a current flows into the corresponding signal input terminal.
-
Page 35: Wiring Of Control Circuit
Control circuit specifications 2.3.3 Wiring of control circuit (1) Standard control circuit terminal layout Recommend wire size: 0.3mm to 0.75mm RUN SE S1 S2 SC STF STR (2) Wiring method Wiring Use a blade terminal and a wire with a sheath stripped off for the control circuit wiring. For a single wire, strip off the sheath of the wire and apply directly. - Page 36 Control circuit specifications 3) Insert the wire into a socket. When using a single wire or a stranded wire without a blade terminal, push an open/close button all the way down with a flathead screw driver, and insert the wire. Open/close button Flathead screwdriver NOTE...
- Page 37 Control circuit specifications (4) Signal inputs by contactless switches The contacted input terminals of the inverter (STF, STR, RH, RM, RL) can be controlled using a transistor +24V instead of a contacted switch as shown on the right. STF, etc. Inverter External signal input using transistor (5) Wiring instructions...
-
Page 38: Safety Stop Function
Circuit Output signals differ by the setting of Pr. 190, Pr. 192 and Pr. 197 (Output terminal function selection). MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MELSEC Safety relay module Input signals differ by the setting of Pr. 178 to Pr. 182 QS90SR2SN-Q (Input terminal function selection). - Page 39 Control circuit specifications (3) Safety stop function operation Input Signal Internal Output Signal Input Power Safety Inverter Operation State S1-SC S2-SC SAFE SAFE2 Circuit --- -- --- -- - ---- Output shutoff (Safe state) No failure Drive enabled Short Short Failure...
-
Page 40: Connection To The Pu Connector
Control circuit specifications 2.3.5 Connection to the PU connector Using the PU connector, you can perform communication operation from the parameter unit (FR-PA07), enclosure surface operation panel (FR-PA07), or a personal computer, etc. Parameter setting and monitoring can be performed by FR Configurator (FR-SW3-SETUP-W). Remove the inverter front cover when connecting. - Page 41 When the PU connector is connected with a personal, FA or other computer by a communication cable, a user program can run and monitor the inverter or read and write to parameters. The protocol can be selected from Mitsubishi Electric inverter and MODBUS RTU. PU connector pin-outs ...
-
Page 42: Connection Of Stand-Alone Option Unit
Connection of stand-alone option unit Connection of stand-alone option unit The inverter accepts a variety of stand-alone option units as required. Incorrect connection will cause inverter damage or accident. Connect and operate the option unit carefully in accordance with the corresponding option unit manual. 2.4.1 Connection of a dedicated external brake resistor (MRS type, MYS type, FR-ABR) Install a dedicated brake resistor (MRS type, MYS type, FR-ABR) outside when the motor driven by the inverter is made to run... - Page 43 (Always install a thermal relay when using a brake resistor whose capacity is 11K or higher.) When the power supply is 400V class, install a step-down transformer. Power Thermal Relay Type Supply Brake Resistor (Mitsubishi Electric Rated Operating Current Voltage product) MRS120W200 TH-T25-0.7A...
-
Page 44: Connection Of The Brake Unit (Fr-Bu2)
Connection of stand-alone option unit 2.4.2 Connection of the brake unit (FR-BU2) Connect the brake unit (FR-BU2(-H)) as shown below to improve the braking capability at deceleration. If the transistors in the brake unit should become faulty, the resistor can be unusually hot. To prevent unusual overheat and fire, install a magnetic contactor on the inverter's input side to configure a circuit so that a current is shut off in case of fault. - Page 45 Connection of stand-alone option unit (2) Connection example with the FR-BR(-H) type resistor FR-BR MCCB Motor R/L1 Three-phase AC S/L2 power supply T/L3 FR-BU2 Inverter 10m or less Connect the inverter terminals (P/+ and N/-) and brake unit (FR-BU2) terminals so that their terminal names match with each other. (Incorrect connection will damage the inverter and brake unit.) ...
-
Page 46: Connection Of The High Power Factor Converter (Fr-Hc2)
Connection of stand-alone option unit 2.4.3 Connection of the high power factor converter (FR-HC2) When connecting the high power factor converter (FR-HC2) to suppress power harmonics, perform wiring securely as shown below. Incorrect connection will damage the FR-HC2 and the inverter. After making sure that the wiring is correct and secure, set the rated motor voltage value in Pr. -
Page 47: Connection Of The Power Regeneration Common Converter (Fr-Cv)
Connection of stand-alone option unit 2.4.4 Connection of the power regeneration common converter (FR-CV) When connecting the power regeneration common converter (FR-CV), connect the inverter terminals (P/+ and N/-) and power regeneration common converter (FR-CV) terminals as shown below so that their symbols match with each other. After making sure that the wiring is correct, set "2"... -
Page 48: Connection Of A Dc Reactor (Fr-Hel)
Connection of stand-alone option unit 2.4.5 Connection of a DC reactor (FR-HEL) (1) Keep the surrounding air temperature within the permissible range (-10C to +50C). Keep enough clearance around the reactor because it heats up. (Take 10cm or more clearance on top and bottom and 5cm or more on left and right regardless of the installation direction.) 10cm or more 5cm or... - Page 49 MEMO...
-
Page 50: Precautions For Use Of The Inverter
PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF THE INVERTER This chapter explains the "PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF THE INVERTER" for use of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. EMC and leakage currents ............40 Installation of power factor improving reactor ......47 Power-OFF and magnetic contactor (MC) ......... -
Page 51: Emc And Leakage Currents
Especially for a completely electromagnetic MCCB, one of a slightly large capacity must be selected since its operation characteristic varies with harmonic currents. (Check it in the data of the corresponding breaker.) As an earth leakage current breaker, use the Mitsubishi Electric earth leakage current breaker designed for harmonics and surge suppression. - Page 52 EMC and leakage currents Selection of rated sensitivity current of earth (ground) leakage current breaker When using the earth leakage current breaker with the inverter circuit, select its rated sensitivity current as follows, independently of the PWM carrier frequency. Breaker designed for harmonic and Ig1, Ig2: Leakage currents in wire path during commercial surge suppression...
-
Page 53: Emc Measures
EMC and leakage currents 3.1.2 EMC measures Some electromagnetic noises enter the inverter to malfunction it and others are radiated by the inverter to malfunction peripheral devices. Though the inverter is designed to have high immunity performance, it handles low-level signals, so it requires the following basic techniques. -
Page 54: Precautions For Use Of The Inverter
EMC and leakage currents Propagation Path Measures When devices that handle low-level signals and are liable to malfunction due to electromagnetic noises, e.g. instruments, receivers and sensors, are contained in the enclosure that contains the inverter or when their signal cables are run near the inverter, the devices may malfunction due to air-propagated electromagnetic noises. -
Page 55: Power Supply Harmonics
EMC and leakage currents 3.1.3 Power supply harmonics The inverter may generate power supply harmonics from its converter circuit to affect the power generator, power capacitor etc. Power supply harmonics are different from noise and leakage currents in source, frequency band and transmission path. Take the following countermeasure suppression techniques. -
Page 56: Harmonic Suppression Guideline In Japan
EMC and leakage currents 3.1.4 Harmonic suppression guideline in Japan Inverters have a converter section (rectifier circuit) and generate a harmonic current. Harmonic currents flow from the inverter to a power receiving point via a power transformer. The Harmonic Suppression Guidelines was established to protect other consumers from these outgoing harmonic currents. - Page 57 EMC and leakage currents Table 4 Harmonic Contents (Values at the fundamental current of 100%) Reactor 11th 13th 17th 19th 23rd 25th Not used Three-phase bridge Used (AC side) 14.5 Used (DC side) (Capacitor smoothing) Used (AC, DC sides) Single-phase bridge ...
-
Page 58: Installation Of Power Factor Improving Reactor
Installation of power factor improving reactor Installation of power factor improving reactor When the inverter is connected near a large-capacity power transformer (500kVA or more) or when a power capacitor is to be switched over, an excessive peak current may flow in the power input circuit, damaging the converter circuit. To prevent this, always install an optional AC reactor (FR-HAL). -
Page 59: Power-Off And Magnetic Contactor (Mc)
Power-OFF and magnetic contactor (MC) Power-OFF and magnetic contactor (MC) (1) Inverter input side magnetic contactor (MC) On the inverter input side, it is recommended to provide an MC for the following purposes. (Refer to page 4 for selection.) 1) To release the inverter from the power supply when the fault occurs or when the drive is not functioning (e.g. emergency stop operation). -
Page 60: Inverter-Driven 400V Class Motor
Inverter-driven 400V class motor Inverter-driven 400V class motor In the PWM type inverter, a surge voltage attributable to wiring constants is generated at the motor terminals. Especially for a 400V class motor, the surge voltage may deteriorate the insulation. When the 400V class motor is driven by the inverter, consider the following measures: Measures ... -
Page 61: Precautions For Use Of The Inverter
Provide a common mode choke on the output side of the inverter. (This is effective regardless of the use of the capacitive filter.) Mitsubishi Electric capacitive filter: FR-BIF, SF[], FR-E5NF-[], FR-S5NFSA[], FR-BFP2-[] ® Recommended common mode choke: FT-3KM F series FINEMET common mode choke cores manufactured by Hitachi Metals, Ltd. - Page 62 Precautions for use of the inverter (10) A short circuit or earth (ground) fault on the inverter output side may damage the inverter modules. Fully check the insulation resistance of the circuit prior to inverter operation since repeated short circuits may damage ...
- Page 63 Precautions for use of the inverter (19) Instructions for overload operation When performing operation of frequent start/stop of the inverter, rise/fall in the temperature of the transistor element of the inverter will repeat due to a repeated flow of large current, shortening the life from thermal fatigue. Since thermal fatigue is related to the amount of current, the life can be increased by reducing current at locked condition, starting current, etc.
-
Page 64: Failsafe Of The System Which Uses The Inverter
When a fault occurs, the inverter output is shut off to output a fault signal. However, a fault output signal may not be output at an inverter fault occurrence when the detection circuit or output circuit fails, etc. Although Mitsubishi Electric assures best... - Page 65 Failsafe of the system which uses the inverter 4)Checking the motor operating status by the start signal input to the inverter and inverter output current detection signal. The output current detection (Y12) signal is output when the inverter operates and currents flows in the motor. Check if the Y12 signal is output when inputting the start signal to the inverter (forward signal is STF signal and reverse signal is STR signal).
-
Page 66: Parameters
PARAMETERS This chapter explains the "PARAMETERS" for use of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. The following marks are used to indicate the controls as below..V/F control ..General-purpose magnetic flux vector control GP MFVC GP MFVC GP MFVC (Parameters without any mark are valid for both controls.) -
Page 67: Operation Panel
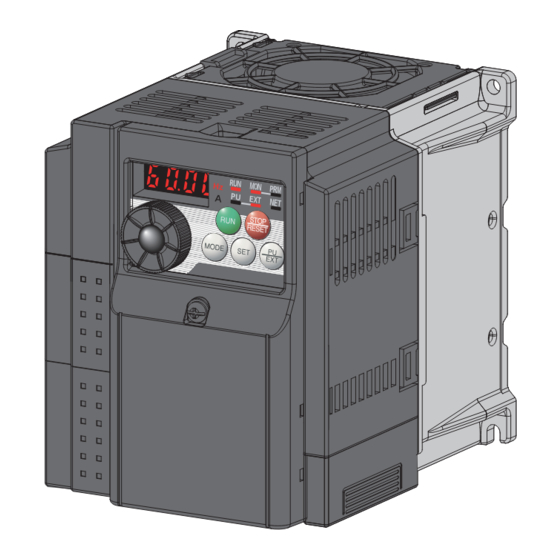
Lit to indicate monitoring mode. etc. Stop operation Setting dial Used to stop Run command. (Setting dial: Mitsubishi Electric inverter Fault can be reset when protective dial) function is activated (fault). Used to change the frequency setting and parameter settings. -
Page 68: Basic Operation (Factory Setting)
Operation panel 4.1.2 Basic operation (factory setting) Operation mode switchover At power-ON (External operation mode) PU Jog operation mode (Example) PU operation mode Value change and frequency appear alternately. (output frequency monitor) Frequency setting has been written and completed. STOP Output current monitor Output voltage monitor The present... -
Page 69: Easy Operation Mode Setting (Easy Setting Mode)
Operation panel 4.1.3 Easy operation mode setting (easy setting mode) Setting of Pr. 79 Operation mode selection according to combination of the start command and speed command can be easily made. Changing Start command: external (STF/STR), frequency command: operate with example Operation Display... -
Page 70: Changing The Parameter Setting Value
Operation panel 4.1.4 Changing the parameter setting value Changing Change the Pr. 1 Maximum frequency setting. example Operation Display Screen at power-ON The monitor display appears. PU indicator is lit. Press to choose the PU operation mode. PRM indicator is lit. Press to choose the parameter setting mode. -
Page 71: Parameter List
Parameter list Parameter list Parameter list 4.2.1 Parameter list For simple variable-speed operation of the inverter, the initial setting of the parameters may be used. Set the necessary parameters to meet the load and operational specifications. Parameter setting, change and check can be made from the operation panel. - Page 72 Parameter list Parameter list Control Mode-based Minimum Refer Instruction Code Parameter Initial Customer Correspondence Table Parameter Name Setting Range Setting Parameter Remarks Value Setting Increments Page Read Write Extended GP MFVC GP MFVC GP MFVC Copy Clear All clear 113, —...
- Page 73 Parameter list Parameter list Control Mode-based Minimum Refer Instruction Code Parameter Initial Customer Correspondence Table Parameter Name Setting Range Setting Parameter Remarks Value Setting Increments Page Read Write Extended GP MFVC GP MFVC GP MFVC Copy Clear All clear Motor capacity 0.1 to 15kW, 9999 0.01kW...
- Page 74 Parameter list Parameter list Control Mode-based Minimum Refer Instruction Code Parameter Initial Customer Correspondence Table Parameter Name Setting Range Setting Parameter Remarks Value Setting Increments Page Read Write Extended GP MFVC GP MFVC GP MFVC Copy Clear All clear Output current detection signal 0 to 10s, 9999 0.1s 0.1s...
- Page 75 Parameter list Parameter list Control Mode-based Minimum Refer Instruction Code Parameter Initial Customer Correspondence Table Parameter Name Setting Range Setting Parameter Remarks Value Setting Increments Page Read Write Extended GP MFVC GP MFVC GP MFVC Copy Clear All clear — Output phase loss protection selection 0, 1 ...
- Page 76 Parameter list Parameter list Control Mode-based Minimum Refer Instruction Code Parameter Initial Customer Correspondence Table Parameter Name Setting Range Setting Parameter Remarks Value Setting Increments Page Read Write Extended GP MFVC GP MFVC GP MFVC Copy Clear All clear ...
- Page 77 Parameter list Parameter list Control Mode-based Minimum Refer Instruction Code Parameter Initial Customer Correspondence Table Parameter Name Setting Range Setting Parameter Remarks Value Setting Increments Page Read Write Extended GP MFVC GP MFVC GP MFVC Copy Clear All clear Pr.CL Parameter clear 0, 1 Pr.CL...
- Page 78 Parameters according to purposes Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor 4.3.1 Manual torque boost (Pr. 0, Pr. 46) ....................77 4.3.2 Acquiring large starting torque and low speed torque (General-purpose magnetic flux vector control (Pr. 71, Pr. 80, Pr. 83, Pr. 84))................. 78 4.3.3 Slip compensation (Pr.
- Page 79 4.10.8 Remote output selection (REM signal, Pr. 495, Pr. 496) ............129 4.11 Monitor display and monitor output signal 4.11.1 Speed display and speed setting (Pr. 37)................... 130 4.11.2 Monitor display selection of DU/PU and terminal FM (Pr. 52, Pr. 54, Pr. 170, Pr. 171, Pr. 268, Pr. 563, Pr. 564, Pr. 891) .......... 131 4.11.3 Reference of the terminal FM (pulse train output) (Pr.
- Page 80 4.19.3 Operation selection at communication error occurrence (Pr. 121, Pr. 122, Pr. 502) ....185 4.19.4 Communication EEPROM write selection (Pr. 342) ..............188 4.19.5 Mitsubishi inverter protocol (computer link communication) ............189 4.19.6 MODBUS RTU communication specifications (Pr. 117, Pr. 118, Pr. 120, Pr. 122, Pr. 343, Pr. 502, Pr. 549) ............ 201 4.20 Special operation and frequency control 4.20.1 PID control (Pr.
-
Page 81: Adjustment Of The Output Torque (Current) Of The Motor
Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Set starting torque manually Manual torque boost Pr. 0, Pr. 46 Automatically control output current General-purpose magnetic Pr. -
Page 82: Acquiring Large Starting Torque And Low Speed Torque (General-Purpose Magnetic Flux Vector Control (Pr. 71, Pr. 80, Pr. 83, Pr. 84))
The motor capacity should be equal to or one rank lower than the inverter capacity (note that the capacity should be 0.1kW or higher). Motor to be used is any of Mitsubishi Electric standard motor (SF-JR 0.2kW or higher), Mitsubishi Electric high efficiency motor (SF-HR 0.2kW or higher),Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor (SF-JRCA 4P, SF-HRCA 0.2kW to 15kW) or Mitsubishi Electric high-performance energy-saving motor (SF-PR). - Page 83 (Pr. 160) (Refer to page 165.) Set "0" in Pr. 160 to display the extended function parameters. Set the motor. (Pr. 71) Pr. 71 Setting Motor Remarks Mitsubishi Electric SF-JR 0 (initial value) standard motor SF-HR Mitsubishi Electric ...
- Page 84 Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor (3) Control method switching by external terminals (X18 signal) Use the V/F switchover signal (X18) to change the control method (V/F control and General-purpose magnetic flux vector control) with external terminal. Turn the X18 signal ON to change the currently selected control method (General-purpose magnetic flux vector control) to V/F control.
-
Page 85: Slip Compensation (Pr. 245 To Pr. 247)
Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor 4.3.3 Slip compensation (Pr. 245 to Pr. 247) Inverter output current may be used to assume motor slip to keep the motor speed constant. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number 0.01 to 50% Rated motor slip... -
Page 86: Stall Prevention Operation (Pr. 22, Pr. 23, Pr. 48, Pr. 66, Pr. 154, Pr. 156, Pr. 157)
Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor 4.3.4 Stall prevention operation (Pr. 22, Pr. 23, Pr. 48, Pr. 66, Pr. 154, Pr. 156, Pr. 157) This function monitors the output current and automatically changes the output frequency to prevent the inverter from coming to trip due to overcurrent, overvoltage, etc. - Page 87 Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor Setting of stall prevention operation level (Pr. 22) Pr. 22 Set in the percentage of the output current to the inverter rated current at which stall prevention operation will Output current be performed.
- Page 88 Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor (4) Setting of stall prevention operation in high frequency range (Pr. 22, Pr. 23, Pr. 66) (Pr. 22 = 150%, Pr. 23 = 100%, Pr. 66 = 60Hz) Setting example Pr. 22 When Pr.
- Page 89 Adjustment of the output torque (current) of the motor Limit the stall prevention operation and fast-response current limit operation according to the operating status (Pr. 156) Refer to the following table and select whether stall prevention operation and fast-response current limit operation will be performed or not and the operation to be performed at OL signal output.
-
Page 90: Limiting The Output Frequency
Limiting the output frequency Limiting the output frequency Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Set upper limit and lower limit of Maximum/minimum Pr. 1, Pr. 2, Pr. 18 output frequency frequency Perform operation by avoiding Frequency jump Pr. -
Page 91: Avoiding Mechanical Resonance Points (Frequency Jumps) (Pr. 31 To Pr. 36, Pr. 552)
Limiting the output frequency 4.4.2 Avoiding mechanical resonance points (frequency jumps) (Pr. 31 to Pr. 36, Pr. 552) When it is desired to avoid resonance attributable to the natural frequency of a mechanical system, these parameters allow resonant frequencies to be jumped. Parameter Name Initial Value... -
Page 92: V/F Pattern
Special care must be taken when "1" (variable torque load) is set in Pr. 14 Load pattern selection. When using the Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor, set Pr. 3 to 60Hz. (2) Set two kinds of base frequencies (Pr. 47) ... - Page 93 V/F pattern Base frequency voltage setting (Pr. 19) Use Pr. 19 Base frequency voltage to set the base voltage (e.g. rated motor voltage). If the setting is less than the power supply voltage (Twice the amount of the power supply voltage for single-phase 100V power input model), the maximum output voltage of the inverter is as set in Pr.
-
Page 94: Load Pattern Selection (Pr. 14)
V/F pattern 4.5.2 Load pattern selection (Pr. 14) Optimum output characteristic (V/F characteristic) for the application and load characteristics can be selected. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number For constant-torque load For variable-torque load For constant-torque elevators Load pattern selection (at reverse rotation boost of 0%) For constant-torque elevators (at forward rotation boost of 0%) - Page 95 V/F pattern Constant-torque load application Pr. 14 = 2 Pr. 14 = 3 (setting "2, 3") For vertical lift loads For vertical lift loads Set "2" when a vertical lift load is fixed as power At forward rotation boost...Pr. 0 (Pr. 46) At forward rotation boost...0% setting At reverse rotation boost...Pr.
-
Page 96: Frequency Setting By External Terminals
Frequency setting by external terminals Frequency setting by external terminals Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Make frequency setting by Pr. 4 to Pr. 6, Pr. 24 to Pr. 27, Multi-speed operation combination of terminals Pr. 232 to Pr. 239 Perform Jog operation Jog operation Pr. - Page 97 Frequency setting by external terminals Multi-speed setting for 4th speed or more (Pr. 24 to Pr. 27, Pr. 232 to Pr. 239) Frequency from 4th speed to 15th speed can be set according to the combination of the RH, RM, RL and REX signals. Set the running frequencies in Pr.
-
Page 98: Jog Operation (Pr. 15, Pr. 16)
Frequency setting by external terminals 4.6.2 Jog operation (Pr. 15, Pr. 16) The frequency and acceleration/deceleration time for Jog operation can be set. Jog operation can be performed in either of the external and the PU operation mode. This operation can be used for conveyor positioning, test operation, etc. Parameter Initial Name... - Page 99 Frequency setting by external terminals Jog operation from PU Select Jog operation mode from the operation panel and PU (FR-PU04/FR-PU07). Operation is performed only while the start button is pressed. Inverter R/L1 Three-phase AC S/L2 Motor power supply T/L3 Operation panel Operation Display Confirmation of the operation status indicator...
-
Page 100: Remote Setting Function (Pr. 59)
Frequency setting by external terminals NOTE When Pr. 29 Acceleration/deceleration pattern selection = "1" (S-pattern acceleration/deceleration A), the acceleration/ deceleration time is the period of time required to reach Pr. 3 Base frequency. The Pr. 15 setting should be equal to or higher than the Pr. 13 Starting frequency. ... - Page 101 Frequency setting by external terminals Remote setting function Use Pr. 59 to select whether the remote setting function is used or not and whether the frequency setting storage function in the remote setting mode is used or not. When Pr. 59 is set to any of "1 to 3" (remote setting function valid), the functions of the RH, RM and RL signals are changed to acceleration (RH), deceleration (RM) and clear (RL).
- Page 102 Frequency setting by external terminals REMARKS During Jog operation or PID control operation, the remote setting function is invalid. Setting frequency is "0" Even when remotely-set frequency is cleared by turning ON the RL (clear) signal after turn Remotely-set frequency stored last time OFF (ON) of both the RH and RM Within 1 minute signals, the inverter operates at...
-
Page 103: Setting Of Acceleration/Deceleration Time And Acceleration/ Deceleration Pattern
Setting of acceleration/deceleration time and acceleration/ deceleration pattern Setting of acceleration/deceleration time and acceleration/ deceleration pattern Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Motor acceleration/deceleration time Acceleration/deceleration Pr. 7, Pr. 8, Pr. 20, Pr. 44, Pr. 45 setting times Starting frequency and start- Starting frequency... - Page 104 Setting of acceleration/deceleration time and acceleration/ deceleration pattern (2) Deceleration time setting (Pr. 8, Pr. 20) Use Pr. 8 Deceleration time to set the deceleration time required to reach 0Hz from Pr. 20 Acceleration/deceleration reference frequency. Set the deceleration time according to the following formula. Deceleration Pr.
-
Page 105: Starting Frequency And Start-Time Hold Function (Pr. 13, Pr. 571)
Setting of acceleration/deceleration time and acceleration/ deceleration pattern 4.7.2 Starting frequency and start-time hold function (Pr. 13, Pr. 571) You can set the starting frequency and hold the set starting frequency for a certain period of time. Set these functions when you need the starting torque or want to smooth motor drive at a start. Parameter Name Initial Value... -
Page 106: Acceleration/Deceleration Pattern (Pr. 29)
Setting of acceleration/deceleration time and acceleration/ deceleration pattern 4.7.3 Acceleration/deceleration pattern (Pr. 29) You can set the acceleration/deceleration pattern suitable for application. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number Linear acceleration/ deceleration Acceleration/deceleration S-pattern acceleration/deceleration A pattern selection S-pattern acceleration/deceleration B The above parameters can be set when Pr. -
Page 107: Selection And Protection Of A Motor
The % value denotes the percentage to the inverter rated output current. It is not the percentage to the motor rated current. When you set the electronic thermal O/L relay dedicated to the Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor, this characteristic curve applies to operation at 6Hz or higher. (Refer to page 106 for the operation characteristic.) NOTE ... - Page 108 Selection and protection of a motor (2) Set two different electronic thermal O/L relays (Pr. 51) Use this function when running two motors of different rated currents individually by a single inverter. (When running two motors together, use external thermal relays.) Set the rated current of the second motor to Pr.
- Page 109 Selection and protection of a motor PTC thermistor protection (Pr. 561) Inverter Motor Terminal 2 and terminal 10 are available for inputting of motor built-in PTC thermistor output. When the PTC thermistor input reaches to the resistance value set in Pr. 561 PTC thermistor protection level, inverter outputs PTC thermistor operation error PTC thermistor input connection signal (E.PTC) and trips.
-
Page 110: Applied Motor (Pr. 71, Pr. 450)
Pr. 71 Pr. 450 Standard Constant-torque (Pr. 71 initial Standard motor (such as SF-JR) value) Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor (such as SF-JRCA) — Mitsubishi Electric high-efficiency motor (SF-HR) — Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor (SF-HRCA) Mitsubishi Electric high-performance ... - Page 111 Set parameters after confirming the function of each terminal. Using the Mitsubishi Electric SF-PR high-performance energy saving motor (Pr. 0, Pr. 14, Pr. 71) To drive the SF-PR motor with a constant-torque load using V/F control, set the following parameters.
-
Page 112: Exhibiting The Best Performance For The Motor (Offline Auto Tuning) (Pr. 71, Pr. 80, Pr. 82 To Pr. 84, Pr. 90, Pr. 96)
Even when motors (other manufacturer's motor, SF-JRC, etc.) other than Mitsubishi Electric standard motor (SF-JR 0.2kW or higher), Mitsubishi Electric high efficiency motor (SF-HR 0.2kW or higher), Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor (SF-JRCA 4P, SF-HRCA 0.2kW to 15kW), or Mitsubishi Electric high-performance energy-saving motor (SF-PR) are used or the wiring length is long (30m or longer as a reference), using the offline auto tuning function runs the motor with the optimum operating characteristics. - Page 113 5) Set Pr. 71 Applied motor according to the motor used. Motor Pr. 71 Setting SF-JR SF-JR 4P 1.5kW or lower Mitsubishi Electric standard motor Mitsubishi Electric high efficiency motor SF-HR Others SF-JRCA 4P Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor SF-HRCA Others (SF-JRC, etc.)
- Page 114 Selection and protection of a motor (3) Execution of tuning POINT Before performing tuning, check the monitor display of the operation panel or parameter unit (FR-PU04/FR-PU07) if the inverter is in the status for tuning. (Refer to 2) below.) When the start command is turned ON under V/F control, the motor starts.
- Page 115 Selection and protection of a motor 3) When offline auto tuning ends, press of the operation panel during PU operation. For External operation, turn OFF the start signal (STF signal or STR signal) once. This operation resets the offline auto tuning and the PU's monitor display returns to the normal indication. (Without this operation, next operation cannot be started.) REMARKS ...
-
Page 116: Motor Brake And Stop Operation
Motor brake and stop operation Motor brake and stop operation Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Motor braking torque adjustment DC Injection brake Pr. 10 to Pr. 12 Improve the motor braking torque with Selection of a Pr. -
Page 117: Selection Of A Regenerative Brake (Pr. 30, Pr. 70)
Motor brake and stop operation REMARKS For the 5.5K and 7.5K, when the Pr. 12 setting is the following, changing the Pr. 71 Applied motor setting automatically changes the Pr. 12 setting. Therefore, it is not necessary to change the Pr. 12 setting. (a) When 4% (initial value) is set in Pr. - Page 118 Motor brake and stop operation (2) Brake resistor (MYS type) used at 100% torque/6%ED (FR-D720-3.7K only) Set "1" in Pr. 30. Set "6%" in Pr. 70. (3) When using the high-duty brake resistor (FR-ABR) (0.4K or higher) Set "1" in Pr. 30. Set Pr.
-
Page 119: Stop Selection (Pr. 250)
Motor brake and stop operation 4.9.3 Stop selection (Pr. 250) Used to select the stopping method (deceleration to a stop or coasting) when the start signal turns OFF. Used to stop the motor with a mechanical brake, etc. together with switching OFF of the start signal. You can also select the operations of the start signals (STF/STR). -
Page 120: Function Assignment Of External Terminal And Control
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10 Function assignment of external terminal and control Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Input terminal function Assign function to input terminal Pr. 178 to Pr. 182 selection Set MRS signal (output shutoff) to MRS input selection Pr. - Page 121 Function assignment of external terminal and control Input terminal function assignment Using Pr. 178 to Pr. 182, set the functions of the input terminals. Refer to the following table and set the parameters: Refer to Setting Signal Function Related Parameters Page Pr.
-
Page 122: Inverter Output Shutoff Signal (Mrs Signal, Pr. 17)
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10.2 Inverter output shutoff signal (MRS signal, Pr. 17) The inverter output can be shut off by the MRS signal. Also, logic for the MRS signal can be selected. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number... -
Page 123: Condition Selection Of Function Validity By Second Function Selection Signal (Rt)
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10.3 Condition selection of function validity by second function selection signal (RT) You can select the second function using the RT signal. When the RT signal turns ON, the second function becomes valid. ... -
Page 124: Start Signal Operation Selection (Stf, Str, Stop Signal, Pr. 250)
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10.4 Start signal operation selection (STF, STR, STOP signal, Pr. 250) You can select the operation of the start signal (STF/STR). Used to select the stopping method (deceleration to a stop or coasting) when the start signal turns OFF. Used to stop the motor with a mechanical brake, etc. - Page 125 Function assignment of external terminal and control Three-wire type (STF, STR, STOP signal) The three-wire connection is shown below. Turning the STOP signal ON makes start self-holding function valid. In this case, the forward/reverse rotation signal is activated only as a start signal. If the start signal (STF or STR) is turned ON and then OFF, the start signal is held and makes a start.
-
Page 126: Output Terminal Function Selection (Pr. 190, Pr. 192, Pr. 197)
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10.5 Output terminal function selection (Pr. 190, Pr. 192, Pr. 197) You can change the functions of the open collector output terminal and relay output terminal. Parameter Initial Name Initial Signal Setting Range Number Value RUN terminal... - Page 127 Function assignment of external terminal and control Setting Refer Related Signal Function Operation Positive Negative Parameter Page logic logic Pr. 127 to Pr. Output when the PID output interruption function is 134, SLEEP PID output interruption executed. Pr. 575 to Pr. SAFE Safety monitor output Output while safety stop function is activated.
- Page 128 Function assignment of external terminal and control (2) Inverter operation ready signal (RY signal) and inverter running signal (RUN signal) Power supply DC injection brake operation point DC injection brake operation Pr. 13 Starting frequency Time Reset processing When the inverter is ready to operate, the output of the operation ready signal (RY) is ON. (It is also ON during inverter running.) ...
- Page 129 Function assignment of external terminal and control Fault output signal (ALM signal) Inverter fault occurrence If the inverter comes to trip, the ALM signal is output. (Trip) Output frequency Time ON OFF Reset processing (about 1s) Reset ON REMARKS ...
-
Page 130: Detection Of Output Frequency (Su, Fu Signal, Pr. 41 To Pr. 43)
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10.6 Detection of output frequency (SU, FU signal, Pr. 41 to Pr. 43) The inverter output frequency is detected and output at the output signals. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number Up-to-frequency 0 to 100% Level where the SU signal turns ON. -
Page 131: Output Current Detection Function (Y12 Signal, Y13 Signal, Pr. 150 To Pr. 153, Pr. 166, Pr. 167)
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10.7 Output current detection function (Y12 signal, Y13 signal, Pr. 150 to Pr. 153, Pr. 166, Pr. 167) The output current during inverter running can be detected and output to the output terminal. Parameter Setting Name... - Page 132 Function assignment of external terminal and control Zero current detection (Y13 signal, Pr. 152, Pr. 153) If the output current remains at the Pr.152 setting or lower during inverter operation for the time set in Pr.153 or longer, the zero current detection (Y13) signal is output from the inverter's open collector or relay output terminal.
-
Page 133: Remote Output Selection (Rem Signal, Pr. 495, Pr. 496)
Function assignment of external terminal and control 4.10.8 Remote output selection (REM signal, Pr. 495, Pr. 496) You can utilize the ON/OFF of the inverter's output signals instead of the remote output terminal of the programmable logic controller. Parameter Initial Setting Name Description... -
Page 134: Monitor Display And Monitor Output Signal
Monitor display and monitor output signal 4.11 Monitor display and monitor output signal Refer to Purpose Parameter that should be Set Page Speed display and speed Display motor speed Pr. 37 Set speed setting Monitor display/PU main Pr. 52, Pr. 54, Pr. 170, Pr. 171, Change PU monitor display data display data selection Pr. -
Page 135: Monitor Display Selection Of Du/Pu And Terminal Fm (Pr. 52, Pr. 54, Pr. 170, Pr. 171, Pr. 268, Pr. 563, Pr. 564, Pr. 891)
Monitor display and monitor output signal 4.11.2 Monitor display selection of DU/PU and terminal FM (Pr. 52, Pr. 54, Pr. 170, Pr. 171, Pr. 268, Pr. 563, Pr. 564, Pr. 891) The monitor to be displayed on the main screen of the operation panel and parameter unit (FR-PU04/FR-PU07) can be selected. - Page 136 Monitor display and monitor output signal Pr. 52 Setting Operation Pr. 54 (FM) Terminal FM Types of Monitor Unit Description panel main Setting Full Scale Value monitor 100V class, Converter output 400V 0.1V 200V class Displays the DC bus voltage value. voltage 400V class 800V Regenerative brake...
- Page 137 Monitor display and monitor output signal Pr. 52 Setting Operation Pr. 54 (FM) Terminal FM Types of Monitor Unit Description panel main Setting Full Scale Value monitor Displays the PTC thermistor resistance at PTC thermistor terminal 2 when PTC thermistor protection ...
- Page 138 Monitor display and monitor output signal (3) Operation panel I/O terminal monitor (Pr. 52) When Pr. 52 = "55", the I/O terminal status can be monitored on the operation panel. The I/O terminal monitor is displayed on the third monitor. The LED is ON when the terminal is ON, and the LED is OFF when the terminal is OFF.
- Page 139 Monitor display and monitor output signal Cumulative energization time and actual operation time monitor (Pr. 171, Pr. 563, Pr. 564) Cumulative energization time monitor (Pr. 52 = "20") accumulates energization time from shipment of the inverter every one hour. On the actual operation time monitor (Pr. 52 = "23"), the inverter running time is added up every hour. (Time is not added up during a stop.) If the monitored value exceeds 65535, it is added up from 0.
-
Page 140: Reference Of The Terminal Fm (Pulse Train Output) (Pr. 55, Pr. 56)
Monitor display and monitor output signal 4.11.3 Reference of the terminal FM (pulse train output) (Pr. 55, Pr. 56) The pulse train output terminal FM is available for monitor output. Set the reference of the signal output from terminal FM. Parameter Name Initial Value... -
Page 141: Terminal Fm Calibration (Calibration Parameter C0 (Pr. 900))
Monitor display and monitor output signal 4.11.4 Terminal FM calibration (calibration parameter C0 (Pr. 900)) By using the operation panel or parameter unit, you can calibrate terminal FM to full scale deflection. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number Calibrates the scale of the meter C0 (900) FM terminal calibration... - Page 142 Monitor display and monitor output signal (2) How to calibrate the terminal FM when using the operation panel Operation Display (When Pr. 54 = 1) Confirm the operation status indicator and operation mode indicator PRM indicator is lit. Press to choose the parameter setting mode.
-
Page 143: Operation Selection At Power Failure And Instantaneous Power Failure
0 to 32767 automatic restart after instantaneous power failure is set as Frequency search gain 9999 well as the motor constants (R1). Uses the Mitsubishi Electric motor (SF-PR, SF-JR, SF-HR, 9999 SF-JRCA, SF-HRCA) constants Without rotation direction detection With rotation direction detection Rotation direction When Pr. - Page 144 Operation selection at power failure and instantaneous power failure When Pr. 162 = 1, 11 (without frequency search) Automatic restart operation selection (Pr. 30, Pr. 162, Pr. 299) Instantaneous (power failure) time Without frequency search Power supply When Pr. 162 = "1 (initial value) or 11", automatic restart (R/L1, S/L2, T/L3) operation is performed in a reduced voltage system, where the voltage is gradually risen with the output...
- Page 145 Operation selection at power failure and instantaneous power failure NOTE When automatic restart operation after instantaneous power failure is activated while the motor is running at a low speed (less than 10Hz), the motor restarts in the direction prior to instantaneous power failure without detecting the rotation direction (Pr. 299 Rotation direction detection selection at restarting = "1").
- Page 146 3) Set Pr. 71 Applied motor according to the motor used. Pr.71 Setting Motor SF-JR SF-JR 4P 1.5kW or lower Mitsubishi Electric standard motor Mitsubishi Electric high efficiency motor SF-HR Others SF-JRCA 4P Mitsubishi Electric constant-torque motor SF-HRCA Others (SF-JRC, etc.)
- Page 147 Operation selection at power failure and instantaneous power failure Execution of tuning POINT Before performing tuning, check the monitor display of the operation panel or parameter unit (FR-PU04/FR-PU07) if the inverter is in the status for tuning. (Refer to 2) below.) 1) When performing PU operation, press of the operation panel.
- Page 148 Operation selection at power failure and instantaneous power failure 4) If offline auto tuning ended in error (see the table below), frequency search gain are not set. Perform an inverter reset and restart tuning. Error Error Cause Remedy Display Forced end Set "21"...
-
Page 149: Power-Failure Deceleration Stop Function (Pr. 261)
Operation selection at power failure and instantaneous power failure 4.12.2 Power-failure deceleration stop function (Pr. 261) When a power failure or undervoltage occurs, the motor can be decelerated to a stop or can be decelerated and re- accelerated to the set frequency. Parameter Initial Setting... - Page 150 Operation selection at power failure and instantaneous power failure (4) Operation continuation at instantaneous power failure function (Pr. 261 = "2") When power is restored during deceleration after a power failure, acceleration is made again up to the set frequency. ...
-
Page 151: Operation Setting At Fault Occurrence
Operation setting at fault occurrence 4.13 Operation setting at fault occurrence Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Recover by retry operation at fault Retry operation Pr. 65, Pr. 67 to Pr. 69 occurrence Do not output input/output phase Input/output phase failure Pr. - Page 152 Operation setting at fault occurrence Using Pr. 65, you can select the fault that will cause a retry to be executed. No retry will be made for the fault not indicated. (Refer to page 258 for the fault description.) ...
-
Page 153: Input/Output Phase Loss Protection Selection (Pr. 251, Pr. 872)
Operation setting at fault occurrence 4.13.2 Input/output phase loss protection selection (Pr. 251, Pr. 872) You can choose whether to make Input/output phase loss protection valid or invalid. Output phase loss protection is a function to stop the inverter output if one of the three phases (U, V, W) on the inverter's output side is lost. -
Page 154: Energy Saving Operation
Energy saving operation 4.14 Energy saving operation Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Energy saving operation Optimum excitation control Pr. 60 4.14.1 Optimum excitation control (Pr. 60) Without a fine parameter setting, the inverter automatically performs energy saving operation. This operation is optimum for fan and pump applications Parameter Name... -
Page 155: Pwm Carrier Frequency And Soft-Pwm Control (Pr. 72, Pr. 240, Pr. 260)
Motor noise, EMI measures, mechanical resonance 4.15 Motor noise, EMI measures, mechanical resonance Purpose of Use Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Reduction of the motor noise Carrier frequency and Measures against EMI and leakage Pr. 72, Pr. 240, Pr. 260 Soft-PWM selection currents Reduce mechanical resonance... -
Page 156: Speed Smoothing Control (Pr. 653)
Motor noise, EMI measures, mechanical resonance 4.15.2 Speed smoothing control (Pr. 653) Vibration due to mechanical resonance influences the inverter control, causing the output current (torque) unstable. In this case, the output current (torque) fluctuation can be reduced to ease vibration by changing the output frequency. Parameter Name Initial Value... -
Page 157: Frequency Setting By Analog Input (Terminal 2, 4)
Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) 4.16 Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Selection of voltage/current input (terminal 2, 4) Analog input selection Pr. 73, Pr. 267 Perform forward/reverse rotation by analog input. - Page 158 Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) NOTE Set Pr. 267 and a voltage/current input switch correctly, then input an analog signal in accordance with the setting. Incorrect setting as in the table below could cause component damage. Incorrect settings other than below can cause abnormal operation.
-
Page 159: Response Level Of Analog Input And Noise Elimination (Pr. 74)
Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) Perform operation by analog input selection Inverter When the pressure or temperature is controlled constantly by a fan, Forward rotation pump, etc., automatic operation can be performed by inputting the output signal 4 to 20mADC of the adjuster across the terminals 4-5. 4 to 20mADC The AU signal must be turned ON to use the terminal 4. -
Page 160: Bias And Gain Of Frequency Setting Voltage (Current) (Pr. 125, Pr. 126, Pr. 241, C2 (Pr. 902) To C7 (Pr. 905))
Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) 4.16.3 Bias and gain of frequency setting voltage (current) (Pr. 125, Pr. 126, Pr. 241, C2 (Pr. 902) to C7 (Pr. 905)) You can set the magnitude (slope) of the output frequency as desired in relation to the frequency setting signal (0 to 5VDC, 0 to 10VDC or 4 to 20mADC). - Page 161 Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) Change frequency maximum analog input (Pr. 125, Pr. 126) Initial value 60Hz Set Pr. 125 (Pr. 126) when changing frequency setting (gain) of the maximum analog input voltage (current) only. (C2 (Pr. 902) to C7 (Pr.905) setting need not be changed) Gain Pr.
- Page 162 Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) (4) Frequency setting signal (current) bias/gain adjustment method (a) Method to adjust any point by application of a voltage (current) across terminals 2 and 5 (4 and 5). Operation Display Confirm the operation status indicator and operation mode indicator ...
- Page 163 Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) (b) Method to adjust any point without application of a voltage (current) across terminals 2 and 5 (4 and 5) (To change from 4V (80%) to 5V (100%)) Operation Display Confirm the operation status indicator and operation mode indicator ...
- Page 164 Frequency setting by analog input (terminal 2, 4) (c) Adjusting only the frequency without adjusting the gain voltage (current). (When changing the gain frequency from 60Hz to 50Hz) Operation Display Turn until " " (Pr. 125) or Terminal 2 input Terminal 4 input is "...
-
Page 165: Misoperation Prevention And Parameter Setting Restriction
Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction 4.17 Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Limits reset function Reset selection/disconnected PU Trips when PU is disconnected Pr. 75 detection/PU stop selection Stops from PU Prevention of parameter rewrite Parameter write disable selection Pr. - Page 166 Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction (3) PU stop selection In any of the PU operation, External operation and Network operation modes, the motor can be stopped by pressing STOP key of the operation panel or parameter unit (FR-PU04/FR-PU07, operation panel for FR-E500 (PA02)). When the inverter is stopped by the PU stop function, "...
- Page 167 Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction Restart (PS reset) method when PU stop (PS display) is made during PU operation PU stop (PS display) is made when the motor is stopped from the unit where control command source is not selected (operation panel, parameter unit (FR-PU04/FR-PU07, operation panel for FR-E500 (PA02)) in the PU operation mode.
-
Page 168: Parameter Write Disable Selection (Pr. 77)
Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction 4.17.2 Parameter write disable selection (Pr. 77) You can select whether write to various parameters can be performed or not. Use this function to prevent parameter values from being rewritten by misoperation. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description... -
Page 169: Reverse Rotation Prevention Selection (Pr. 78)
Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction 4.17.3 Reverse rotation prevention selection (Pr. 78) This function can prevent reverse rotation fault resulting from the incorrect input of the start signal. Parameter Initial Name Setting Range Description Number Value Both forward and reverse rotations allowed Reverse rotation prevention Reverse rotation disabled selection... -
Page 170: Password Function (Pr. 296, Pr. 297)
Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction 4.17.5 Password function (Pr. 296, Pr. 297) Registering a 4-digit password can restrict parameter reading/writing. Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number Select restriction level of parameter reading/ 1 to 6, 101 to 106 writing when a password is registered. - Page 171 Misoperation prevention and parameter setting restriction Password lock/unlock (Pr.296, Pr.297) <Lock> 1) Set parameter reading/writing restriction level. (Pr. 296 9999) Pr.296 Setting Restriction of Password Pr.297 Display Value Unlock Error 1 to 6 No restriction Always 0 Displays error count 101 to 106 Restricted at fifth error (0 to 5)
-
Page 172: Selection Of Operation Mode And Operation Location
Selection of operation mode and operation location 4.18 Selection of operation mode and operation location Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Operation mode selection Operation mode selection Pr. 79 Started in Network operation mode Operation mode at power-on Pr. - Page 173 Selection of operation mode and operation location Operation mode basics The operation mode specifies the source of the start command and the frequency command for the inverter. Basically, there are following operation modes. External operation mode: For inputting start command and frequency command with an external potentiometer and switches which are connected to the control circuit terminal.
- Page 174 Selection of operation mode and operation location (3) Operation mode selection flow In the following flowchart, select the basic parameter setting and terminal connection related to the operation mode. START Connection Parameter setting Operation Where is the start command source? From outside (STF/STR terminal) Where is the frequency...
- Page 175 Selection of operation mode and operation location External operation mode (setting "0" (initial value), "2") Select the External operation mode when the start command and the frequency command are applied from a frequency setting potentiometer, start switch, etc. which are provided externally and connected to the control circuit terminals of the inverter.
- Page 176 Selection of operation mode and operation location (6) PU/External combined operation mode 1 (setting "3") Select the PU/External combined operation mode 1 when applying frequency command from the operation panel or parameter unit (FR-PU04/FR- PU07) and inputting the start command with the external start switch.
- Page 177 Selection of operation mode and operation location Switchover mode (setting "6") While continuing operation, you can switch among the PU operation, External operation and Network operation (NET operation). Operation Mode Switching Switching Operation/Operating Status Select the PU operation mode with the operation panel or parameter unit. Rotation direction is the same as that of External operation.
- Page 178 Selection of operation mode and operation location NOTE If the X12 (MRS) signal is ON, the operation mode cannot be switched to the PU operation mode when the start signal (STF, STR) is ON. When the MRS signal is used as the PU interlock signal, the MRS signal serves as the normal MRS function (output stop) by turning ON the MRS signal and then changing the Pr.
- Page 179 Selection of operation mode and operation location (11) Switching of operation mode by external signals (X65, X66 signals) When Pr. 79 = any of "0, 2, 6", the operation mode switching signals (X65, X66) can be used to change the PU or External operation mode to the Network operation mode during a stop (during a motor stop or start command OFF).
-
Page 180: Operation Mode At Power-On (Pr. 79, Pr. 340)
Selection of operation mode and operation location 4.18.2 Operation mode at power-ON (Pr. 79, Pr. 340) When power is switched ON or when power comes back ON after instantaneous power failure, the inverter can be started up in the Network operation mode. After the inverter has started up in the Network operation mode, parameter write and operation can be performed from a program. -
Page 181: Start Command Source And Frequency Command Source During Communication Operation (Pr. 338, Pr. 339, Pr. 551)
Selection of operation mode and operation location 4.18.3 Start command source and frequency command source during communication operation (Pr. 338, Pr. 339, Pr. 551) When the RS-485 communication with the PU connector is used, the external start command and frequency command can be valid. - Page 182 Selection of operation mode and operation location (2) Controllability through communication Controllability through communication in each operation mode is shown below. Monitoring and parameter read can be performed from any operation regardless of operation mode. Operation External/PU External/PU Mode Operation Condition External Combined...
- Page 183 Selection of operation mode and operation location Selection of control source in Network operation mode (Pr. 338, Pr. 339) There are two control sources: operation command source, which controls the signals related to the inverter start command and function selection, and speed command source, which controls signals related to frequency setting. In Network operation mode, the commands from the external terminals and communication are as listed below.
- Page 184 Selection of operation mode and operation location (5) Switching of command source by external signal (X67) In the Network operation mode, the command source switching signal (X67) can be used to switch the start command source and speed command source. ...
-
Page 185: Communication Operation And Setting
Communication operation and setting 4.19 Communication operation and setting Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Initial setting of computer link Pr. 117 to Pr. 124 communication (PU connector) Communication operation from PU Pr. 117, Pr. 118, Pr. 120, connector MODBUS RTU communication Pr. - Page 186 Communication operation and setting (2) PU connector communication system configuration Connection of a computer to the inverter (1:1 connection) Station 0 Station 0 Computer Computer Inverter Inverter Inverter RS-232C connector FR-PU07 RS-485 RS-232C connector Maximum connector connector cable interface/terminals RS-232C RS-485 RJ-45 connector 2) converter...
- Page 187 Communication operation and setting Connection with RS-485 computer Wiring of one RS-485 computer and one inverter Cable connection and signal direction Inverter Computer side terminals *1 PU connector Communication cable Receive data Receive data Send data Send data 0.2mm or more Signal ground Wiring of one RS-485 computer and "n"...
-
Page 188: Initial Settings And Specifications Of Rs-485 Communication (Pr. 117 To Pr. 120, Pr. 123, Pr. 124, Pr. 549)
Communication operation and setting 4.19.2 Initial settings and specifications of RS-485 communication (Pr. 117 to Pr. 120, Pr. 123, Pr. 124, Pr. 549) The following parameters are used to perform required settings for RS-485 communication between the inverter and personal computer. ... -
Page 189: Operation Selection At Communication Error Occurrence (Pr. 121, Pr. 122, Pr. 502)
Communication operation and setting 4.19.3 Operation selection at communication error occurrence (Pr. 121, Pr. 122, Pr. 502) You can select the inverter operation when a communication line error occurs during RS-485 communication from the PU connector. Parameter Initial Setting Name Description Number Value... - Page 190 Communication operation and setting (2) Signal loss detection (Pr.122) If a signal loss (communication stop) is detected between the inverter and computer as a result of a signal loss detection, a communication fault (E.PUE) occurs and the inverter output is shut off. (as set in Pr. 502). When the setting is "9999", communication check (signal loss detection) is not made.
- Page 191 Communication operation and setting Stop operation selection at occurrence of communication fault (Pr. 502) Stop operation when retry count exceeds (Mitsubishi inverter protocol only) or signal loss detection error occurs can be selected. Operation at fault occurrence Pr. 502 Setting Operation Indication Fault Output...
-
Page 192: Communication Eeprom Write Selection (Pr. 342)
Communication operation and setting 4.19.4 Communication EEPROM write selection (Pr. 342) When parameter write is performed from RS-485 communication with the inverter PU connector, parameters storage device can be changed from EEPROM + RAM to RAM only. Set when a frequent parameter change is necessary. Parameter Name Initial Value... -
Page 193: Mitsubishi Inverter Protocol (Computer Link Communication)
Communication operation and setting 4.19.5 Mitsubishi inverter protocol (computer link communication) You can perform parameter setting, monitoring, etc. from the PU connector of the inverter using the Mitsubishi inverter protocol (computer link communication). Communication The communication specifications are given below. Related Item Description... - Page 194 Communication operation and setting (3) Communication operation presence/absence and data format types Data communication between the computer and inverter is made in ASCII code (hexadecimal code). Communication operation presence/absence and data format types are as follows: Operation Multi Parameter Inverter Parameter Operation Monitor...
- Page 195 Communication operation and setting Data reading format Communication request data from the computer to the inverter 1) Number of Characters Format Inverter Instruction code check station number Reply data from the inverter to the computer 3) (No data error detected) Number of Characters Format Inverter...
- Page 196 Communication operation and setting (4) Data definitions 1) Control code Signal ASCII Code Description Start of Text (Start of data) End of Text (End of data) Enquiry (Communication request) Acknowledge (No data error detected) Line Feed Carriage Return Negative Acknowledge (Data error detected) 2) Inverter station number Specify the station number of the inverter which communicates with the computer.
- Page 197 Communication operation and setting 7) Error code If any error is found in the data received by the inverter, its definition is sent back to the computer together with the NAK code. Error Error Item Error Description Inverter Operation Code The number of errors detected consecutively in communication request Computer NAK error data from the computer is greater than allowed number of retries.
- Page 198 Communication operation and setting (6) Instructions for the program 1) When data from the computer has any error, the inverter does not accept that data. Hence, in the user program, always insert a retry program for data error. 2) All data communication, for example, run command or monitoring, are started when the computer gives a communication request.
- Page 199 Communication operation and setting General flowchart Port open Communication setting Time out setting Send data processing Data setting Sum code calculation Data transmission Receive data waiting Receive data processing Data retrieval Screen display CAUTION Always set the communication check time interval before starting operation to prevent hazardous conditions. Data communication is not started automatically but is made only once when the computer provides a communication request.
- Page 200 Communication operation and setting (7) Setting items and set data After completion of parameter settings, set the instruction codes and data then start communication from the computer to allow various types of operation control and monitoring. Number of Instruction Read/ Item Data Definition Data Digits...
- Page 201 Communication operation and setting Number of Instruction Read/ Item Data Definition Data Digits Write Code (Format) H9696: resets the inverter 4 digits As the inverter is reset at start of communication by the computer, the inverter (A, C/D) cannot send reply data back to the computer. Inverter reset Write H9966: resets the inverter...
- Page 202 Communication operation and setting REMARKS Set 65520 (HFFF0) as a parameter value "8888" and 65535 (HFFFF) as "9999". For the instruction codes HFF, HEC and HF3, their values are held once written but cleared to zero when an inverter reset or all clear is performed.
- Page 203 Communication operation and setting [Fault data] Refer to page 257 for details of fault description. Fault record display example (instruction code H74) Data Definition Data Definition Data Definition No fault E.THM E.PE For read data H3010 present E.FIN E.PUE (Second latest fault ..THT) (Latest fault...OC1) E.OC1 E.ILF...
- Page 204 Communication operation and setting [Multi command (HF0)] Sending data format from computer to inverter Number of Characters Format Send Receive Inverter Instruction Data2 Waiting data data station Code Data1 CR/LF time check number (HF0) type type Reply data format from inverter to computer (No data error detected) Number of Characters Format...
-
Page 205: Modbus Rtu Communication Specifications (Pr. 117, Pr. 118, Pr. 120, Pr. 122, Pr. 343, Pr. 502, Pr. 549)
Communication operation and setting 4.19.6 MODBUS RTU communication specifications (Pr. 117, Pr. 118, Pr. 120, Pr. 122, Pr. 343, Pr. 502, Pr. 549) Using the MODBUS RTU communication protocol, communication operation or parameter setting can be performed from the PU connector of the inverter. Setting Parameter Name... - Page 206 Communication operation and setting (1) Communication specification The communication specifications are given below. Related Item Description Parameter Communication protocol MODBUS RTU protocol Pr. 549 Conforming standard EIA-485(RS-485) — Number of connectable devices 1:N (maximum 32 units), setting is 0 to 247 stations Pr.
- Page 207 Communication operation and setting Message format Inverter response time Query communication (Refer to the following table for the data check time.) Programmable controller (master) Query message Response message Inverter (slave) Data absence time (3.5 bytes or more) Broadcast communication Query message Programmable controller (master) No Response Inverter (slave)
- Page 208 Communication operation and setting (4) Message frame (protocol) Communication method Basically, the master sends a query message (question) and the slave returns a response message (response). When communication is normal, Device Address and Function Code are copied, and when communication is abnormal (function code or data code is illegal), bit 7 (= 80h) of Function Code is turned ON and the error code is set to Data Bytes.
- Page 209 Communication operation and setting Message format types The message formats corresponding to the function codes in Table 1 on page 204 will be explained. Read holding register data (H03 or 03) Can read the description of 1) system environment variables, 2) real-time monitor, 3) fault history, and 4) inverter parameters assigned to the holding register area (refer to the register list (page 210)).
- Page 210 Communication operation and setting Write holding register data (H06 or 06) Can write the description of 1) system environment variables and 4) inverter parameters assigned to the holding register area (refer to the register list (page 210)). Query message 1) Slave Address 2) Function 3) Register Address...
- Page 211 Communication operation and setting Function diagnosis (H08 or 08) A communication check can be made since the query message sent is returned unchanged as a response message (function of sub function code H00). Sub function code H00 (Return Query Data) Query message 1) Slave Address 2) Function...
- Page 212 Communication operation and setting Description of normal response 1) to 4) (including CRC check) of the normal response are the same as those of the query message. Example: To write 0.5s (H05) to 41007 (Pr. 7) at the slave address 25 (H19) and 1s (H0A) to 41008 (Pr.8). Query message Slave Starting...
- Page 213 Communication operation and setting Error response An error response is returned if the query message received from the master has an illegal function, address or data. No response is returned for a parity, CRC, overrun, framing or busy error. NOTE No response message is sent in the case of broadcast communication also.
- Page 214 Communication operation and setting (6) MODBUS registers The following shows the MODBUS registers for system environment variables (read/write), real time monitor items (read), parameters (read/write), and fault history data (read/write). System environment variable Register Definition Read/write Remarks 40002 Inverter reset Write Any value can be written...
- Page 215 Communication operation and setting Real time monitor Refer to page 131 for details of the monitor description. Register Description Unit Register Description Unit Output frequency/speed 40201 0.01Hz/1 40215 Input terminal status — Output current 40202 0.01A 40216 Output terminal status...
- Page 216 Communication operation and setting Fault history Register Definition Read/write Remarks 40501 Fault record 1 Read/write Being 2 bytes in length, the data is stored as 40502 Fault record 2 Read "H00". 40503 Fault record 3 Read Refer to the lowest 1 byte for the error code. 40504 Fault record 4 Read...
-
Page 217: Special Operation And Frequency Control
Special operation and frequency control 4.20 Special operation and frequency control Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Perform process control such as Pr. 127 to Pr. 134, PID control pump and air volume. Pr. 575 to Pr. 577 PID control (dancer control Dancer control Pr. - Page 218 Special operation and frequency control (1) PID control basic configuration Pr. 128 = "20, 21" (measured value input) Inverter circuit Motor Pr. 133 Manipulated PID operation or terminal 2 variable Kp 1+ Set point 0 to 5VDC (0 to 10VDC) Terminal 4 Feedback signal (measured value) 4 to 20mADC (0 to 5V, 0 to 10V)
- Page 219 Special operation and frequency control 3) PID action The PI action and PD action are combined to utilize the advantages of both Set point actions for control. Deviation (Note) PID action is the sum of P, I and D actions. Measured value action Time...
- Page 220 Special operation and frequency control (3) Connection diagram Sink logic Inverter Pr. 128 = 20 MCCB Pump Pr. 182 = 14 Motor R/L1 Pr. 190 = 15 Power supply S/L2 T/L3 Forward rotation Reverse rotation RH(X14) PID control selection 2-wire type 3-wire type Detector Upper limit...
- Page 221 Special operation and frequency control I/O signals and parameter setting Set "20, 21" in Pr. 128 to perform PID operation. Set "14" in any of Pr. 178 to Pr. 182 (input terminal function selection) to assign PID control selection signal (X14) to turn the X14 signal ON.
- Page 222 Special operation and frequency control (5) PID automatic switchover control (Pr. 127) The system can be started up without PID control only at a start. When the frequency is set to Pr. 127 PID control automatic switchover frequency within the range 0 to 400Hz, the inverter starts up without PID control from a start until output frequency is reached to the set frequency of Pr.
- Page 223 Special operation and frequency control Adjustment procedure Parameter setting Adjust the PID control parameters, Pr. 127 to Pr. 134. Set the I/O terminals for PID control (Pr. 178 to Pr. 182 (input terminal Terminal setting function selection), Pr. 190 , Pr. 192, Pr. 197 (output terminal function selection)) When X14 signal is not assigned, setting a value other than "0"...
- Page 224 Special operation and frequency control <Set point input calibration> 1. Apply the input voltage of 0% set point setting (e.g. 0V) across terminals 2-5. 2. Enter in C2 (Pr. 902) the frequency which should be output by the inverter at the deviation of 0% (e.g. 0Hz). 3.
-
Page 225: Dancer Control (Pr. 44, Pr. 45, Pr. 128 To Pr. 134)
Special operation and frequency control 4.20.2 Dancer control (Pr. 44, Pr. 45, Pr. 128 to Pr. 134) Performs PID control by feedbacking the position detection of the dancer roller, controlling the dancer roller is in the specified position. Parameter Setting Name Initial Value Description... - Page 226 Special operation and frequency control (1) Dancer control block diagram Acceleration/deceleration of main speed Main speed command Target frequency ∗1 Ratio PID deviation Acceleration/ Limit deceleration Pr. 128 = 42, 43 PID control Dancer roll setting point + Td S) Kp(1+ Ti S Pr.
- Page 227 Special operation and frequency control Dancer control overview Dancer control is performed by setting "40 to 43" in Pr.128 PID action selection. The main speed command is the speed command for each operation mode (External, PU, and communication). PID control is performed by the dancer roll position detection signal, and the control result is added to the main speed command.
- Page 228 Special operation and frequency control (4) I/O signals and parameter setting Set "40 to 43" in Pr. 128 to perform dancer control. Set "14" in any of Pr. 178 to Pr. 182 (input terminal function selection) to assign PID control selection signal (X14) to turn the X14 signal ON.
- Page 229 Special operation and frequency control Parameter details When ratio (Pr. 128 = "42, 43") is selected for addition method, PID Initial value 60Hz control (ratio of main speed) is added to the main speed. The ratio is determined by the Pr. 125 Terminal 2 frequency setting gain frequency and C2 (Pr.
- Page 230 Special operation and frequency control (9) Adjustment procedure Dancer roller position detection signal adjustment When terminal 4 input is voltage input, 0V is the minimum position and 5V (10V) is the maximum position. When current is input, 4mA is the minimum position and 20mA is the maximum position (initial value). When 0 to 7V is output from the potentiometer, it is necessary to calibrate C7 (Pr.
-
Page 231: Regeneration Avoidance Function (Pr. 665, Pr. 882, Pr. 883, Pr. 885, Pr. 886)
Special operation and frequency control 4.20.3 Regeneration avoidance function (Pr. 665, Pr. 882, Pr. 883, Pr. 885, Pr. 886) This function detects a regeneration status and increases the frequency to avoid the regenerative status. Possible to avoid regeneration by automatically increasing the frequency to continue operation if the fan happens to rotate faster than the set speed due to the effect of another fan in the same duct. - Page 232 Special operation and frequency control REMARKS The acceleration/deceleration ramp while the regeneration avoidance function is operating changes depending on the regeneration load. The DC bus voltage of the inverter is about times of normal input voltage. (For 100V class, twice the amount of the power input voltage.) When the input voltage is 100VAC, bus voltage is approximately 283VDC.
-
Page 233: Useful Functions
Useful functions 4.21 Useful functions Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Cooling fan operation To increase cooling fan life Pr. 244 selection Inverter part life display Pr. 255 to Pr. 259 Maintenance output To determine the maintenance time Pr. -
Page 234: Display Of The Lives Of The Inverter Parts (Pr. 255 To Pr. 259)
Useful functions 4.21.2 Display of the lives of the inverter parts (Pr. 255 to Pr. 259) Degrees of deterioration of main circuit capacitor, control circuit capacitor, cooling fan and inrush current limit circuit can be diagnosed by a monitor. When any part has approached to the end of its life, an alarm can be output by self diagnosis to prevent a fault. (Use the life check of this function as a guideline since the life except the main circuit capacitor is calculated theoretically.) For the life check of the main circuit capacitor, the alarm signal (Y90) will not be output if a measuring method of (4) is... - Page 235 Useful functions Life alarm display and signal output (Y90 signal, Pr. 255) Whether any of the control circuit capacitor, main circuit capacitor, cooling fan and inrush current limit circuit has reached the life alarm output level or not can be checked by Pr. 255 Life alarm status display and life alarm signal (Y90). 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 Pr.
- Page 236 Useful functions (4) Main circuit capacitor life display (Pr. 258, Pr. 259) The deterioration degree of the control circuit capacitor is displayed in Pr. 258 as a life. On the assumption that the main circuit capacitor capacitance at factory shipment is 100%, the capacitor life is displayed in Pr.
- Page 237 When the inverter is mounted with two or more cooling fans, "FN" is displayed with one or more fans with speed of 50% or less. NOTE For replacement of each part, contact the nearest Mitsubishi Electric FA center.
-
Page 238: Maintenance Timer Alarm (Pr. 503, Pr. 504)
Useful functions 4.21.3 Maintenance timer alarm (Pr. 503, Pr. 504) When the cumulative energization time of the inverter reaches the parameter set time, the maintenance timer output signal (Y95) is output. " " (MT) is displayed on the operation panel. This can be used as a guideline for the maintenance time of peripheral devices. -
Page 239: Current Average Value Monitor Signal (Pr. 555 To Pr. 557)
Useful functions 4.21.4 Current average value monitor signal (Pr. 555 to Pr. 557) The average value of the output current during Programmable controller constant speed operation and the maintenance timer Output unit Input unit Inverter value are output as a pulse to the current average value monitor signal (Y93). - Page 240 Useful functions 2) Setting of Pr. 555 Current average time The average output current is calculated during Hi output of start pulse (1s). Set the time taken to average the current during start pulse output in Pr. 555. 3) Setting of Pr.557 Current average value monitor signal output reference current Set the reference (100%) for outputting the signal of the current average value.
-
Page 241: Free Parameter (Pr. 888, Pr. 889)
Useful functions 4.21.5 Free parameter (Pr. 888, Pr. 889) You can input any number within the setting range of 0 to 9999. For example, the number can be used: As a unit number when multiple units are used. As a pattern number for each operation application when multiple units are used. ... -
Page 242: Setting The Parameter Unit And Operation Panel
Setting the parameter unit and operation panel 4.22 Setting the parameter unit and operation panel Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Selection of rotation direction by RUN key rotation Pr. 40 direction selection of the operation panel Switch the display language of the PU display language Pr. -
Page 243: Operation Panel Frequency Setting/Key Lock Selection (Pr. 161)
Setting the parameter unit and operation panel 4.22.3 Operation panel frequency setting/key lock selection (Pr. 161) The setting dial of the operation panel can be used for setting like a potentiometer. The key operation of the operation panel can be disabled. Parameter Setting Name... - Page 244 Setting the parameter unit and operation panel REMARKS If the display changes from blinking "60.00" to "0.00", the setting of Pr. 161 Frequency setting/key lock operation selection may not be "1". Independently of whether the inverter is running or at a stop, the frequency can be set by merely turning the dial. ...
-
Page 245: Magnitude Of Frequency Change Setting (Pr. 295)
Setting the parameter unit and operation panel 4.22.4 Magnitude of frequency change setting (Pr. 295) When setting the set frequency with the setting dial, frequency changes in 0.01Hz increments in the initial status. Setting this parameter increases the magnitude of frequency which changes according to the rotated amount of the setting dial, improving operability. -
Page 246: Buzzer Control (Pr. 990)
Setting the parameter unit and operation panel 4.22.5 Buzzer control (Pr. 990) You can make the buzzer "beep" when you press the key of the parameter unit (FR-PU04/FR-PU07). Parameter Name Initial Value Setting Range Description Number Without buzzer PU buzzer control With buzzer The above parameter can be set when Pr. -
Page 247: E500 Series Operation Panel (Pa02) Setting
FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting 4.23 FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting The operation panel (PA02) for the FR-E500 series can be hooked up with the PU cable for use. (The inverter cannot be directly connected.) Purpose Parameter that should be Set Refer to Page Select the frequency setting method Frequency setting... -
Page 248: Bias And Gain Of The Built-In Frequency Setting Potentiometer (C22 (Pr. 922) To C25 (Pr. 923))
FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting 4.23.2 Bias and gain of the built-in frequency setting potentiometer (C22 (Pr. 922) to C25 (Pr. 923)) When the operation panel (PA02) for the FR-E500 series is hooked up with the PU cable, the magnitude (slope) of the output frequency to the frequency setting potentiometer of the operation panel can be set as desired. - Page 249 FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting Pr. 923 "Built-in frequency setting potentiometer gain" (Pr. 922 can be adjusted in a similar manner.) Set the magnitude (slope) of the output frequency by the built-in potentiometer as desired using the built-in frequency setting potentiometer.
- Page 250 FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting Operation Set the gain frequency in Pr.923 to display the analog voltage value of the built-in frequency setting potentiometer in %. (80Hz maximum) Current setting of gain Changing the gain frequency frequency Press to change the set frequency. Press for 1.5s Analog voltage value (%) of the built-in frequency setting potentiometer...
- Page 251 FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting Method to adjust any point without turning the potentiometer (changing from 4V (80%) to 5V (100%)) Operation Perform steps 1. to 4. on page 245, 246. Set the gain voltage (%). Analog voltage Press the Set the gain voltage (%) with value (%) of the...
- Page 252 FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting [Setting with the inverter operation panel without fitting the FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02)] a) Method to adjust any point (to change to 80% from 100%) Operation Display Confirm the operation status indicator and operation mode indicator ...
- Page 253 FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) setting b) Method to set frequency only without adjusting gain analog value (When changing the gain frequency from 60Hz to 50Hz) Operation Display Confirm the operation status indicator and operation mode indicator The inverter should be at a stop. The inverter should be in the PU operation mode (depends on The parameter...
-
Page 254: Parameter Clear/ All Parameter Clear
Parameter clear/ All parameter clear 4.24 Parameter clear/ All parameter clear POINT Set "1" in Pr.CL Parameter clear, ALLC all parameter clear to initialize parameters. (Parameters are not cleared when "1" is set in Pr. 77 Parameter write selection.) ... -
Page 255: Initial Value Change List
Initial value change list 4.25 Initial value change list Displays and sets the parameters changed from the initial value. Operation Display Screen at power-ON The monitor display appears. PU indicator is lit. Press to choose the PU operation mode. PRM indicator is lit. Press to choose the parameter setting mode. -
Page 256: Check And Clear Of The Fault History
Check and clear of the fault history 4.26 Check and clear of the fault history (1) Check for the fault history Monitor/frequency setting Parameter setting [Operation panel is [Parameter setting change] used for operation] Fault history [Operation for displaying fault history] The last eight fault records can be displayed. - Page 257 Check and clear of the fault history Clearing procedure POINT Set "1" in Er.CL Fault history clear to clear the fault history. Operation Display Screen at power-ON The monitor display appears. PRM indicator is lit. Press to choose the parameter setting mode. (The parameter number read previously appears.) Turn...
- Page 258 MEMO...
-
Page 259: Troubleshooting
TROUBLESHOOTING This chapter provides the "TROUBLESHOOTING" of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. Reset method of protective function ......... 256 List of fault or alarm indications ..........257 Causes and corrective actions ........... 258 Correspondences between digital and actual characters ..267 Check first when you have a trouble ......... -
Page 260: Reset Method Of Protective Function
Reset method of protective function When a fault occurs in the inverter, the inverter output is shut off and the PU display automatically changes to one of the following fault or alarm indications. If the fault does not correspond to any of the following faults or if you have any other problem, please contact your sales representative. -
Page 261: List Of Fault Or Alarm Indications
List of fault or alarm indications List of fault or alarm indications Refer Refer Operation Panel Operation Panel Name Name Indication Indication Page Page E.ILF Input phase loss E--- Fault history E.OLT Stall prevention stop HOLD Operation panel lock Brake transistor alarm E. -
Page 262: Causes And Corrective Actions
Causes and corrective actions Causes and corrective actions (1) Error message A message regarding operational troubles is displayed. Output is not shut off. Operation panel HOLD indication Name Operation panel lock Description Operation lock mode is set. Operation other than is invalid. - Page 263 Causes and corrective actions Operation panel Err. indication Name Inverter reset Executing reset using RES signal, or reset command from communication or PU Description Displays at powering OFF. Corrective action Turn OFF the reset command (2) Warning When a warning occurs, the output is not shut off.
- Page 264 Causes and corrective actions Operation panel FR-PU04 indication FR-PU07 Name PU stop Stop with of the PU is set in Pr. 75 Reset selection/disconnected PU detection/PU stop selection. (For Pr. 75 refer to Description page 161.) Check point Check for a stop made by pressing of the operation panel.
- Page 265 Causes and corrective actions Operation panel FR-PU04 —— indication FR-PU07 Name Safety stop Description Appears when safety stop function is activated (during output shutoff). (Refer to page 27.) Check if the shorting wire between S1 and SC or between S2 and SC is disconnected when not using the safety stop Check point function.
- Page 266 Causes and corrective actions Operation panel FR-PU04 E.OC3 OC During Dec indication FR-PU07 Name Overcurrent trip during deceleration or stop When the inverter output current reaches or exceeds approximately 200% of the inverter rated current during Description deceleration (other than acceleration or constant speed), the protective circuit is activated and the inverter output is shut off.
- Page 267 Causes and corrective actions Operation panel FR-PU04 E.THT Inv. Overload indication FR-PU07 Name Inverter overload trip (electronic thermal O/L relay function) If the temperature of the output transistor element exceeds the protection level under the condition that a current not Description less than the inverter rated current flows and overcurrent trip does not occur (200% or less), the electronic thermal relay activates to stop the inverter output.
- Page 268 Causes and corrective actions Operation panel FR-PU04 Fault 14 E.ILF FR-PU07 Input phase loss indication Name Input phase loss Inverter output is shut off when function valid setting (=1) is selected in Pr. 872 Input phase loss protection selection and one phase of the three phase power input is lost.
- Page 269 Causes and corrective actions Operation panel FR-PU04 E.OHT OH Fault FR-PU07 indication Name External thermal relay operation If the external thermal relay provided for motor overheat protection or the internally mounted temperature relay in the motor, etc. switches ON (contacts open), the inverter output is stopped. Description This function is available when "7"...
- Page 270 Causes and corrective actions Fault 5 FR-PU04 Operation panel indication FR-PU07 E.CPU CPU Fault Name CPU fault Description Stops the inverter output if the communication fault of the built-in CPU occurs. Check point Check for devices producing excess electrical noises around the inverter. ...
-
Page 271: Correspondences Between Digital And Actual Characters
Correspondences between digital and actual characters Correspondences between digital and actual characters There are the following correspondences between the actual alphanumeric characters and the digital characters displayed on the operation panel: Actual Digital Actual Digital Actual Digital... -
Page 272: Check First When You Have A Trouble
Check first when you have a trouble Check first when you have a trouble POINT If the cause is still unknown after every check, it is recommended to initialize the parameters (initial value) then set the required parameter values and check again. 5.5.1 Motor does not start Refer... - Page 273 Check first when you have a trouble Refer Check Possible Cause Countermeasures Points Page Increase Pr. 0 setting by 0.5% increments while Pr. 0 Torque boost setting is improper when V/F control is observing the rotation of a motor. used. If that makes no difference, decrease the setting.
-
Page 274: Motor Or Machine Is Making Abnormal Acoustic Noise
Check first when you have a trouble 5.5.2 Motor or machine is making abnormal acoustic noise Refer Check Possible Cause Countermeasures Points Page Input Take countermeasures against EMI. Signal Disturbance due to EMI when frequency command is Parameter given from analog input (terminal 2, 4). Increase the Pr. -
Page 275: Inverter Generates Abnormal Noise
Check first when you have a trouble 5.5.3 Inverter generates abnormal noise Refer Check Possible Cause Countermeasures Points Page Fan cover was not correctly installed when a cooling fan Install the fan cover correctly. was replaced. 5.5.4 Motor generates heat abnormally Refer Check Possible Cause... -
Page 276: Acceleration/Deceleration Is Not Smooth
Check first when you have a trouble 5.5.7 Acceleration/deceleration is not smooth Refer Check Possible Cause Countermeasures Points Page Acceleration/deceleration time is too short. Increase acceleration/deceleration time. Torque boost (Pr. 0, Pr. 46) setting is improper under V/F Increase/decrease Pr. 0 Torque boost setting value by control, so the stall prevention function is activated. -
Page 277: Operation Mode Is Not Changed Properly
Check first when you have a trouble 5.5.9 Operation mode is not changed properly Refer Check Possible Cause Countermeasures Points Page Check that the STF and STR signals are OFF. Input Start signal (STF or STR) is ON. When either is ON, the operation mode cannot be Signal changed. -
Page 278: Speed Does Not Accelerate
Check first when you have a trouble 5.5.12 Speed does not accelerate Refer Check Possible Cause Countermeasures Points Page Check if the start command and the frequency Start command and frequency command are chattering. — command are correct. Input The wiring length used for analog frequency command Perform analog input bias/gain calibration. - Page 279 PRECAUTIONS FOR MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION This chapter provides the "PRECAUTIONS FOR MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION" of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. Inspection items................276 Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers ..284...
-
Page 280: Precautions For Maintenance And Inspection
Inspection items The inverter is a static unit mainly consisting of semiconductor devices. Daily inspection must be performed to prevent any fault from occurring due to the adverse effects of the operating environment, such as temperature, humidity, dust, dirt and vibration, changes in the parts with time, service life, and other factors. -
Page 281: Daily And Periodic Inspection
Inspection items 6.1.3 Daily and periodic inspection Interval Area of Corrective Action at Customer's Inspection Item Description Periodic Inspection Daily Alarm Occurrence Check Surrounding Check the surrounding air temperature, Improve environment. environment humidity, dirt, corrosive gas, oil mist, etc. Check alarm location and ... -
Page 282: Display Of The Life Of The Inverter Parts
Inspection items Interval Area of Corrective Action at Customer's Inspection Item Description Periodic Inspection Daily Alarm Occurrence Check (1) Check that display is normal. Contact the manufacturer. Indication (2) Check for stains. Clean. Display Stop the device and ... -
Page 283: Checking The Inverter And Converter Modules
Inspection items 6.1.5 Checking the inverter and converter modules <Preparation> (1) Disconnect the external power supply cables (R/L1, S/L2, T/L3) and motor cables (U, V, W). (2) Prepare a tester. (Use 100 range.) <Checking method> Change the polarity of the tester alternately at the inverter terminals R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U, V, W, + and -, and check for continuity. -
Page 284: Replacement Of Parts
Estimated lifespan for when the yearly average surrounding air temperature is 40°C (without corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt etc.) Output current: 80% of the inverter rated current NOTE For parts replacement, contact the nearest Mitsubishi Electric FA Center. - Page 285 Inspection items Cooling fan The replacement interval of the cooling fan used for cooling the parts generating heat such as the main circuit semiconductor is greatly affected by the surrounding air temperature. When unusual noise and/or vibration is noticed during inspection, the cooling fan must be replaced immediately.
- Page 286 Inspection items Reinstallation 1) After confirming the orientation of the fan, reinstall the fan so that the arrow on the left of "AIR FLOW" faces up. AIR FLOW <Fan side face> 2) Reconnect the fan connectors. 3) When wiring, avoid the cables being caught by the fan. 5.5K or higher 3.7K or lower 4) Reinstall the fan cover.
- Page 287 Inspection items Smoothing capacitors A large-capacity aluminum electrolytic capacitor is used for smoothing in the main circuit DC section, and an aluminum electrolytic capacitor is used for stabilizing the control power in the control circuit. Their characteristics are deteriorated by the adverse effects of ripple currents, etc.
-
Page 288: Measurement Of Main Circuit Voltages, Currents And Powers
Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers Since the voltages and currents on the inverter power supply and output sides include harmonics, measurement data depends on the instruments used and circuits measured. When instruments for commercial frequency are used for measurement, measure the following circuits with the instruments given on the next page. - Page 289 Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers Measuring Points and Instruments Item Measuring Point Measuring Instrument Remarks (Reference Measured Value) R/L1 and S/L2 Commercial power supply Power supply voltage Moving-iron type AC S/L2 and T/L3 Within permissible AC voltage fluctuation (Refer to voltmeter...
-
Page 290: Measurement Of Powers
Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers 6.2.1 Measurement of powers Use digital power meters (for inverter) for the both of inverter input and output side. Alternatively, measure using electrodynamic type single-phase wattmeters for the both of inverter input and output side in two-wattmeter or three- wattmeter method. -
Page 291: Measurement Of Currents
Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers 6.2.3 Measurement of currents Use moving-iron type meters on both the input and output sides of the inverter. However, if the carrier frequency exceeds 5kHz, do not use that meter since an overcurrent losses produced in the internal metal parts of the meter will increase and the meter may burn out. -
Page 292: Insulation Resistance Test Using Megger
Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers 6.2.8 Insulation resistance test using megger For the inverter, conduct the insulation resistance test on the main circuit only as shown below and do not perform the test on the control circuit. (Use a 500VDC megger.) Motor R/L1 Power... -
Page 293: Specifications
SPECIFICATIONS This chapter provides the "SPECIFICATIONS" of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. Rating..................... 290 Common specifications ............... 292 Outline dimension drawings............293... -
Page 294: Rating
Approximate mass (kg) The applicable motor capacity indicated is the maximum capacity applicable for use of the Mitsubishi Electric 4-pole standard motor. The rated output capacity indicated assumes that the output voltage is 230V for three-phase 200V class and 440V for three-phase 400V class. - Page 295 Cooling system Natural Approximate mass (kg) The applicable motor capacity indicated is the maximum capacity applicable for use of the Mitsubishi Electric 4-pole standard motor. The rated output capacity indicated assumes that the output voltage is 230V. ...
-
Page 296: Common Specifications
Common specifications Common specifications Soft-PWM control/high carrier frequency PWM control (V/F control, General-purpose magnetic flux vector control, Control method and Optimum excitation control are available) Output frequency range 0.2 to 400Hz 0.06Hz/60Hz (terminal 2, 4: 0 to 10V/10 bits) Analog input 0.12Hz/60Hz (terminal 2, 4: 0 to 5V/9 bits) Frequency setting 0.06Hz/60Hz (terminal 4: 0 to 20mA/10 bits) -
Page 297: Outline Dimension Drawings
Outline dimension drawings Outline dimension drawings FR-D720-0.1K to 0.75K FR-D720S-0.1K to 0.75K FR-D710W-0.1K to 0.4K 1-φ5 hole Rating plate Inverter Model FR-D720-0.1K, 0.2K FR-D720S-0.1K, 0.2K 80.5 FR-D710W-0.1K FR-D710W-0.2K 110.5 FR-D720-0.4K 112.5 FR-D720-0.75K 132.5 FR-D720S-0.4K 142.5 FR-D710W-0.4K FR-D720S-0.75K 162.5 (Unit: mm) FR-D720-1.5K to 3.7K FR-D740-0.4K to 3.7K FR-D720S-1.5K... - Page 298 Outline dimension drawings FR-D720S-2.2K 2- φ 5 hole Rating plate (Unit: mm) FR-D720-5.5K, 7.5K FR-D740-5.5K, 7.5K 2-φ5 hole Rating plate (Unit: mm)
- Page 299 Outline dimension drawings FR-D720-11K, 15K FR-D740-11K, 15K 2-φ6 hole 10.5 84.5 Rating plate (Unit: mm) Parameter unit (option) (FR-PU07) Outline drawing > Panel cut dimension drawing < < > 25.05 (14.2) (11.45) Air-bleeding hole 4-R1 4-φ4 hole 26.5 26.5 Effective depth of the installation screw hole 5.0) M3 screw *2...
- Page 300 MEMO...
-
Page 301: Appendix
APPENDIX This chapter provides the "APPENDIX" of this product. Always read the instructions before using the equipment. -
Page 302: Appendix 1 For Customers Replacing The Conventional Model With This Inverter
APPENDIX Appendix 1 For customers replacing the conventional model with this inverter Appendix 1-1 Replacement of the FR-S500 series (1) Instructions for installation 1) Removal procedure of the front cover and wiring cover was changed. (Refer to page 5.) 2) FR-SW0-SETUP, FR-SW1-SETUP, FR-SW2-SETUP (setup softwares) cannot be used. (2) Instructions for continuous use of the FR-PU04 (parameter unit) 1) For the FR-D700 series, many functions (parameters) have been added. - Page 303 Item FR-S500 FR-D700 Pr. 52 Control panel display data selection Pr.52 DU/PU main display data selection 0/100: Output current (select with 1: Output current Pr.54 FM terminal function selection 0: Output frequency (initial value), 1: Output frequency (initial value), 1: Output current 2: Output current Pr.
- Page 304 Item FR-S500 FR-D700 Parameter Parameter Name Name Number Number Pr. 17 RUN key rotation direction selection Pr. 40 RUN key rotation direction selection Pr. 21 Stall prevention function selection Pr. 156 Stall prevention operation selection Stall prevention operation reduction Stall prevention operation reduction Pr.
-
Page 305: Appendix 2 Specification Change Check
Appendix 2 Specification change check Check the serial number printed on the rating plate or on the package of the inverter. To find the SERIAL, refer to page 2. Appendix 2-1 Changed function Addition of output signal for the safety function The change applies to the February 2009 production or later. -
Page 306: Appendix 3 Index
Appendix 3 Index Numerics Display of the life of the inverter parts (Pr. 255 to Pr. 259) ............230, 278 15-speed selection (REX signal)........92, 116 During PID control activated (PID signal)..... 122, 213, 221 During retry (Y64 signal) ..........122, 147 Acceleration time, deceleration time setting (Pr. - Page 307 Overcurrent trip during acceleration (E.OC1) ......261 Overcurrent trip during constant speed (E.OC2)....261 Jog operation (Pr. 15, Pr. 16)........... 94 Overcurrent trip during deceleration or stop (E.OC3)..262 Jog operation selection (JOG signal) ......94, 116 Overload alarm (OL signal)..........82, 122 Leakage currents and countermeasures ....... 40 Parameter list ................60 Life alarm (Y90 signal) ............
- Page 308 Reverse rotation command (assigned to STR terminal (Pr. 179) only) (STR signal)..........116, 120 Reverse rotation prevention selection (Pr. 78) ....165 RUN key rotation direction selection (Pr. 40).......238 Safety circuit fault (E.SAF) ..........27, 266 Safety monitor output (SAFE signal) ........122 Safety monitor output 2 (SAFE2 signal) .......122 Safety stop (SA)..............27, 261 Safety stop function..............27 Second function selection (RT signal)......116, 119...
- Page 309 MEMO...
- Page 310 Pr.552 Frequency jump range For Maximum Safety • Mitsubishi Electric inverters are not designed or manufactured to be used in equipment or systems in situations that can affect or endanger human life. • When considering this product for operation in special applications such as machinery or systems used in passenger transportation, medical, aerospace, atomic power, electric power, or submarine repeating applications, please contact your nearest Mitsubishi Electric sales representative.
- Page 311 HEAD OFFICE: TOKYO BUILDING 2-7-3, MARUNOUCHI, CHIYODA-KU, TOKYO 100-8310, JAPAN FR-D700 TORISETSU OUYOU MODEL EIBUN MODEL 1AJ016 CODE IB(NA)-0600366ENG-H (1806)MEE Printed in Japan Specifications subject to change without notice.









