Summary of Contents for Mindray A5
- Page 1 Service Manual ™ ™ Anesthesia System A N E S T H E S I A S YS T E M A N E S T H E S I A S YS T E M...
- Page 2 Service Manual ™ ™ Anesthesia System A N E S T H E S I A S YS T E M A N E S T H E S I A S YS T E M...
- Page 3 A5™ and A3™ are U.S. trademarks of Mindray DS USA, Inc. ® Selectatec is a registered trademark of Ohmeda. © Copyright Mindray DS USA, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved. Contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any form without permission of Mindray DS USA, Inc.
-
Page 4: Table Of Contents
1 Theory of Operation ......................1-4 1.1 Introduction........................1-4 1.2 Electrical and Pneumatic Connections................1-6 1.2.1 Electrical Connections (A3)................1-6 1.2.2 Electrical Connections (A5)................1-8 1.2.3 Pneumatic Connection (A3)................1-10 1.2.4 Pneumatic Connection (A5)................1-13 1.2.5 Connections Between Pneumatic Circuit, Breathing System and Ventilator Control Board ...........................1-16 1.3 Gas Flow........................1-18... - Page 5 2.2.5 Emergency Cylinder(s) ..................2-16 2.2.6 Breathing Circuit, CO2 Absorbent and Liquid Vaporizer Agent.......2-16 2.2.7 Monitoring Products Mounting and Electrical Connection (if available)..2-16 2.2.8 Agent Monitor Waste Gas Scavenging..............2-16 2.3 Functional Tests ......................2-17 2.3.1 Gas Delivery System Tests ................2-17 2.3.2 Breathing System Leak Test ................2-17 2.3.3 O2 Sensor Calibration..................2-23 2.4 Pneumatic Leak Tests.....................2-39 2.4.1 N2O Cylinder Leak Test ...................2-39...
- Page 6 3.7.5 Check the Pressure Sensor Accuracy ..............3-22 3.8 Pneumatic Leak Tests.....................3-26 3.8.1 N2O Cylinder Leak Test ...................3-26 3.8.2 O2 Cylinder Leak Test ..................3-26 3.8.3 AIR Cylinder Leak Test ..................3-26 3.8.4 N2O Line Pressure Leak Test ................3-26 3.8.5 O2 Line Pressure Leak Test ................3-26 3.8.6 AIR Line Pressure Leak Test................3-27 3.9 Breathing System Checks ....................3-27 3.9.1 Waste Gas Scavenger Test (if available) ............3-27...
- Page 7 5.1.4 Clean up the repair area ..................5-1 5.2 Technical Alarms Check ....................5-1 5.2.1 Startup Alarm Messages..................5-2 5.2.2 CPU Board Runtime Alarm ................5-6 5.2.3 Power Board Runtime Alarm................5-6 5.2.4 Fresh Flow Sensor Board Alarm.................5-8 5.2.5 Ventilator Control Board Runtime Alarm ............5-10 5.3 Pneumatic Circuit System Problems................5-13 5.3.1 Tools for on-site Maintenance................5-13 5.3.2 Gas Supplies and Drive Gas ................5-27...
- Page 8 7.3.1 A5/A3 Structure ....................7-2 7.3.2 A5/A3 Upper Half....................7-4 7.3.3 A5/A3 Hardware Box ..................7-5 7.3.4 A5/A3 Work Surface...................7-6 7.3.5 A5/A3 Patient Circuit Main Body...............7-7 7.3.6 A5/A3 Pre-pak Absorber Canister Assembly............7-8 7.3.7 A5/A3 Valve assembly ..................7-9 7.3.8 A5/A3 O2 Cable Assembly ................7-10 7.3.9 A5/A3 Display Assembly..................7-11...
- Page 9 This page intentionally left blank.
-
Page 10: Foreword
Foreword This Service Manual is intended as a guide for technically qualified personnel performing repair and calibration procedures. Warnings, Cautions, and Notes Warnings, Cautions and Notes Please read and adhere to all warnings, cautions, and notes listed here and in the appropriate areas throughout this manual. -
Page 11: Cautions
When connecting gas supply lines attach the hose connection to the machine before connecting the quick disconnect fitting to the hospital source. Disconnect the supply hose from the hospital source connection prior to disconnecting it from the A5/A3 gas connection fittings. -
Page 12: Notes
Notes NOTE: Unauthorized servicing may void the remainder of the warranty. Check with the factory or with a local authorized distributor to determine the warranty status of a particular instrument. - Page 13 This page intentionally left blank.
-
Page 14: Theory Of Operation
The A5/A3 fresh gas dosing subsystem offers the ease of use and features of a traditional anesthesia system. The dual-flow tubes electronic flowmeter, which includes redundant numerical readouts, displays the O2, N2O, and Air flows at all times. A knob guard prevents inadvertent movement of the flow control knobs. - Page 15 (A5). A recessed main switch is provided to power the system ON and OFF. Four (4) auxiliary AC outlets on the A5 and three (3) auxiliary AC outlets on the A3 at the rear of the machine operate independently of the main switch position.
-
Page 16: Electrical And Pneumatic Connections
1.2 Electrical and Pneumatic Connections 1.2.1 Electrical Connections (A3) - Page 17 801-0631-00108-00 Warning Light Board 801-0631-00019-00 Indicator Light Board 801-0631-00004-00 Touch Screen Control Board 801-0631-00018-00 Display Interface Board 801-0631-00017-00 CPU Board PCBA (A5) 801-0631-00026-00 B9-11 Ventilator Control Board 801-0631-00027-00 Sensor Interface board 801-0631-00089-00 Top Lighting Board 801-0631-00039-00 Fresh Flow Sensor Board...
-
Page 18: Electrical Connections (A5)
1.2.2 Electrical Connections (A5) Lout Nout Lout Nout Lout Nout Lout Nout Lout Nout J4:RS-232 Board to board Connection Board to board Connection B8 J9:Ethernet J8:USB Board to board Connection Board to board Connection J8( Valve Brd) J4( Valve Brd)... - Page 19 Breaker (3.0A) 801-0631-00031-00 P11-12 Lithium-ion Battery 022-000008-00 Speaker and Connecting Cable 801-0631-00038-00 801-0631-00028-00 Touchpad 801-0631-00052-00 Main Body of Drive Gas Assembly 801-0631-00088-00 Display Exchange Package 801-0631-00075-00 Circuit Heater 801-0631-00069-00 Solenoid valve assembly 801-0631-00046-00 A5 calibration set FRU 801-0631-00121-00 Touch Screen 801-0631-00014-00...
-
Page 20: Pneumatic Connection (A3)
1.2.3 Pneumatic Connection (A3) - Page 21 From Total Flow Meter Vaporizer Manifold M6G-020014--- Back Pressure Regulator Total Flow Meter M6G-020014--- N2O Flow Sensor Gas Mixer 082-000524-00 Air Flow Sensor Gas Mixer 082-000520-00 O2 Flow Sensor Gas Mixer 082-000522-00 082-000524-00 Restrictor Assembly ORC Assembly 082-000520-00 Restrictor Assembly Air Flow Sensor ORC Assembly N2O Flow Sensor...
- Page 22 From Auxiliary Air Assembly 082-000520-00 O2 Needle Valve 082-000522-00 082-000522-00 O2 Poppet Valve 082-000522-00 O2 Poppet Valve 082-000522-00 O2 Poppet Valve 082-000522-00 O2 Flow Sensor 082-000522-00 O2 Pipeline Assembly 082-000521-00 082-000521-00 082-000520-00 Air Needle Valve Restrictor Assembly 082-000524-00 N2O Needle Valve Restrictor Assembly Three-way Connector 082-000583-00...
-
Page 23: Pneumatic Connection (A5)
1.2.4 Pneumatic Connection (A5) 1-10... - Page 24 From Total Flow Meter Vaporizer Manifold M6G-020014--- Back Pressure Regulator Total Flow Meter M6G-020014--- N2O Flow Sensor Gas Mixer 082-000524-00 Air Flow Sensor Gas Mixer 082-000520-00 O2 Flow Sensor Gas Mixer 082-000522-00 082-000524-00 Restrictor Assembly ORC Assembly 082-000520-00 Restrictor Assembly Air Flow Sensor ORC Assembly N2O Flow Sensor...
- Page 25 From Auxiliary Gas Outlet M6G-020026--- Auxiliary Air Assembly 082-000520-00 Auxiliary Gas Outlet 082-000521-00 O2 Needle Valve 082-000522-00 082-000522-00 O2 Poppet Valve 082-000522-00 O2 Poppet Valve 082-000522-00 O2 Poppet Valve 082-000522-00 O2 Flow Sensor 082-000522-00 O2 Pipeline Assembly 082-000521-00 082-000521-00 082-000520-00 Air Needle Valve Restrictor Assembly 082-000524-00...
-
Page 26: Connections Between Pneumatic Circuit, Breathing System And Ventilator Control Board
1.2.5 Connections Between Pneumatic Circuit, Breathing System and Ventilator Control Board 1-13... - Page 27 From Exhalation Gas Assembly Flow Sensor connector A21-000007--- Exhalation Gas Assembly Hardware Box Connector A21-000007--- Exhalation Gas Assembly Flow sensor connector A21-000007--- Three-way Valve Ventilator Control Board A21-000007--- Three-way Valve A21-000007--- Three-way Valve Ventilator Control Board A21-000007--- Three-way Valve A21-000007--- Ventilator Control Board A21-000007--- Ventilator Control Board...
-
Page 28: Gas Flow
1.3 Gas Flow 1.3.1 Pneumatic Circuit Diagram 1.3.2 Parts List O2 Pipeline Auxiliary Air Supply O2 Cylinder Inspiratory Valve N2O Pipeline CO2 Absorber Canister 1-15... - Page 29 N2O Cylinder Bypass Valve Air Pipeline O2 Sensor Air Cylinder Airway Pressure Gauge Regulator (0.4 MPa) Inspiratory Flow Sensor Pressure Relief Valve Patient Filter Expiratory Flow Sensor 10 Regulator (0.2 MPa) Water Collection Cup 11 Inpiratory Flow Valve Expiratory Valve 12 Flow Sensor Auto/Manual Ventilation Switch Mechanical Overpressure Valve...
-
Page 30: Key To Symbols
1.3.3 Key to Symbols Filter Regulator Pressure Gauge Check Valve Gas Supply Connector Pressure Relief Valve Flowmeter Flow Control Valve Pressure Switch Flow Restrictor 1.3.4 Description 1.3.4.1 Anesthetic Gas Delivery System The Anesthetic Gas Delivery System is connected to the anesthetic agent delivery device (vaporizer), breathing system, and anesthetic ventilator;... - Page 31 The following picture illustrates how gas supplies are outputted. O2 is divided into four pathways – system switch (24), O2 flush valve (20), auxiliary O2 supply (51), and high pressure O2 output (44), respectively. Air enters two pathways – one pathway to the needle valve (58) and the other to the auxiliary Air supply (3).
- Page 32 sensor (26). Air enters the electronic flow sensor (26) after passing through the needle valve (58) and the electronic flow meter monitors, and displays the gas flow. 56. Back pressure valve 26. Flow sensor 50. Total flow meter The converged gas goes from the total flow meter (50) to the anesthetic agent delivery device (vaporizer), forming fresh gas after mixed with the anesthetic agent.
- Page 33 Gas Supplies 8. Pressure Relief Valve 22. Pressure switch O2 pipeline supply inlet Pressure sampling tube for O2 supply gas pressure gauge The above picture shows the O2 pipeline supply inlet assembly. The anesthesia machine’s pneumatic circuit starts from the gas supplies, which function to introduce the external pipeline or cylinder gases into the machine.
- Page 34 System Switch Assembly O2 goes into the system switch (24); and flows into the needle valve. The system switch has an electrical outlet that controls the power-on status of the system. When the system switch is turned on, O2 enters the needle valve and the system is powered on simultaneously. The anesthetic ventilator starts to monitor the status of the system.
- Page 35 Flow Display Assembly The electronic flowmeter (26) and total flow meter (50) constitute the flow display assembly. Gases from the flow adjust and control assembly and mixed gas going through the anesthetic agent delivery device (vaporizer) are outputted. The electronic flowmeter (26) measures and displays the flow of each gas.
- Page 36 Vaporizer Manifold The above picture shows the vaporizer manifold assembly. The anesthetic agent delivery device (vaporizer) is connected to the anesthetic gas delivery system. The mixed gas of N2O, O2, and Air go into the device; the fresh gas containing these three gases and anesthetic agent is finally outputted to the CGO assembly.
- Page 37 High Pressure O2 Output Assembly (A5 Only) The high pressure O2 output (available on the A5 only) comes from the gas source directly and provides high pressure O2 for the external ventilation device (jet ventilation devices) without passing through the pressure regulator. When no external device is connected, the high pressure O2 output is closed.
- Page 38 1.3.4.2 Anesthetic Ventilator The anesthetic ventilator provides drive gas for the patient to breathe. O2 from the gas supply inlet assembly enters the anesthetic ventilator and is outputted in three pathways: drive gas entering the breathing system, drive gas discharged through the AGSS outlet, and drive gas discharged through the PEEP outlet.
- Page 39 (42) to supply gas for the breathing system. The APL valve (43) is used to adjust the pressure inside the pneumatic circuit in case of manual ventilation. When the Auto/Manual switch is placed in the Auto position, the A5/A3 starts its ventilator to 1-26...
- Page 40 mechanically assist or replace the spontaneous breathing of the patient. The ventilator controls the drive gas to depress the folding bag inside bellows (45) and supply gas for the breathing system according to the selected ventilation mode. The breathing system is connected to the anesthesia machine main unit through the circuit adapter.
- Page 41 33. Built-in BYPASS valve 32. CO2 Absorber Canister Operating handle In case of mechanical ventilation, during inspiration, gas flows through the Auto/Manual ventilation switch (41), BYPASS valve (33) or CO2 absorber canister (32), inspiratory valve (31), O2 sensor (34), airway pressure gauge (35), and inspiratory flow sensor (36) to the patient.
- Page 42 The following figure shows the operational theory of the AGSS. The throttling holes reduce the effect of negative pressure at the AGSS outlet onto the flow at the entrance. The float helps the user determine if the disposal system meets the requirement for the minimum pump rate.
-
Page 43: Anesthesia System Components
The A3 anesthesia system has three 125V 15A Hospital Grade auxiliary outlets. Each outlet has one 250V 3A breaker. The A5 anesthesia system has four 125V 15A Hospital Grade auxiliary outlets. Each outlet has one 250V 3A breaker. Additionally, a main breaker limits the combined current of the four outlets to 10A. -
Page 44: The Breathing System
Flow Meter Lighting Control Signal 1.5 The Breathing System 1.5.1 Brief Introduction The A5/A3 Breathing System supports three types of operational modes: mechanical ventilation, manual ventilation, and standby. These modes allow the operator to apply proper ventilation strategy based on the patient’s needs. -
Page 45: Automatic Mode, Inspiration
1.5.2 Automatic Mode, Inspiration When the Auto/Manual switch is positioned at Auto, the system closes the manual ventilation path. Drive gas pushes down on the bellows. Gas flows from the bellows, through the CO2 absorber canister, and through the inspiratory check valve to the patient. During inspiration, fresh gas flows into the inspiratory limb, upstream of the inspiratory check valve. -
Page 46: Automatic Mode, Expiration
1.5.3 Automatic Mode, Expiration When the Auto/Manual switch is set to Auto, the system closes the manual ventilation path. Drive-gas flow stops and the exhaust valve opens. Exhaled gas flows from the patient, through the expiratory check valve, and into the bellows. Residual drive gas flows out of the bellows dome through the exhaust valve to the scavenging system (AGSS). -
Page 47: Manual Mode, Inspiration
1.5.4 Manual Mode, Inspiration When the Auto/Manual switch is set to Manual, the system closes the Auto ventilation path. Gas flows from the breathing bag when compressed, through the CO2 absorber canister, into the breathing circuit, and through the inspiratory check valve to the patient. During inspiration, fresh gas flows from the machine into the inspiratory limb, upstream of the inspiratory check valve. -
Page 48: Manual Mode, Expiration
1.5.5 Manual Mode, Expiration When the Auto/Manual switch is set to Manual, the system closes the Auto ventilation path. Gas flows from the patient, through the expiratory check valve, and into the breathing bag. During exhalation, fresh gas enters the Breathing System. Residual fresh gas passes through the APL valve to the AGSS. -
Page 49: Breathing System Components
1.5.8 Breathing System Components 1.5.8.1 Ventilation Bellows System The ventilator's driving system is a flow generator. Driving gas fills the bellows dome to compress the bellows. The breathing gas is pressed out of the bellows into the patient breathing circuit. The bellows is refilled with fresh gas and the expired gas from the patient. 1.5.8.2 Manual Breathing Bag In manual mode, this device acts as a normal breathing bag, enabling the user to ventilate the patient manually. -
Page 50: Ventilator Ui
1.6 Ventilator UI 1.6.1 Display 1.6.1.1 Display Interface Board Display Interface Board, Top View Display Interface Board, Bottom View Inverter interface,J1 NAME FUNCTION Inverter 12V Power Supply Inverter 12V Power Supply Ground Ground LCD_EN LCD Backlight Enable LCD_BR LCD Backlight Brightness Control 1-37... - Page 51 Warning Light Board Interface,J2 NAME FUNCTION Warning Light Board 12V Power Supply Ground SDA_CPU CPU Board I2C Data Signal SCL_CPU CPU Board I2C Clock Signal 3_3V 3.3V Power Supply Ground Touch Screen Control Board interface,J4 NAME Function 5V Power Supply RXD_TOUCH_PANEL Touch Screen Control Board Serial Port Receive Signal TXD_TOUCH_PANEL...
- Page 52 1.6.1.2 Warning Light Board Warning Light Board,Top View Warning Light Board,Bottom View Warning Light Board interface,J1 NAME FUNCTION 12V Power Supply Ground MAIN_BRD_SDA CPU Board I2C Data Signal MAIN_BRD_SCL CPU Board I2C Clock Signal 3_3V 3.3V Power Supply 1.6.1.3 Display The anesthesia system display is a 15-inch, 24-bit, 1024x768 LVDS touch screen.
- Page 53 1.6.1.4 Fresh Flow Sensor Board Fresh Flow Sensor Board,Top View Fresh Flow Sensor Board,Bottom View Fresh Flow Sensor Board Interface,J1 NAME FUNCTION TXD_FLOW_BRD Fresh Flow Sensor Board Serial Port Transmit Signal RXD_FLOW_BRD Fresh Flow Sensor Board Serial Port Receive Signal Ground Fresh Flow Sensor Board 12V Power Ssupply 1-40...
- Page 54 1.6.1.5 Indicator Light Board Indicator Light Board, Top View Indicator Light Board, Bottom View Indicator Light Board interface,J1 NAME FUNCTION LED_AC AC Indicator Light Drive Signal LED_BAT Battery Indicator Light Drive Signal Ground 1-41...
-
Page 55: Cpu Board
1.6.2 CPU Board CPU Board , Top View CPU Board, Bottom View 1-42... - Page 56 Network Port, J9 NAME FUNCTION Positive End of Transmit Signal Negative End of Transmit Signal Positive End of Receive Signal No Definition No Definition Negative End of Receive Signal No Definition No Definition USB Interface, J8 NAME FUNCTION USB Power Supply USB Data Signal –...
-
Page 57: Ventilator Control And Drive
1.7 Ventilator Control and Drive 1.7.1 Mother Board Mother Board, Top View Mother Board , Bottom View 1-44... - Page 58 VCM Interface,J1 NAME FUNCTION SAFE_VALVE Pressure Relief Valve Drive Signal 7VIN Inspiration Valve Drive Signal INSP_VALVE Inspiration Valve Drive Signal 7VIN PEEP Valve Drive Signal PEEP_VALVE PEEP Valve Drive Signal SOLENOID_VALVE1 Three-way Valve 1 SOLENOID_VALVE2 Three-way Valve 2 SOLENOID_VALVE3 Three-way Valve 3 SOLENOID_VALVE4 Three-way Valve 4 PNEUM_PRES_SW...
- Page 59 Pneumatic Assembly Interface,J2 NAME FUNCTION 7Vout Pressure Relief Valve Power Supply SAFE_VALVE Pressure Relief Valve Drive Signal 7Vout Inspiration Valve Power Supply INSP_VALVE Inspiration Valve Drive Signal 7Vout PEEP Valve Power Supply PEEP_VALVE PEEP Valve Drive Signal Three-way Valve Power Supply SOLENOID_VALVE1 Three-way Valve Drive Signal 1 Three-way Valve Power Supply...
- Page 60 Display Interface,J3 NAME FUNCTION LCD_EN Inverter Enable Signal LCD_BR Inverter Brightness Adjustment Signal RXD_TOUCH_PANEL Touch Screen Control Board Serial Port Receive Signal TXD_TOUCH_PANEL Touch Screen Control Board Serial Port Transmit Signal No Connection LED_AC AC Indicator Light Drive Signal LED_BAT Battery Indicator Light Drive Signal MAIN_BRD_SDA CPU Board I2C Signal...
- Page 61 RSVD Reserved RSVD Reserved Ground LED_BAT Battery Indicator Light Drive Signal PCON-_NON Power ON/OFF Inverse Phase Signal Ground PCON+ Power ON/OFF Circuit 3.3V PCON- Power ON/OFF Signal TOUCHPAD_5V 5V Power Supply TOUCHPAD_GND Ground TOUCHPAD_USB+ TOUCHPAD_USB Difference to Positive Signal TOUCHPAD_USB- TOUCHPAD_USB Difference to Negative Signal 12V Power Supply Ground...
- Page 62 Power Board Interface,J10 NAME FUNCTION PLAM Buzzer Drive Signal (drives the buzzer directly) RXD_PWR_BRD Power Board Serial Port (receives signal) LOOP_SW Circuit Switch (reflects if the circuit is in position) TXD_PWR_BRD Power Board Serial Port (transmits signal) Power Board Cooling Fan Drive Ground LED-BAT Battery Status Indicator Light Drive Output...
- Page 63 NAME FUNCTION 15V2 15.2V Supply Voltage Output No Connection 15V2 15.2V Supply Voltage Output CPU Board Interface,J11 NAME FUNCTION LCD_VDD LCD Power Supply LCD Ground No Connection No Connection Serial Port Transmit Signal RSVD Serial Port Receive Signal RSVD Ground Serial Port Transmit Signal RSVD Serial Port Receive Signal...
- Page 64 NAME FUNCTION Speaker Drive Signal - SPK_OUT- Ground No Connection No Connection No Connection No Connection No Connection Ground Power Board Serial Port Transmit Signal TXD_PWR_BRD Power Board Serial Port Receive Signal RXD_PWR_BRD Ground Fresh Flow Sensor Board Serial Port Transmit Signal TXD_FLOW_BRD Fresh Flow Sensor Board Serial Port Receive Signal RXD_FLOW_BRD...
- Page 65 NAME FUNCTION LVDS Clock Signal LVDS-TOC+ LVDS Clock Signal LVDS-TOC- Ground Ventilator Control Board Serial Port Transmit Signal TXD_MON_BRD Ventilator Control Board Serial Port Receive Signal RXD_MON_BRD Ground Auxiliary Ventilator Control Board Serial Port Transmit TXD_AUX_BRD Signal Auxiliary Ventilator Control Board Serial Port Receive RXD_AUX_BRD Signal Ground...
-
Page 66: Ventilator Control And Drive Board
DESIGNATOR NAME FUNCTION RANGE (Unit: V) RXD_33209 VPM Serial Port Receive High level 2.4~5; Signal Low level 0~0.4 RXD_FLOW Fresh Flow Sensor Board High level 2.4~5; Serial Port Receive Signal Low level 0~0.4 TXD_POWER Power Board Serial Port High level 2.4~5; Transmit Signal Low level 0~0.4 RXD_POWER Power Board Serial Port... - Page 67 1.7.2.1 Monitor Signal Detection Board Monitor Signal Detection Board, Top View Monitor Signal Detection Board, Bottom View 1-54...
- Page 68 Monitor Signal Detection Board Communication Interface, J1 NAME FUNCTION Serial Port Transmit Serial Port Receive 12V Power Supply Ground Ground 12V Power Supply PRST Pressure Relief Valve Control Signal 5V Power Supply Ventilator Sensor Interface, J3 NAME FUNCTION I2C Data Signal I2C Clock Signal Thermal Mass Flow Sensor Temperature Signal Thermal Mass Flow Sensor Flow Signal...
- Page 69 VPM Communication Interface, J5 NAME FUNCTION TXD_AUX_BRD VPM Serial Port Transmit Signal RXD_AUX_BRD VPM Serial Port Receive Signal Ground 12V Power Supply O2 Cell Detection Interface, J12 NAME FUNCTION O2 Cell + O2 Cell - Ground Test Point Definition DESIGNATOR NAME FUNCTION RANGE (unit: V) O2 Concentration Voltage...
- Page 70 1.7.2.2 Valve Drive Board Valve Drive Board, Top View Valve Drive Board, Bottom View 1-57...
- Page 71 Proportional Valve and Pressure Relief Valve Drive Interface, J4 NAME FUNCTION Pressure Relief Valve Power Supply SAFE_VALVE Pressure Relief Valve Control Signal Inspiration Valve Power Supply INSP_VALVE Inspiration Valve Control Signal PEEP Valve Power Supply PEEP_VALVE PEEP Valve Control Signal Power Supply Interface, J2 NAME FUNCTION...
- Page 72 1.7.2.3 Sensor Interface Board Sensor Interface Board, Top View Sensor Interface Board, Bottom View Sensor Interface Board Interface, J2 NAME FUNCTION MON_BRD_SDA VCM I2C Data Signal MON_BRD_SCL VCM I2C Clock Signal Thermal Mass Flow Sensor Temperature Signal Thermal Mass Flow Sensor Flow Signal 12V Power Supply Ground 1-59...
-
Page 73: Battery
Battery: 11.1V, 4.5Ah×1V Lithium-ion battery (sealed) Battery running time: 75 minutes (new battery) Battery charge time: 8 hours max from an initial charge of 10% For A5 anesthesia system: Battery: 11.1V, 4.5Ah×2V Lithium-ion Battery (sealed) Battery Run Time: 150 minutes (new battery) Battery Charge Time: 8 hours max from an initial charge of 10% 1.7.3.2 Battery Adaptation Board... -
Page 74: Breathing System Heater
Battery Cable Interface, J3 NAME FUNCTION VBAT1 Battery Voltage NTC1 Battery Internal Thermistor Battery In-position Signal Ground VBAT2 Battery Voltage NTC2 Battery Internal Thermistor Battery In-position Signal Ground 1.7.4 Breathing System Heater The anesthesia system heater provides software and hardware dual-protection from overheating. - Page 75 This page intentionally left blank. 1-62...
-
Page 76: Installation Guide
Calibration.) 2.2.1 Unpacking and Setup When the A5/A3 is delivered, IMMEDIATELY inspect the box for any damage. a. If there is NO damage and ALL tip indicators on the box exterior are intact, then sign and date the bill of lading or airway bill to indicate safe receipt of the anesthesia system. - Page 77 3. Pull the box top straight up off the box and place on the floor near the unit. The box top will be used later as a ramp when rolling down the A5/A3 onto the floor. 4. Pull the box straight up and over the unit.
- Page 78 Cut the plastic tie wrap as shown below. Roll down the plastic bag from the unit. Using a pair of scissors, cut the plastic wrap from the A5/A3 near the back of the unit, using care to not scratch or otherwise damage the unit. Remove and discard the plastic...
- Page 79 After removing the plastic wrap and foam, check that there is a box on the side of the unit, as shown below. 10. At the base of the box platform, remove both sets of orange straps. Save the straps in case the A5/A3 needs to be repacked.
- Page 80 11. Remove the piece of wood at the front of the A5/A3. Then, remove the foam packing material from around the front of the unit. 12. Remove the foam packing material from around the back of the unit. 13. Create a ramp for the unit by placing the top of the container next to the base of the container as shown.
- Page 81 15. Open the bottom drawer and remove the Breathing Assembly (P/N: 115-006542-00) and the Bag Arm Assembly (P/N: 115-006543-00). 16. Install the Breathing Assembly on the side of the A5/A3. Align the Assembly carefully, and then push it firmly towards the A5/A3 until the Assembly clicks into place.
- Page 82 18. Install the bellows on the Breathing System. Ensure that the bellows is stretched completely around the lip on the breathing system when installed. 19. Install the bellows dome by placing it down on the breathing system and turning it clockwise to lock it in place (the gradation markings on the bellows dome should face front and be visible to the operator).
- Page 83 20. Install the Bag Arm Assembly, aligning the keyed features as shown below. 21. Then, push the Bag Arm Assembly into the Breathing System and tighten the knurled collar as shown below.
- Page 84 22. Open the middle and bottom drawers and carefully remove the Removable Absorber Assembly (P/N: 115-007453-00), Waste Gas Scavenger Hose (P/N: 115-006557-00) and the Waste Gas Scavenger Assembly (P/N: 115-006556-00). 23. Install the white Absorber hose on the Absorber Assembly. Then, install the Absorber Assembly without the canister in place.
- Page 85 Breathing Assembly) of the A5/A3 and tighten the thumbscrew on the Scavenger Assembly to lock it in place. Install one side of the Scavenger Hose to the Scavenger Assembly and the other side of the Hose to the A5/A3 as shown below. 2-10...
- Page 86 Install one or two batteries with the proper polarity. Close the compartment and tighten the thumbscrews. 28. Before installing the gas cylinders at the rear of the A5/A3, verify that the tank washers are installed. Remove the tape holding washers in place. Then, install the gas cylinders.
- Page 87 WARNING: Use only Mindray-approved monitors and arms with the A5/A3. 38. Connect Hose (P/N: 801-0631-00078-00 or P/N: 115-008426-00) to the outlet of the gas module and to the Colder fitting at the back of the A5/A3. Place the unused hose in the bottom drawer.
-
Page 88: Breathing System And Breathing System Accessories And Checkout Procedures2-13
A5/A3. 2.2.3.1 Tank Wrench and Pre-operation Checklist 1. Mount the tank wrench on the rear of the A5/A3 so that it can be used to open or close each cylinder without disconnecting it from the machine. 2. Attach the pre-operation checklist to a location on the A5/A3 where the operator can access... -
Page 89: Vaporizers
ISO 8835-4. Refer to the vaporizer manufacturer’s Instructions For Use for filling or draining the vaporizer and other information. WARNING: For the A5/A3 Anesthesia System, using or turning on more than one vaporizer simultaneously is mechanically prevented by the Selectatec mount system. Do not attempt to override this safety feature. - Page 90 Instructions for Use of the Desflurane vaporizer. 2.2.4.2 Fill the Vaporizer NOTE: The A5/A3 should use vaporizers with Selectatec mounting system that are compliant to ISO 8835-4. Refer to the vaporizer manufacturer’s Instructions For Use for filling or draining the vaporizer and other information.
-
Page 91: Emergency Cylinder(S)
NOTE: Use of other monitors and mounting hardware is the responsibility of the installer. 2. After mounting a monitor to the A5/A3, connect it to one of the AC outlets located on the rear of the A5/A3. 3. Turn on each monitor one at a time. Verify that the circuit breaker holds without tripping. -
Page 92: Functional Tests
Refer to 4 Calibration if any values are out of specification. NOTE: The A5/A3 system must be powered on (AC power, not battery) and the Breathing System Warmer set to ON (version 2.01.00 and higher) at least an hour before performing the Ventilation Tests starting in Section 2.6.5. - Page 93 2. Set up the machine as per the instructions on the screen. Then, select Continue to execute manual circuit leak test. 3. The ongoing manual circuit leak test is as shown below. You can select Cancel to cancel the ongoing leak test. The following screen is displayed if the manual circuit leak test is failed.
- Page 94 NOTE: If there is a leak, check the pneumatic circuit system for leakage and troubleshoot the problems as described in 5.3 Pneumatic Circuit System Problems. Repeat the leak test after the source of the failure has been resolved. 2-19...
- Page 95 2.3.2.2 Breathing System Leak Test in Mechanical Ventilation Mode This test checks the pneumatic circuit for leaks in mechanical ventilation mode. Test items include the bellows, drive gas circuit, CO2 absorber canister, patient tubes, flow sensors, and flow sensor connectors. To perform the breathing system leak test in mechanical ventilation mode: 1.
- Page 96 Both automatic ventilation and manual ventilation can still be applied applied using the previous compliance value in the A5/A3 system memory, but may not meet the accuracy of the delivered volume. The following screen is displayed if the safety valve control test is failed. You can select Service Access and enter the required service password to access service mode.
- Page 97 The following screen is displayed if the compliance test is failed. You can select Override to enter Standby mode.You can select Retry to perform automatic circuit leak test again. The following screen is displayed if the automatic circuit leak test is completed. Select Continue to enter Standby mode.
-
Page 98: O2 Sensor Calibration
NOTE: Both a 21% and 100% O2 calibration MUST BE performed before first use of the A5/A3. The O2 sensor is not calibrated with the machine at the factory. NOTE: Calibrate the O2 sensor when a great deviation of O2 concentration monitored value occurs or when the O2 sensor or ventilator control board is replaced or when prompted by the anesthesia system. - Page 99 2.3.3.1 21% O2 Calibration (Version 01.03.02 and earlier) NOTE: In version 01.03.02 and earlier, 21% O2 sensor calibration can be performed from the Setup > Calibrate menu and Setup > Service menu. Follow these steps to calibrate the O2 sensor at 21% O2. Select Setup >...
- Page 100 The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to repeat the calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen shown below is displayed if the calibration has failed. Select Try Again to repeat the calibration.
- Page 101 The screen shown below is displayed after a successful calibration (in standby mode). Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen as shown below is displayed after a successful calibration (in non-standby mode). Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 2-26...
- Page 102 2.3.3.2 100% O2 Calibration (Version 01.03.02 and earlier) NOTE: In version 01.03.02 and earlier, 100% O2 sensor calibration can be performed from the Setup > Calibrate menu and Setup > Service menu. NOTE: 100% O2 calibration must performed in standby mode. NOTE: 100% O2 calibration must performed only after a successful 21% O2 calibration.
- Page 103 The calibration screen shown below is displayed when 100% is selected. Set up the machine as per the instructions on the screen and select Next. Set the AUTO/MANUAL lever to the AUTO position. 2-28...
- Page 104 The calibration screen shown below is displayed when Next is selected. Set up the machine as per the instructions on the screen and select Next. Wait 2 minutes to ensure that the O2 cell voltage has stabilized at the maximum value for at least 30s. The calibration screen as shown below is displayed when Next is selected.
- Page 105 The calibration screen as shown below is displayed when Begin is selected. During the calibration, you can select Cancel to cancel the calibration. The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to repeat the calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 2-30...
- Page 106 The screen shown below is displayed if the calibration has failed. Select Try Again to repeat the calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen as shown below is displayed after a successful calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 2-31...
- Page 107 2.3.3.3 21% O2 Calibration (Version 02.01.00 and higher) NOTE: In version 02.01.00 and higher, 21% O2 sensor calibration can be performed from the Setup > General menu, Setup > System menu and Setup > Service menu. Follow these steps to calibrate the O2 sensor at 21% O2: Select Setup >...
- Page 108 The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is canceled. Select Try Again to repeat the calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen shown below is displayed if the calibration has failed. A Fail code is displayed in red.
- Page 109 The screen shown below is displayed after a successful calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 2.3.3.4 100% O2 Calibration (Version 02.01.00 and higher) NOTE: In version 02.01.00 and higher, 100% O2 sensor calibration can be performed from the Setup > System menu and Setup > Service menu. NOTE: 100% O2 calibration must be performed in standby mode.
- Page 110 Enter Standby. Select Setup > System > Calibrate O2 Sensor or Setup > Service > Calibration > O2 Sensor. The System and Service tabs require passwords and shows both 21% and 100% O2 Sensor calibration. The calibration screen shown below is displayed when 100% is selected.
- Page 111 The calibration screen as shown below is displayed when Begin is selected. During the calibration, you can select Cancel to cancel the calibration. The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to repeat the calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 2-36...
- Page 112 The screen shown below is displayed if the calibration has failed. A Fail code is displayed in red. Select Try Again to repeat the calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen as shown below is displayed after a successful calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen.
- Page 113 2.3.3.5 Troubleshooting: O2 Sensor Calibration Failure Possible cause Recommended action description After [Start] is If the alarm [O2 Sensor Unconnected] Connect the O2 sensor. selected, calibration is displayed, it indicates that O2 failure is prompted sensor is not connected. very soon. O2 supply pressure is insufficient Change or connect the gas supply (lower than 200 kPa).
-
Page 114: Pneumatic Leak Tests
Turn all fresh gas flows to 0 psi. 2.4.1 N2O Cylinder Leak Test 1. Remove the N2O line pressure hose from the line pressure inlet on the A5/A3. 2. Mount a full N2O cylinder to the rear panel yoke. If necessary, place a new clean tank washer between the cylinder and the yoke to minimize any leaks at the yoke connection. -
Page 115: N2O Line Pressure Leak Test
2.4.4 N2O Line Pressure Leak Test 1. Remove the N2O cylinder from the anesthesia system. 2. Connect the N2O line pressure hose to the line pressure inlet on the anesthesia system. 3. Pinch the N2O line pressure hose to stop N2O line flow. 4. -
Page 116: Breathing System Checks
2. Connect only the AIR line pressure hose to the anesthesia system from the wall supply. Leave all other line pressure hoses disconnected. 3. With the A5/A3 powered ON, rotate the AIR flow control knob to ensure a continuous flow increase throughout its full range. -
Page 117: Performance Verification
2.6 Performance Verification 2.6.1 Standby Mode Ventilation Test 1. Ensure that the gas pressure for O2, N2O, and AIR is within specifications. 2. Power ON the anesthesia system. 3. Perform the start up tests per the on-screen instructions. Ensure successful completion. 4. -
Page 118: Vcv Adult Ventilation Mode Test
2.6.5 VCV Adult Ventilation Mode Test 1. Attach a breathing circuit and breathing bag. NOTE: For testing purposes, always use a reusable breathing circuit. 2. Attach an adult test lung to the Y-fitting of the breathing circuit. 3. Attach a Vent Tester between the EXP port and the expiratory hose. 4. -
Page 119: Vcv Child Ventilation Mode Test
2.6.6 VCV Child Ventilation Mode Test 1. Attach a breathing circuit and breathing bag. NOTE: For testing purposes always use a reusable breathing circuit. 2. Attach an adult test lung to the Y-fitting of the breathing circuit. NOTE: Limit the volume in the test lung to provide sufficient airway pressure to satisfy the Low Peak Pressure alarm. -
Page 120: Pressure Support (Ps) Ventilation Mode Test
5. Set the ventilator controls to: Ventilator Controls Ventilator Settings Patient Type Adult Ventilation Mode Pinsp Rate PEEP Tslope PlimVG 6. Press Set Mode button to begin ventilation. 7. Verify the Peak Pressure reading of the display is within ±2 cmH2O of the set Pinsp. 8. -
Page 121: Alarms And Fail Safe Functions
2.7 Alarms and Fail safe Functions 2.7.1 Set Up 1. Ensure that the gas pressure for O2, N2O, and AIR are is within specifications. 2. Power ON the anesthesia system. 3. Perform the Startup Tests per the on-screen instructions. Ensure successful completion. 4. -
Page 122: Peak Pressure Alarms Test
2.7.4 Peak Pressure Alarms Test 1. Set the PEAK low alarm to the lowest setting. 2. Set the PEAK high alarm limit set point about 5 to 8 digits below the Peak Pressure displayed on the screen. 3. Verify the following (high) peak pressure alarms activate: a. -
Page 123: Miscellaneous Tests
2.8 Miscellaneous Tests 2.8.1 Test the Line Voltage Alarm 1. Interrupt AC line voltage. 2. Verify that the following alarms activate: An alarm tone sounds. Battery in use message appears on the screen. 3. Plug the anesthesia system into AC line voltage. 4. -
Page 124: Vaporizer Accuracy Test
2.10 Vaporizer Accuracy Test Set the APL Valve to 70 cmH2O. Put the AUTO / MANUAL lever in the MANUAL position. Connect one end of a breathing hose to the expiratory port. Connect the other end to the bag arm. Connect the sampling tee of the Gas analyzer to the inspiratory port. -
Page 125: Electrical Tests
2.11 Electrical Tests CAUTION: Perform the electrical safety inspection as the last step after completing a repair or after routine maintenance. Perform this inspection with all covers, panels, and screws installed. 2.11.1 Auxiliary AC Outlets Test WARNING: Perform the electrical safety inspection as the last step after completing a repair or after routine maintenance. -
Page 126: Periodic Maintenance
Periodic Maintenance 3.1 Maintenance Schedule The following is a list of activities required for periodic maintenance of the A5/A3 Anesthesia System. Physical inspection, replacement of consumables, and performance checks should be periodically performed per the schedule listed below. The manufacturer is not responsible for component failure or loss resulting from the use of stated consumables beyond their recommended replacement interval. -
Page 127: List Of Parts Inside The Periodical Maintenance Consumable Parts Kits
The following table lists the parts to be replaced periodically inside the consumable parts kits. The replacement date starts from the date when the machine is assembled. Consumable Parts Amount 12 Month 36 Month Part Nunber Lithium-ion battery 2 (A5) Check Replace 022-000008-00 1 (A3) Cell battery Lithium 3V35mAh Check Replace M05-010R03--- D12.5*2.0 (for main control board) - Page 128 O-ring 4.47X1.78 (for CO2 Bypass Check Check 082-000679-00 shaft) Tank Washer Replace Replace 0348-00-0185 O-Ring 52X2 Auto/Manual Check Check 082-000630-00 ventilation switch O-Ring 40X2.2 Auto/Manual Check Check 082-000648-00 ventilation switch O-Ring 30X2 bag arm base Check Check 082-000624-00 O-Ring 8.5X2.0 O2 cell port Check Replace 082-000654-00...
-
Page 130: Battery Maintenance And Replacement
3.6 Battery Maintenance and Replacement Maintenance is not required for the lithium-ion battery supply in the A5/A3. If the battery supply does not function normally, replace it as follows:... -
Page 131: Functional Tests
4.Install the new battery. 5.Close the battery box. 6.Close the rear cover. 7.Use only Mindray approved batteries (P/N 022-000008-00). 3.7 Functional Tests Refer to Chapter 4 Calibration if any values are out of specification. NOTE: The anesthesia system system must be turned on (AC power, not battery) at least an hour before performing the Ventilation Tests. -
Page 132: Breathing System Leak Test
3.7.2 Breathing System Leak Test NOTE: Always perform the leak test after servicing the anesthesia machine, replacing the components, or reconnecting the tubes. 3.7.2.1 Breathing System Leak Test in Manual Ventilation Mode This test aims to check if the pneumatic circuit has leaks in manual ventilation mode. Test items include APL valve, check valve, CO2 absorber canister, patient tubes, flow sensors, and the flow sensor connectors. - Page 133 The ongoing manual circuit leak test is as shown below. You can select Cancel to cancel the ongoing leak test. The following screen is displayed if the manual circuit leak test is failed. You can select [Retry] to perform the leak test again or click [Override] to proceed with automatic circuit leak test.
- Page 134 The following screen is displayed if the manual circuit leak test is completed. Select Continue to enter automatic circuit leak test. NOTE: If there is a leak, check the pneumatic circuit system for leakage and troubleshoot the problems as described in Section 5.3 Pneumatic Circuit System Problems.. NOTE: After troubleshooting the leak failure, repeat the leak test.
- Page 135 3.7.2.2 Breathing System Leak Test in Mechanical Ventilation Mode The test aims to check if the pneumatic circuit has leaks in mechanical ventilation mode. Test items include bellows, drive gas circuit, CO2 absorber canister, patient tubes, flow sensors, and flow sensor connectors. To perform the breathing system leak test in mechanical ventilation mode: You can access the automatic circuit leak test screen after the manual circuit leak test is passed.
- Page 136 During the automatic circuit leak test, the safety valve control test is also being conducted. The automatic circuit leak test results are listed in the following table. Test results System limitation Safety valve control failed The machine cannot be used. Upgrade to 02.00.00 software or higher, and repeat test.
- Page 137 The following screen is displayed if the compliance test is failed. You can select Override to enter Standby mode.You can select Retry to perform automatic circuit leak test again. The following screen is displayed if the automatic circuit leak test is completed. Select Continue to enter Standby mode.
- Page 138 NOTE: In case of leak test failure, check all of the possible leak sources, including bellows, breathing system tubes and CO2 absorber canister. Check that they are correctly connected and their connectors are not damaged. NOTE: If there is a leak, check the pneumatic circuit system for leakage and troubleshoot the problems as described in Section 5.3.4 Breathing System.
-
Page 139: Check The Sensor Zero Point
3.7.2.3 Troubleshooting: Leak Test The following table lists the commonly-encountered problems and recommends actions for Section 3.7.2.2 Breathing System Leak Test in Mechanical Ventilation Mode.. Failure description Possible cause Recommended action Leak test failure is The Auto/Manual Set the Auto/Manual prompted immediately ventilation switch is set to the ventilation switch to the... - Page 140 4. The second column is the zero point in case of factory calibration and the third column is the zero point of the current sensor. The following table lists the normal range of the zero point of A5/A3 pressure and flow sensors.
- Page 141 of the Paw waveform is not at the zero point and a great deviation occurs between pressure control and measurement. NOTE: If the zero point of the inspiratory/expiratory flow sensor has an error, in ventilation status, the baseline of the flow waveform is not at the zero point and a great deviation occurs between TV control and measurement.
-
Page 142: Check The Flow Sensor Accuracy
3.7.4 Check the Flow Sensor Accuracy NOTE : If a great deviation of Vt measured value occurs, test the measurement accuracy of flow sensors so as to determine whether to perform flow calibration again. NOTE: You can use any flow meter that has an accuracy of at least ±2% for the accuracy measurement of the flow sensors. - Page 143 Gas Settings: Press the Setup button, select Setting->ENTER->Gas Settings->MODIFY->Gas Type->O2. Select BACK->BACK-> BACK. 3-18...
- Page 144 When the system is Standby, select the Setup-> Service-> Diagnostic Tests->Valves to access the following menu. Set safety valve to [ON]. Set the PEEP valve pressure to 30 cmH2O. Set the Insp Valve Flow to the following values: (3±0.5)L/min, (10±1)L/min, (20±1)L/min, (30±2)L/min, (60±3)L/min. Make sure that the deviation between the measured data of the inspiratory flow sensor, expiratory flow sensor and ventilator flow sensor and that of the anesthesia machine calibration device must not exceed 1 L/min or 5% of the measured value of the...
-
Page 145: Check The Pressure Sensor Accuracy
3.7.5 Check the Pressure Sensor Accuracy NOTE: Generally, measurement deviations do not easily occur to pressure sensors. However, in case of replacing the ventilator control board, solenoid valve assembly, or expiratory valve assembly, you need to perform pressure calibration and check the flow sensors accuracy so as to confirm the effectiveness of calibration. - Page 146 VT Pl us Low Press + Calibration Device (VT Plus) Set up the calibration device as described below. To set the VT-Plus: Pressure Setting: Press the PRESSURE button on the front control panel of the calibration, select Range and then set it to Low Press. 3-21...
- Page 147 Gas Settings: Press the Setup button, select Setting->ENTER->Gas Settings->MODIFY->Gas Type->O Select BACK->BACK-> BACK. 3-22...
- Page 148 When the system is Standby, select the Setup->Service-> Diagnostic Tests-> Valves to access the following menu. Set safety valve to ON. Set the PEEP valve pressure to the following values: (5±1) cmH2O, (20±1) cmH2O, (50±1) cmH2O, (70±2) cmH2O, (90±2) cmH2O. Make sure that the deviation between the measured data of the airway pressure sensor, PEEP pressure sensor and that of the anesthesia machine calibration device must not exceed 1 cmH2O or 2% of the measured value of the calibration device, whichever is...
-
Page 149: Pneumatic Leak Tests
Turn all fresh gas flows to 0. 3.8.1 N2O Cylinder Leak Test 1. Remove the N2O line pressure hose from the line pressure inlet on the A5/A3. 2. Mount a full N2O cylinder to the rear panel yoke. If necessary, place a new clean tank washer between the cylinder and the yoke to minimize any leaks at the yoke connection. -
Page 150: O2 Line Pressure Leak Test
3.8.5 O2 Line Pressure Leak Test 1. Remove the O2 cylinder from the A5/A3. 2. Connect the O2 line pressure hose to the line pressure inlet on the A5/A3. 3. Pinch the O2 line pressure hose to stop O2 line flow. -
Page 151: Internal Gas Connections Test
3.9.2 Internal Gas Connections Test 1. Close and remove all gas cylinders from the A5/A3 2. Connect only the AIR line pressure hose to the A5/A3 from the wall supply. Leave all other line pressure hoses disconnected. 3. With the A5/A3 powered ON, rotate the AIR flow control knob to ensure a continuous flow increase throughout its full range 4. -
Page 152: Drive Gas Pressure Loss Alarm, N2O Cutoff Test
3. Set the AIR flow to 2 L/min using the flow control valve. 4. Interrupt the O2 supply to the A5/A3. 5. Verify that the flow of N2O and O2 stops within 2 minutes and that the flow of AIR (if available) continues to flow at 2 L/min. -
Page 153: Apnea Alarm Test
6. Verify that an airway pressure waveform and all numeric values appear on screen during bag compressions. 7. Stop squeezing the breathing bag and set the APL Valve to the open position (SP). 3.10.3 APNEA Alarm Test 1. While in the Manual Ventilation Mode, stop ventilating the test lung. 2. -
Page 154: Alarm Silence Test
3.10.4 Alarm Silence Test 1. While the APNEA alarm is sounding, press the Silence soft key. 2. Verify the audio portion of the alarm stops and resumes after 2 minutes. 3.10.5 VCV Adult Ventilation Mode Test 1. Attach a breathing circuit and breathing bag. NOTE: For testing purposes always use a reusable breathing circuit. -
Page 155: Vcv Child Ventilation Mode Test
3.10.6 VCV Child Ventilation Mode Test 1. Attach a breathing circuit and breathing bag. NOTE: For testing purposes always use a reusable breathing circuit. 2. Attach an adult test lung to the Y-fitting of the breathing circuit. NOTE: Limit the volume in the test lung to provide sufficient airway pressure to satisfy the Low Peak Pressure alarm. -
Page 156: Pcv Adult Ventilation Mode Test
3.10.8 PCV Adult Ventilation Mode Test 1. Attach a breathing circuit and breathing bag. NOTE: For testing purposes always use a reusable breathing circuit. 2. Attach an adult test lung to the Y-fitting of the breathing circuit. 3. Attach a Vent Tester between the EXP port and the expiratory hose. 4. -
Page 157: Alarms And Fail Safe Functions
3.11.1 Set Up 1. Ensure that the gas pressure for O2, N2O, and AIR are is within specifications. 2. Power ON the A5/A3. 3. Perform the Startup Tests per the on-screen instructions. Ensure successful completion. 4. Attach a breathing circuit and breathing bag. -
Page 158: Low Fio2 Alarm Test
3.11.2 Low FiO2 Alarm Test 1. Set the Low FiO2 Alarm limit to 50%. 2. Set the AIR flow control valve to 5 L/min. 3. Set the O2 flow control to minimum flow. 4. Verify the following Low FiO2 alarm signals activate, within three ventilation cycles: ... -
Page 159: Minute Volume Alarm Test
Battery in use message appears on the screen. 3. Plug the A5/A3 into AC line voltage. 4. Verify that the alarm signals cease. 5. Verify the presence of the battery charging icon in the upper right corner of the screen. -
Page 160: Auxiliary Ac Outlets Test
Perform this inspection with all covers, panels, and screws installed. Verify AC voltage is present at each AC outlet with the A5/A3 3A Breaker in both the ON and OFF positions. 3.12.4 Anesthesia System Installation Checklist Refer to Chapter 2 Installation Guide for the installation checkout procedure. -
Page 161: Electrical Tests
Verify the scavenger is connected at the wall and the floater is between MIN and MAX. Mount the vaporizers and fill with anesthetic agent (if necessary). NOTE: Do not overfill by filling past the indicator line on the vaporizer. Turn on the Unit Test the vaporizer accuracy per the manufacturer’s instructions. -
Page 162: Convenience Ac Outlets Test
3.15.1 Convenience AC Outlets Test Verify AC voltage is present at each AC outlet with the A5/A3 system switch in both the ON and OFF positions. 3.15.2 Electrical Safety Inspection Test 1. Unplug the Power cable(s) from the convenience receptacles at the rear of the A5/A3. - Page 163 This page intentionally left blank. 3-38...
-
Page 164: Calibration
Calibration 4.1 Introduction This section provides detailed information required to properly test and calibrate the A5/A3 anesthesia system. Calibration consists of making mechanical and electrical adjustments with the proper test equipment. The instrument should be tested and calibrated after repairs have been completed or at regular intervals as part of a periodic maintenance procedure. -
Page 165: System Calibration
4.2.1.3 Notes NOTE: Only bacterial filters with a low flow resistance must be connected to the patient module and/or the patient connection. NOTE: Use surgical gloves whenever touching or disassembling valves or other internal components of the Breathing System. NOTE: Ensure that the gas supply of the machine always complies with the technical specification. -
Page 166: Flow Calibration (User)
Calibration item Functional description Calibration time Pressure Calibrate the pressure 1. The ventilator control board is calibration sensors and PEEP valve replaced. (Service) of the anesthesia 2. The expiratory valve assembly is machine. replaced. 3. The deviation between the measured value of the machine’s pressure sensor and that of the standard pressure gauge exceeds more than 5% of the reading or 2... - Page 167 Follow these steps to calibrate flow sensors. Enter Standby. Select Setup-> Calibrate-> Calibrate Flow Sensor (version 1.03.02 and earlier) or Setup-> Calibrate-> Calibrate Flow Sensor (version 2.01.00 and higher) to access the screen shown below. Set up the machine as per the instructions on the screen and select Next to open the menu shown below.
- Page 168 Select Begin to calibrate flow sensors. During the calibration, you can select Cancel to cancel the calibration. The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to do the calibration again. Select Done to exit the calibration screen.
- Page 169 The screen shown below is displayed if the flow sensor calibration is failed. Select Try Again to do the calibration again. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen shown below is displayed after a successful flow sensor calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen.
-
Page 170: Flow Calibration (Service)
4.3.2 Flow Calibration (Service) NOTE: Flow Calibration (Service) is necessary in case of replacing the ventilator control board, drive gas assembly or solenoid valve assembly. NOTE:When a great deviation is detected between the measured value of the built-in flow sensor and that of the standard flow measurement device, you need to perform Flow Calibration (Service). - Page 171 Enter Standby. Select Setup-> Service-> Calibration-> Flow Sensors to access the screen as shown. Select Calibrate Automatically button to open the menu shown below. Then select the desired calibration device.
- Page 172 Connect the calibration device with the anesthesia machine using a communication cable. Power cord for the Connector Board RS232 Connector to the Anesthesia machine Cable connections at the anesthesia machine end...
- Page 173 RS232 Connector to the Calibration Device RS232 Connector to the Anesthesia machine Power cord for the Connector Board Calibration Device Connector Board Cable connections at the calibration device (VT Plus ) end 4-10...
- Page 174 Set up the calibration device as described below. To set the VT-Plus: Gas Settings: Press the Setup button, select Setting->ENTER->Gas Settings- >MODIFY->Gas Type->O ->BACK->BACK. b. Zero Mode Settings: Press the Setup button, select Setting->ENTER->Zero Mode- >Manual->BACK->BACK. Serial Mode Settings: Press the Setup button, select Setting->System->Enter->Serial Mode ->OTIS Ctrl->BACK->BACK.
- Page 175 Press the Next button to open the menu shown below. 7. Connect the inspiration port and expiration port of the anesthesia machine following the on- screen instructions, shown below. Press the Begin button to open the menu shown below. 4-12...
- Page 176 The menu shown below is displayed after the above steps are completed. Connect the pneumatic circuit of calibration device with that of anesthesia machine following the on-screen instructions. Connect the low flow channel of the calibration device first, shown below. Pneumatic connection with the calibration device (VT Plus) 11.
- Page 177 12. The menu shown below is displayed after the low flow channel calibration is completed. 13. Connect the high flow channel of the calibration device following the on-screen instructions shown below. Pneumatic connection with the calibration device (VT Plus) 14. Press the Continue button to open the menu shown below. 4-14...
- Page 178 15. The screen shown below is displayed after the calibration is completed. The screen shown below is displayed if the flow sensor calibration is failed. When the calibration has failed, read the screen of the calibration device for further information on the cause of the failure.
- Page 179 16. The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to do the calibration again. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. Manual Calibration (01.03.00 and later) Follow these steps to calibrate flow sensors. Enter Standby.
- Page 180 Select Calibrate Manually button to open the menu shown below. Connect the inspiration port and expiration port of the anesthesia machine following the on-screen instruction by referring to step 7 of section Auto Calibration. Press the Begin button to open the menu shown below. 6.
- Page 181 Connect the low flow channel (If available) of calibration device with the pneumatic circuit of anesthesia machine following the on-screen instructions by referring to step 10 of section Auto Calibration. Determine when to switch to the high flow channel of calibration device. Refer to step 13 of section Auto Calibration on how to connect the high flow channel.
- Page 182 4-19...
- Page 183 The screen shown below is displayed if the flow sensor calibration is failed. 11. Select Cancel and the screen shown below is displayed. NOTE: After flow calibration, check the accuracy of flow sensors by referring to Section 3.7.4 Check the Flow Sensor Accuracy NOTE:In case of calibration failure, first fix the problem and then perform flow calibration again.
- Page 184 4.3.2.2 Commonly-encountered Problems and Recommended Actions Failure Possible cause Recommended action description After [Begin] is [Manual Vent.] is prompted. Set the Auto/Manual ventilation selected, no The Auto/Manual ventilation switch to the mechanical ventilation switch is set to the bag ventilation position. sound is heard.
- Page 185 Failure Possible cause Recommended action description [00 00 00 02] The drive gas pressure is too 1. Check the drive gas supply. is displayed. low. 2. If there is no problem on the gas supply, check the gas supply pressure switch. [00 00 00 04] The Auto/Manual switch is 1.
- Page 186 Failure Possible cause Recommended action description 2. Replace the inspiratory flow sensor. 3. Replace the board. 4-23...
- Page 187 Failure Possible cause Recommended action description [00 00 20 00] Resolution error occurs to the 1. Check if the sampling line is is displayed. expiratory flow sensor. properly connected. 2. Replace the expiratory flow sensor. 3. Replace the board. [00 00 40 00] Resolution error occurs to the 1.
-
Page 188: Pressure Calibration (Service)
4.3.3 Pressure Calibration (Service) NOTE: Pressure Calibration (Service) is necessary in case of replacing the ventilator control board, drive gas assembly or solenoid valve assembly. NOTE:When a great deviation is detected between the measured value of the built-in pressure sensor and that of the standard pressure measurement device, you need to perform Pressure Calibration (Service). - Page 189 Select Calibrate Automatically button to open the menu shown below. Connect the calibration device with the anesthesia machine using communication cable by referring to step 4 of Auto Calibration of 4.3.2.1Calibration Procedures Press the Next button to open the menu shown below. 4-26...
- Page 190 A four-way device is required to connect the sampling lines for pressure calibration. The following pictures show the four-way device, connectors on the calibration device and ventilator control board involved for pressure calibration. Four-way device connecting the sampling lines for pressure calibration a.
- Page 191 Pneumatic connections with the calibration device (VT-Plus) Let the anesthesia machine calibration device be powered and manually zero the calibration device first. Set up the calibration device Refer to step 5 of Auto Calibration of 4.3.2.1Calibration Procedures . Press the Next button to open the menu shown below. 4-28...
- Page 192 After selecting the desired auto calibration device, select Begin to access the calibration screen shown below. During the calibration, you can select Cancel to cancel the calibration. 10. The screens shown below are displayed after the calibration is completed. The screen shown below is displayed if the pressure sensor calibration is failed.
- Page 193 The screen shown below is displayed after a successful pressure sensor calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 11. The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to do the calibration again. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 4-30...
- Page 194 Manual Calibration NOTE: Manual calibration is available in software version 01.03.00 and later. Follow these steps to calibrate pressure sensors and PEEP proportional valve. Make sure that the anesthesia machine is in standby mode. Select Setup-> Service-> Calibration-> Pressure Sensors to access the screen shown below.
- Page 195 Press the Begin button to open the menu shown below. The menu shown below is displayed after the first step of manual calibration is completed. 4-32...
- Page 196 Select Continue to access the menu shown below. The system will calibrate the 32 calibration points one by one. Of the 32 calibration points, points 1 to 16 correspond to the rising curve while points 17-32 correspond to the falling curves. During the calibration, you can select to re-calibrate any calibration point.
- Page 197 The screen shown below is displayed if the pressure sensor calibration is failed. 10. Select Cancel and the screen shown below is displayed. NOTE:After pressure calibration, test the accuracy of pressure sensors by referring to 3.7.5 Check the Pressure Sensor Accuracy. NOTE:In case of calibration failure, first fix the problem and then perform pressure calibration again.
- Page 198 4.3.3.2 Commonly-encountered Problems and Recommended Actions Failure Possible cause Recommended action description After [Begin] is [Drive Gas Pressure Low] is Replace or connect the selected, no alarmed. The pressure indicated gas supplies to make sure ventilation sound is by the drive gas (O2) pressure that drive gas pressure is heard.
- Page 199 Failure Possible cause Recommended action description again.] is displayed. [00 00 00 02] is The drive gas pressure is too 1. Check the drive gas displayed. low. supply. 2. If there is no problem on the gas supply, check the gas supply pressure switch.
- Page 200 Failure Possible cause Recommended action description [00 00 40 00] is The system fails to write 1. Perform calibration displayed. EEPROM. again. 2. Replace the monitoring board. [00 00 80 00] is ACGO switch is on “ON” 1. Check if ACGO is displayed.
-
Page 201: Pressure And Flow Zeroing (Service)
4.3.4 Pressure and Flow Zeroing (Service) During the operation of the anesthesia machine, pressure and flow are zeroed automatically at a specific interval. You can also zero pressure and flow manually in the factory maintenance menu. Manual zeroing can eliminate the measurement deviations caused by zero offset immediately. - Page 202 The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing zeroing is cancelled. Select Try Again to do the zeroing again.Select Done to exit the zeroing screen. The screen shown below is displayed if the zeroing is failed. Select Try Again to do the zeroing again.Select Done to exit the zeroing screen.
-
Page 203: Electronic Flowmeter Zeroing (User)
The screen shown below is displayed after a successful zeroing. Select Done to exit the zeroing screen. NOTE:In case of zeroing failure, other faults may exist. You must isolate and eliminate the problem. 4.3.4.2 Troubleshoot Pressure and Flow Zeroing Failure In case of zeroing failure, troubleshoot as follows: Set the anesthesia machine to manual ventilation or standby mode. - Page 204 4.3.5.1 Zeroing Procedures Follow these steps to zero the electronic flowmeter. Select Setup-> Calibrate-> Zero Flow Meters to access the screen shown below. Set up the machine as per the instructions on the screen and select Begin to start zeroing. The zeroing screen shown below is displayed when Begin is selected.
- Page 205 The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing zeroing is cancelled. Select Try Again to do the zeroing again.Select Done to exit the zeroing screen. The screen shown below is displayed if the zeroing is failed. Select Try Again to do the zeroing again.Select Done to exit the zeroing screen.
-
Page 206: O2 Sensor Calibration
The screen shown below is displayed after a successful zeroing. Select Done to exit the zeroing screen. NOTE: In case of zeroing failure, other faults may exist. You must isolate and eliminate the problem. 4.3.5.2 Troubleshoot Electronic Flowmeter Zeroing Failure In case of zeroing failure, troubleshoot as follows: Disconnect the gas supplies. - Page 207 4.3.6.1 21% O2 Calibration Follow these steps to calibrate O2 sensor at 21% O2. Version 01.03.02 and earlier: Select Setup > Calibrate > Calibrate O2 Sensor or Setup > Service > Calibration > O2 Sensor to access the Calibrate O2 Sensor screen (see figure below).
- Page 208 The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to do the calibration again.Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen shown below is displayed if the calibration is failed. Select Try Again to do the calibration again.Select Done to exit the calibration screen.
- Page 209 The screen shown below is displayed after a successful calibration (in standby mode). Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen shown below is displayed after a successful calibration (in non-standby mode). Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 4-46...
- Page 210 4.3.6.2 100% O2 Calibration NOTE: Version 01.03.02 and earlier – The 100% O2 Calibration screen is accessed via Setup > Calibrate > Calibrate O2 Sensor and Setup > Service > Calibration > O2 Sensor NOTE: Version 02.01.00 and later – The 100% O2 Calibration screen is accessed via Setup > System >...
- Page 211 The calibration screen shown below is displayed when 100% is selected. Set up the machine as per the instructions on the screen. Wait 2 minutes and ensure that O2 cell voltage has stabilized at the maximum value for at least 30s. Select Begin. The calibration screen shown below is displayed when Begin is selected.
- Page 212 The screen shown below is displayed if the ongoing calibration is cancelled. Select Try Again to do the calibration again.Select Done to exit the calibration screen. The screen shown below is displayed if the calibration is failed. Select Try Again to do the calibration again.Select Done to exit the calibration screen.
- Page 213 10. The screen shown below is displayed after a successful calibration. Select Done to exit the calibration screen. 4.3.6.3 Commonly-encountered Problems and Recommended Actions Failure Description Possible Cause Recommended Action After [Start] is If the alarm [O2 Sensor Connect the O2 sensor. selected, calibration Unconnected] is displayed, it failure is prompted...
- Page 214 . Replace the O2 sensor. . Check that the O2 sensor is connected to 00 00 00 08 21% calibration value is the cable correctly. outside of the expected range . Check that the O2 sensor is in 21% O2. (150~500) .
-
Page 215: Orc Calibration
4.3.7 ORC Calibration Follow these steps to perform ORC calibration: Connect the anesthesia machine to the O2, AIR and N2O supplies. Close the O2, AIR and N2O needle valves. Switch the screen to Standby. Turn the N2O needle valve to the maximum position. Slowly turn the O2 needle valve to produce O2 flow of 0.3 L/min. - Page 216 O2 resister 4-53...
- Page 217 Keep the N2O needle valve at the maximum position. Close the O2 needle valve knob and then slowly open the O2 needle valve. Observe if the O2 flow falls within 0.25 to 03 L/min when the N2O flow begins. If not, repeat step 2 until the requirement is satisfied. 4-54...
- Page 218 Keep the N2O needle valve at the maximum position. Turn O2 flow to 3 L/min and observe N2O flow. If the N2O flow is less than 9 L/min, turn the N2O resistor on the ORC anti-clockwise with the flathead screwdriver until the N2O flow is 9 L/min. If the N2O flow is less than 9 L/min, turn the N2O resistor on the ORC clockwise with the flathead screwdriver until the N2O flow is 9 L/min.
- Page 219 Turn the O2, AIR and N2O needle valves to the maximum positions. Turn the AIR resistor on the pneumatic resistor block assembly to cause the AIR flow to fall within 15 to 15.5 L/min. Turn the N2O resistor on the pneumatic resistor block assembly to cause the N2O flow to fall within 10 to 10.5 L/min.
- Page 220 AIR resister 4-57...
- Page 221 N2O resister 4-58...
-
Page 222: Cylinder Yoke Regulator Calibration
4.3.8 Cylinder Yoke Regulator Calibration Follow these steps to perform cylinder yoke regulator calibration (the following takes N2O cylinder yoke assembly as an example. The calibration steps of O2 and Air cylinder yoke regulators are same to those of N2O). For O2 and Air, the pressure in the cylinder must be at least 1000 psi. - Page 223 Remove the sheet metal at the rear of the equipment. 3. Disconnect the hose connected to the pipeline assembly and attach it to the pressure meter (For O2 hose #59; for AIR hose #54; for N2O hose #62). 4. Set the fresh gas flow of the gas being adjusted to 1 L/min. 4-60...
- Page 224 Remove the self-locking acorn nut at the head of the regulator. Install the cylinder. Self-locking nut 4-61...
- Page 225 Turn on the gas supply. Rotate the regulator screw at the head slowly with a flathead screwdriver to adjust the pressure range (rotate clockwise to increase pressure value and counterclockwise to decrease pressure value) until the pressure after adjustment is within the range specified by the table (±5%).
-
Page 226: Repair And Troubleshooting
Repair and Troubleshooting 5.1 Troubleshooting Guidelines 5.1.1 Identify the problem Due to the wide variety of potential symptoms, certain problems may be more subtle than others. Following the guidelines of the tests will help determine the problem, if one exists. 5.1.2 Avoid shorting component leads together During repair procedures, it can be tempting to make a quick series of measurements. - Page 227 Power Board Runtime Alarm Fresh Flow Sensor Board Alarm Ventilation Control Board Runtime Alarm Before troubleshooting the anesthesia machine, check for technical alarm message. If an alarm message is presented, eliminate the alarm first. The following sections detail how to troubleshoot technical alarms related to the modules mentioned above.
-
Page 228: Startup Alarm Messages
5.2.1 Startup Alarm Messages Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Restart the machine. 2. Measure the 12V input voltage (voltage on the power cable) of the electronic flowmeter to see if it is DVCC, AVDD or within specifications. Check if the Flowmeter Voltage Error High VC voltage error... - Page 229 Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Restart the machine. 2. Measure the input voltage (voltage on the power cable) of the ventilator control module to see if it is within specifications. Check if 5V or 12V voltage the cable is defective. Ventilator Voltage Error High error...
- Page 230 Message Priority Cause Solution 5. Replace the expiratory valve assembly. 6. Replace the power board when necessary 1. Measure the voltage at the corresponding test point 2. Check the connection between power supply and expiratory valve assembly PEEP safety valve PEEP Safety Valve Failure 3.
- Page 231 Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Check if the zero point of the flow sensor is within specifications. 2. Check if the measurement performed by the flow sensor is Ventilator flow is within specifications. Flow Sensor Failure out of range. 3. Replace the flow sensor and perform calibration.
- Page 232 Message Priority Cause Solution ventilator control board and check the socket. 3. If the above two items are within specifications, replace the ventilator control board. Use the same method to drive gas O2 Supply Failure High O2 Supply Failure pressure low to check the O2 pressure switch.
-
Page 233: Cpu Board Runtime Alarm
5.2.2 CPU Board Runtime Alarm Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Set the IP address again. The IP address is same with other 2. If the problem persists, update IP Address Conflict machine in the local the system software code or network. - Page 234 Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Measure the voltage at the corresponding test point. 2. Disconnect the battery from the AC mains. After the power board processor is powered off for 5 Power Supply Voltage 3.3V, 5V, 12V minutes, power it on again. Repeat High Error voltage error...
- Page 235 Message Priority Cause Solution mains. 2. If the AC mains supply is connected correctly and the voltage is within specifications, check the connection between the AC mains and the power board. Check the AC mains inlet. 3. If the problem persists, replace the power board.
-
Page 236: Fresh Flow Sensor Board Alarm
Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Check the fan for the power module. Power board temp 2. Stop using the machine for a Power Board High Temp High is greater than 95 C period of time. If the problem persists after the machine is restarted, replace the power board. - Page 237 Message Priority Cause Solution valve at Max value. Measure fresh gas flow at the inspiration connector. Check the measurement error of electronic flowmeter. 3. If the problem persists, replace the flowmeter relative subassembly. O2 flow is greater Use the same method as “N2O O2 Flow Too High than 15L/min for 1 Flow Too High”...
- Page 238 Message Priority Cause Solution 3. Check the ORC for leakage. Connect the tubes again. If an error occurs, replace the ORC. 4. If the problem persists, replace the fresh flow sensor board. 1. Restart the machine. 2. Check the measurement correctness of flow sensors.
-
Page 239: Ventilator Control Board Runtime Alarm
5.2.5 Ventilator Control Board Runtime Alarm Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Restart the machine. 2. Re-plug or replace the communication cable between the CPU Board and the ventilator Lost control board. Aux Control Module communication High Comm Stop with CPU board for 3. - Page 240 Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Check if the inspiratory flow sensor is within specifications. Perform flow sensor calibration in the service menu or replace the flow sensor when the flow error. 2. Measure the voltage at the corresponding test point 1.
- Page 241 Message Priority Cause Solution board and perform calibration. 1. Check the check valve. 2. Check if the sampling lines of 1.Insp reverse flow the sensor are connected in correct Check Flow Sensors High 2.Exp reverse flow order. 3. Test the measurement status of the sensor in the valves test tool.
- Page 242 Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Check for breathing circuit leakage. 2. Check the measurement Ppeak doesn't reach accuracy of the pressure sensor. Pinsp Not Achieved the setting Pinsp in 3. Perform calibration in case of pressure mode. measurement failure. 4. Replace the ventilator control board and perform calibration.
- Page 243 Message Priority Cause Solution than 5% outputted in calibration menu. 2. Calibrate the O2 sensor again. 3. Replace the O2 sensor. O2 value is greater 1. Calibrate the O2 sensor again. than 110% or 2. Replace the O2 sensor. Calibrate O2 Sensor between 5% and 15% for 3 seconds.
- Page 244 Message Priority Cause Solution 1. Restart the machine. 2. Re-plug or replace the communication cable between the Lost CPU board and the ventilator communication control board. Ventilator Comm Stop High with CPU board for 3. If the problem persists, replace 10 seconds.
-
Page 245: Pneumatic Circuit System Problems
5.3 Pneumatic Circuit System Problems The pneumatic circuit system is mainly composed of anesthetic gas delivery system, anesthetic agent delivery device (vaporizer), anesthetic ventilator, breathing system and anesthetic gas scavenging system. This chapter details possible failures regarding the pneumatic circuit system and how to troubleshoot them. 5.3.1 Tools for on-site Maintenance The tools required for troubleshooting are listed below. - Page 246 Hand tools, Allen wrench set Metric Gas Flow Analyzer with 2% accuracy Communication box (required if using Fluke VT Plus Gas Flow Analyzer) Lucer adapter connector Ethernet Crossover Cable 0012-00-1392-06 USB flash drive 0992-00-0297-01 * = is part of the 115-009450-00 A5/A3 troubleshooting kit. 5-21...
- Page 247 The following pictures show the tools listed above. (2) (3) (4) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) (17) (18) (19) (1) PU tube (4X200); (2) PU tube (6X100); (3) PU tube (6X200); (4) PU tube (6X300); (5) PU tube (8X200); (6)Φ6 silicone tube; (7)Breathing tube; (8) 3106-04-06 adapter connector;...
- Page 248 Negative pressure ball: Circuit adapter test fixture: Flow sensor pressure sampling pipeline test fixture: 5-23...
- Page 249 Vaporizer manifold test fixture: Anesthesia machine calibration device: 5-24...
- Page 250 1 MPa (10bar) test pressure gauge: 5-25...
- Page 251 5.3.1.1 Precautions for Use of Circuit Adapter Test Fixture There are four connectors for pressure sampling lines and four 6 quick plug-in connectors with number marked on the circuit adapter test fixture, as shown below. Connector for 6 quick plug-in pressure sampling connector line...
- Page 252 The circuit adapter test fixture can be mounted either onto the circuit adapter or onto the removed breathing system. The following pictures show the test fixture mounted in position. 5-27...
- Page 253 If it is hard to install and remove the test fixture, apply a layer of KRYTOX lubricant to the seals (as shown below). Seal(082-000665-00) Seal(082-000667-00) Seal(M6M-010058---) 5-28...
- Page 254 5.3.1.2 Precautions for Use of Flow Sensor Pressure Sampling Pipeline Test Fixture There are two connectors for pressure sampling lines on the flow sensor pressure sampling pipeline test fixture, as shown below. Connector for pressure sampling line The connector for pressure sampling line can be connected with Φ6 silicone tubes. When using the flow sensor pressure sampling pipeline test fixture, remove the expiratory or inspiratory flow sensor from the breathing system first.
- Page 255 5-30...
- Page 256 5.3.1.3 Precautions for Use of Vaporizer Manifold Test Fixture When using the vaporizer manifold test fixture, remove the o-ring seal on the vaporizer manifold assembly. Then slide the test fixture onto the connector, as shown below. After the test fixture is slid on Before the test fixture is slid on Turn the knob clockwise until the bottom surface of the pressure head is in contact with the top surface of the connector, as shown below.
- Page 257 5.3.1.4 Precautions for Use of Negative Pressure Ball Besides one sealing cover, the negative pressure ball also has two one-way valves at its front end, as shown below. The built-in one is connected with the gas inlet of the ball which permits the gas come in only, and the exterior one only permits the gas come out.
-
Page 258: Gas Supplies And Drive Gas
5.3.2 Gas Supplies and Drive Gas The following table lists gas supplies and drive gas related failures. Failure description Possible cause Recommended action Leak The gas supply tube is Replace the gas supply tube or the seal at the damaged or the seal at connection. - Page 259 Failure description Possible cause Recommended action No “O2 Supply The gas pressure switch Adjust the pressure switch of the O2 supply Failure” alarm of the O2 supply inlet inlet assembly to cause O2 supply pressure to occurs when the O2 assembly is ineffective.
- Page 260 Turn on O2 pipeline supply and record the reading on the O2 pipeline pressure gauge. Observe the test pressure gauge. If the reading on the test pressure gauge is not within the range of 0.15 to 0.25 MPa (namely 1.5 to 2.5bar), adjust the regulator of the O2 supply inlet assembly to cause the reading on the test pressure gauge to reach 0.2 MPa (namely, 2bar).
- Page 261 more than 0.1 MPa (1bar), it indicates that the O2 pipeline pressure gauge is damaged. Handle this problem as described in the troubleshooting table. 10. Reconnect tube 39. Note 1: For numbers of all PU tubes, refer to Sections 1.2.3 and 1.2.4 Pneumatic Connections.
- Page 262 Turn on the N2O pipeline supply and record the reading on the test pressure gauge. If the difference between this reading and the reading on the N2O pipeline pressure gauge is more than 0.1 MPa (1bar), it indicates that the N2O pipeline pressure gauge is damaged.
- Page 263 Reconnect PU tube No.50 into the “Y” fitting. Reconnect tube 67. Pull out No.41 PU tube which connects the AIR supply inlet assembly to the AIR pipeline pressure gauge. Remove the tube end which connects AIR supply inlet assembly.. Connect 1MPa test pressure gauge to the outlet of AIR supply inlet assembly through “3106-04-06 adapter connector”.
- Page 264 Test procedures: Turn off the pipeline gas supply and bleed the residual pressure by pushing the O2 flush button. Disconnect tube 47. The end of the tube which connects pressure regulator assembly is pulled out but the other end is not pulled out. Connect one PU tube (8X200) to the O2 inlet of pressure regulator assembly and connect the other end of the PU tube and also the pulled-out end of tube 47 to the two connectors of “3140-08-00 Y piece”...
- Page 265 O2 supply inlet assembly is defective. Troubleshoot this problem as described in the relevant failure table. 11. Adjust the O2 flow regulator until O2 flow is approximately 0.5 L/min, causing the reading on the test pressure gauge to fall gradually to 0.2 MPa (2bar). 12.
- Page 266 5.3.2.3 Adjust the Pressure Switch Adjust the O2 supply pressure switch and drive gas pressure switch as described below. Use a flathead screwdriver to adjust the O2 supply pressure switch as shown below. Turn for small degrees each time such as 30 degrees. Note that turning the pressure switch clockwise will decrease its alarm limits and counterclockwise increase its alarm limits.
- Page 267 5.3.2.4 Adjust the Regulator of the Pipeline Gas Supply Inlet Assembly Pull up the knob cover of the regulator. Turn the cover clockwise to increase pressure or counterclockwise to decrease pressure, as shown below. Bleed the inside pressure of the pipeline gas supply inlet assembly after each pressure adjustment is made, using the Regulator Calibration hose (PN 0453-00-1216).
-
Page 268: Anesthetic Gas Delivery System
5.3.3 Anesthetic Gas Delivery System The following table lists anaesthetic gas delivery system related failures. Failure description Possible cause Recommended action Leak The O2 flush button assembly Replace the seal on the O2 flush leaks. button assembly or replace the O2 flush button assembly. - Page 269 Failure description Possible cause Recommended action The gas supplies cannot be The seal inside the system Replace the system switch. turned off after the machine switch assembly is damaged. is turned off. The machine cannot be The contact switch is Replace the contact switch of the powered on after turned on.
- Page 270 5.3.3.2 Leak Test of the Flowmeter Related Assembly Perform a leak test of the flowmeter related assembly (from flow regulator to total flowmeter) by using the following tools: Negative pressure ball (quantity:1) 3106-06-00 adapter connector (quantity:1) 3106-06-08 adapter connector (quantity:1) ...
- Page 271 Connect the other end of the negative pressure ball to the pulled-out end of No.25 PU tube through 3106-06-08 adapter connector, as shown below, and then flatten the negative pressure ball to remove the gas inside. Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds, it indicates that the total flowmeter assembly is damaged.
- Page 272 Occlude the pulled-out tube end on the total flowmeter by using 3126-08-00 tube plug. 10. Compress the negative pressure ball still connected to tube 25 to bleed the air inside. 11. Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds, it indicates that the total flowmeter leaks.
- Page 273 13. Occlude the pulled-out tube end on the back pressure regulator by using one 3126-08-00 tube plug and connect the negative pressure ball to the pulled-out end of No.26 PU tube through 3106-06-08 adapter connector. 14. Compress the negative pressure ball to bleed the air inside. 15.
- Page 274 20. Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds, it indicates that the gas mixer leaks. 21. For N2O branch, disconnect tube 32 and pull out its end connecting the sensor (disconnect tube 31 for AIR branch and tube 78 for O2 branch. 22.
- Page 275 24. Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds, it indicates that the flow sensor leaks. 25. For N2O branch, disconnect tube 49 and pull out its end connecting the needle valve (disconnect tube 51 for AIR branch and tube 45 for O2 branch).
- Page 276 5-51...
- Page 277 28. Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds, it indicates that the needle valve leaks. 5.3.3.3 Leak Test of the System Switch Assembly Perform a leak test of the system switch assembly by using the following tools: ...
- Page 278 Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds during one of the two tests, it indicates that the system switch assembly is damaged. 5.3.3.4 Leak Test of the Oxygen Ratio Controller(ORC) Perform a leak test of the ORC assembly by using the following tools: ...
- Page 279 NO. 33 PU tube NO. 46 PU tube Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds, it indicates that the Oxygen Ratio Controller is damaged. Handle this problem as described in the troubleshooting table. If not, continue the following test. Re-connect the tube.
- Page 280 Flatten the negative pressure ball to remove the gas inside. Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30 seconds, it indicates that the Oxygen Ratio Controller is damaged. Handle this problem as described in the troubleshooting table. 5-55...
- Page 281 5.3.3.5 Leak Test of the Vaporizer Manifold Assembly Perform a leak test of the vaporizer manifold assembly by using the following tools: Negative pressure ball (quantity:1) 3106-06-08 adapter connector (quantity:1) 3126-06-00 tube plug (quantity:1) PU tube (6X100) (quantity:1) ...
- Page 282 Release the negative pressure ball. If the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30s, it indicates that the rubber plain washers or its upper surface contacted mechanical surface are damaged. Handle this problem as described in the troubleshooting table. If not, continue the following tests.
- Page 283 10. Repeat step 5 and step 6 every time when the vaporizer manifold test fixture is transferred to the next position. Once the negative pressure ball is fully expanded within 30s, it indicates that the seal rings are damaged. If the two tests are both past, then the vaporizer manifold assembly and the four seal rings are OK.
-
Page 284: Breathing System
5.3.4 Breathing System The following table lists breathing system related failures. Failure description Possible cause Recommended action Leak The CO2 absorber canister is not Re-install the CO2 absorber canister. installed properly. Remove the sodalime at the sealing connection. Ensure the correct installation of sadalime canister. - Page 285 Failure description Possible cause Recommended action The seal for the valve cover of Replace the seal. the breathing valve assembly is damaged. The O2 sensor is not installed Re-install the O2 sensor and ensure its properly. correct installation. The seal for the O2 sensor or the Replace the seal.
- Page 286 Failure description Possible cause Recommended action The membrane of the flow Enter the service mode and calibrate sensor assembly is distorted, the flow sensor as per section dirty or its inside resistance 4.3.2Flow Calibration (Service). changes. Zero drift occurs to the pressure sensor of the fresh flow sensor board.
- Page 287 5.3.4.1 Leak Test of Flow Sensor Pressure Sampling Pipeline If the flow waveform is displayed irregularly, the flow sensor pressure sampling pipeline may be leaky. Perform the leak test by using the following tools: Anesthesia machine calibration device (quantity:1) ...
- Page 288 anesthesia machine calibration device does not fall more than 5cmH O within 15 s, this test is passed. II Leak test of the flow sensor pressure sampling pipeline inside the main unit (perform this test if test “I” fails) Mount the circuit adapter test fixture onto the circuit adapter assembly. Connect the Φ6 silicone tubes to the pressure sensor connector (positive pressure end) on the anesthesia machine calibration device), injector (before mounting, pull out the push rod of the injector) connector and the connector (one connector out of No.3...
- Page 289 5.3.4.2 Leak Test of Low-pressure Pneumatic Circuit System After making sure that the flow sensor pressure sampling pipeline is not leaky, perform leak tests of the low-pressure pneumatic circuit system as shown in the following figures (figures a through d). 1.
- Page 290 Check the lifting device and sealing components of the sodalime canister 7. Check the APL valve. Fail support tube on the medium plate, and sealing 2. Leak test of the 6. Check the 2. Leak test of the 5. Check the Completed Fail Fail...
- Page 291 (5) Occlude the inspiratory&expiratory ports and bag arm port by using three breathing tubes and one breathing tube Y piece as shown below. Turn on the O2 flow regulator and adjust O2 flow to 0.2L/min, (6) Push the O2 flush button to let the reading on the Paw pressure gauge rise to (7)...
- Page 292 (1) Remove the bellows. (2) Mount the bellows housing properly. Set the Auto/Manual ventilation switch to the Manual position (3) Remove the breathing system. (4) Mount the circuit adapter test fixture onto the breathing system. (5) (6) Connect the Φ6 silicone tubes and PU tube (6X300) to the injector connector, pressure sensor (of the anesthesia machine calibration device) connector (positive pressure end), and No.2 connector to which drive gas corresponds on the circuit adapter test fixture by using a Y piece, as shown below.
- Page 293 (3) Remove the breathing system. (4) Mount the circuit adapter test fixture onto the circuit adapter. Flatten the negative pressure ball to remove the gas inside. Then re-install the plug (5) to seal the ball. Connect the other end of the negative pressure ball to the No.7 connector (on the circuit adapter test fixture) fresh gas pipeline of the circuit adapter test fixture, as shown below.
- Page 294 (8) Select [Setup] → [Service] → [Diagnostic Tests] → [Valves] to set the A/D value of the PEEP valve to make PEEP exceed 50 cmH2O. Set the A/D value of the inspiratory valve to “0” to produce 0 L/min of flow. Set PEEP safety valve to ON, as shown below.
- Page 295 Check the absorb canister assembly Tools required: VT PLUS (quantity: 1) Lucer adapter connector (quantity: 1) Injector (quantity: 1) Φ6 silicone tube (quantity: 2) PU tube (6X300) (quantity: 1) Breathing tube (quantity: 3) Y piece (quantity: 1) ...
- Page 296 Connected to the Φ6 silicone tube Connected to the VT plus Turn the blue part to lock the connector to the VT plus Lucer adapter connector 5-71...
- Page 297 Lucer adapter connector Bypass off Lucer adapter connector Bypass on Check the seals on the two connections of the lifting device. It they are damaged, (6) replace the seal and then re-mount the lifting device onto the breathing system. Check the accessories and circuit inspiratory and expiratory parts Test procedures: Turn off the system switch.
- Page 298 (6) Remove the O2 sensor (if there is no O2 sensor, remove the plug where the O2 sensor should be installed). Check the seal and replace if damaged. (7) Remove the check valve dome. Check the seal and replace if damaged. Remove the bag arm.
- Page 299 (1) Turn off the system switch. (2) Pull out No.22 PU tube which connects the CGO assembly to the circuit adapter assembly. The end of the tube which connect the CGO assembly is pulled out but the other end is not, as shown below. Occlude the pulled-out tube end by using one 3106-10-00 adapter connector and (3)...
- Page 300 (6) Occlude the pulled-out tube ends by using 3126-06-00 and 3126-08-00 tube plugs, as shown below. Repeat steps 3 through 7 in “4 Leak test of all pipelines on the circuit adapter”. If (7) the test fails, it indicates the CGO assembly is damaged. Check the seals in the CGO assembly and replace any damaged seals.
-
Page 301: Tidal Volume
5.3.5 Tidal Volume The following table lists tidal volume inaccuracy related failures. Failure Possible cause Recommended action description Inaccurate tidal The flow sensor is not installed Re-install the flow sensor. volume properly. The setting of fresh gas flow is Adjust the fresh gas flow. inappropriate. - Page 302 The displayed TVe and TVi are In the valves test tool, compare the not the same. measurement error made by three sensors and judge whether to perform calibration as per 4.3.2 Flow Calibration (Service). In the above table, possible causes marked “*” are related to inaccurate measured values by flow sensors.
- Page 303 Set the A/D value of the inspiratory valve to cause the flow of inspiratory valve to reach a certain value. In this case, the flows measured by the ventilator flow sensor, inspiratory flow sensor, and expiratory flow sensor should be the same. Test multiple points by setting the A/D value of the inspiratory valve.
-
Page 304: Sensors And Valves Problems
5.4 Sensors and Valves Problems To use Diagnostic Tests to troubleshoot the sensors or valves related failures, you must be familiar with the one-to-one correspondence between the menu options on the Diagnostic Tests screen and the actual pneumatic circuit and hardware components. 5.4.1 Correspondence with Pneumatic Circuit Components The following figure shows the one-to-one correspondence between the sensors &... -
Page 305: Correspondence With Hardware Components
5.4.2 Correspondence with Hardware Components The following figure shows how the sampling lines of the sensors are actually connected on the ventilator control board. 5.4.3 Preparations before Using Diagnostic Tests Make the following preparations before using the valves-test tool to locate the valves or sensors related failures: Connect the pneumatic circuit according to the type of sensor or valve to be checked. -
Page 306: Connections And Measurement Of The Flow Sensors Problems
Check the A/D counts of the sensors in the valve-test tool menu, which are the zero points of the sensors. If the zero point of one sensor is outside of specifications, it indicates that the ventilator control board is defective. You need to replace the board. You can also detect the zero points of the sensors by referring to 3.7.3 Check the Sensor Zero Point. -
Page 307: Connections And Measurement Of The Pressure Sensors Problems
With the gradual increase of actual flow, the measured value of the flow sensor should also increase. Otherwise, the calibration data have errors. You need to calibrate the flow sensor again. Compared with the measured value of the standard flow measurement device (anesthesia machine calibration device), the measured value of the flow sensor should be accurate. - Page 308 If the A/D value of one sensor remains unchanged, it is possible that the sampling line of the sensor is not connected. The pressure of the airway pressure gauge should increase. If not, it is possible that the airway pressure gauge is defective. If sampling line connection errors are detected, re-connect the sampling lines and verify proper connection of all lines.
-
Page 309: Opening State Of The Inspiratory Valve Problems
5.4.7 Opening State of the Inspiratory Valve Problems By using [Diagnostic Tests], you can detect if the opening state of the inspiratory valve is correct. The methods for tube connections and settings of the anesthesia machine are the same as those for sampling line connections of the flow sensors. -
Page 310: Opening State Of The Peep Valve Problems
Switch off the PEEP safety valve. The pressure measured by the PEEP pressure sensor should drop to 0 cmH2O immediately. Switch on the PEEP safety valve again. The measured value of the PEEP pressure sensor rapidly restores almost the same value to that before PEEP safety valve is switched off. -
Page 311: Hardware And Electrical Problems
5.5 Hardware and Electrical Problems Failure description Possible cause Recommended action When switch ON, AC and power supply is not Check and make sure that the battery indicator lamps are connected batty AC power supply is connected not lit, the machine can not capacity is insufficient. - Page 312 Failure description Possible cause Recommended action The screen of anesthesia The cable connected to the Check and make sure that the machine can not be lit. inverter falls off. cable is connected properly. The inverter is damaged. Replace the inverter. The power board hardware Replace the power board.
- Page 313 Failure description Possible cause Recommended action detected, replace the valve or ventilator control board. Exiting Standby fails. The ventilator control board Replace the ventilator control hardware selftest is failed. board. Alarm messages The speaker is damaged. Replace the speaker. displayed on the screen but speaker cable Check and make sure that the...
- Page 314 Failure description Possible cause Recommended action Network connection The cables connected to Properly insert the cables. failed. the network connection board get loose The network cable is too Shorten the network cable. long. Recommended cable length is approximately 1.5 m. The network cable is used The network cable has two incorrectly.
- Page 315 Board (P/N: 801-0631-00025-00) or the Fresh Flow Sensor Board (P/N: 801-0631-00040-00). Connect the Ethernet port of the PC to the Ethernet port of the A5/A3 using the Ethernet Crossover Cable. Before running Mindray Patient Monitor System Update Tool 4.3, verify that the IP address of the PC is set to 192.168.23.1., and the Subnet mask is set to 255.255.255.0.
- Page 316 Upgrade Software: (1). From the Desktop, run the Mindray Anesthesia Machine and Ventilator Software Upgrade Tool 4.3 Icon. When the “Select Product Series” dialog is displayed select A Series followed by OK. Once the System Update Tool starts perform the following to update the software: (2).
- Page 317 Checksum, Version and Note are correct from the table above. If they are correct then click OK. (9). Turn on the A5/A3 unit on, wait at least ten seconds before proceeding to the next step. (10). Click “Start(Single)” on the Mindray Anesthesia Machine and Ventilator Software Upgrade Tool 4.0.
- Page 318 (15).Once the last file is upgraded turn off the A5/A3 unit and then restart A5/A3 unit. (16).Check the software version on the A5/A3 by clicking Setup then Service, enter the service password "789789" followed by Enter, then go to System Info and then SW Versions.
- Page 319 This page intentionally left blank. 5-94...
-
Page 320: Repair And Disassembly
Repair and Disassembly 6.1 Prepare for Disassembly 6.1.1 Tools During parts disassembly and replacement, the following tools may be required: Metric Allen wrench es (2.5, 3, 4, 5, 8mm) Phillips screwdriver (#1 and #2) Diagonal pliers Flathead screwdriver ... -
Page 321: Bleed Gas Pressure
6.1.3 Bleed Gas Pressure Make sure to bleed down the gas pressure inside the anesthesia machine before disassembling pneumatic fittings to avoid personal injury or equipment damage. To bleed gas pressure: Close other cylinder valves and disconnect pipeline gas supplies. Do not disconnect the O2 pipeline. - Page 322 6.2.1.2 Remove the Gas Supply Inlet Assembly 1.Open the service door. 2.Disconnect the tubes from the N2O, AIR and O2 supply inlet assemblies. 3.Unscrew the two screws from the N2O and AIR supply inlet assemblies. 4.Unplug the related cables from O2 supply inlet assembly and unscrew the two screws to remove the assembly.
- Page 323 6.2.1.4 Remove the Electronic Flowmeter Assembly 1.Open the service door. 2.Unplug the related cables and tubes from the electronic flowmeter. 3.Unscrew the four screws and remove the electronic flowmeter. 6.2.1.5 Remove the Poppet Valve Assembly 1.Open the service door. 2.Unplug the tubes from the poppet valve assembly. 3.Unscrew the two screws on the valve to remove the poppet valve.
- Page 324 6.2.1.6 Remove the Gas Mixer Assembly 1.Open the service door . 2.Unplug the tubes from the gas mixer assembly. 3.Unscrew the four screws on the gas mixer assembly to remove the assembly. 6.2.1.7 Remove the ORC Assembly 1.Open the service door. 2.Unplug the tubes from ORC assembly.
- Page 325 6.2.1.8 Remove the Back Pressure Valve Assembly 1.Open the service door . 2.Unplug the tubes from back pressure valve assembly. 3.Unscrew the four screws on the back pressure valve assembly to remove the assembly.
- Page 326 6.2.1.9 Replace the Lithium-ion battery 1.Open the service door. 2.Unscrew the two screws on the battery box cover, and then you can take out the lithium-ion battery. 3.Place the new lithium-ion battery into the battery box in the original direction to complete battery replacement.
-
Page 327: Disassemble Hardware Box
6.2.2 Disassemble Hardware Box 6.2.2.1 Remove the Top Plate of the Hardware Box 1.Unscrew the three screws from the top plate of the hardware box. 2.Lift off the top plate to remove it. 6.2.2.2 Remove the CPU Board NOTE: When replacing the CPU Board, software reinstallation may be required. 1.Remove the top plate assembly. - Page 328 6.2.2.3 Remove the Ventilator Control Board NOTE: When replacing the Ventilator Control Board, software reinstallation may be required. 1.Remove the top plate assembly. 2.Unplug the related cables and tubes from the ventilator control board. 3.Unscrew the four screws fastening the ventilator control board to remove it. Refer to the Section 1.2.5 Connections Between Pneumatic Circuit, Breathing System and Ventilator Control Board.
- Page 329 6.2.2.4 Remove the Power Board 1.Disassemble the top panel assembly. 2.Unscrew the four screws fastening the power board to remove the board. 6-10...
- Page 330 6.2.2.5 Remove the Three-Way Valve 1.Remove the top plate assembly. 2.Unplug the related tubes and cables from the three-way valve. 3.Unscrew the four screws on the three-way valve to remove the valve. Refer to the Section 1.2.5 Connections Between Pneumatic Circuit, Breathing System and Ventilator Control Board.
- Page 331 6.2.2.7 Disassemble the Rear Panel Assembly 1.Remove the top plate assembly. 2.Remove the cables and tubes from the hardware box assembly and other A5/A3 assemblies. 3.Unscrew the eight screws on the hardware box and lift off the hardware box to remove it.
- Page 332 Remove the Fan 1.Remove the rear panel of hardware box. 2.Unscrew the four screws on the fan to remove the fan. Remove the Filter 1.Remove the rear panel assembly of hardware box. 2.Unscrew the five screws on the filter to remove the filter. 6-13...
- Page 333 1.Remove the rear panel assembly of the hardware box. 2.Unscrew the screw on each auxiliary outlet cover plate to remove the cover plate(s). The figure bellow shows the auxiliary outlet cover plates (2) of the A5. The cover plate of the A3 is a single plate.
-
Page 334: Disassemble The Work Surface
6.2.3 Disassemble the Work Surface 6.2.3.1 Remove the Drawer Assembly 1.Pull out the drawer until the black locking piece on the rail can be seen. 2.Lift up the locking piece on the right rail of drawer, and press down on the locking piece on the left rail at the same time. - Page 335 6.2.3.2 Remove the Work Surface Cover Plate 1.Remove the first drawer. 2.Unscrew the five screws on the work surface cover plate. 3.Lift off the cover plate from the work surface. When the cover plate is removed, the internal structure of the work surface is shown as below: 6-16...
- Page 336 6.2.3.3 Remove the Metal Cover Plate 1.Remove the work surface cover plate. 2.Unscrew the eight screws on the metal cover plate to remove the cover plate. 6.2.3.4 Remove the Rear Panel Assembly 1.Rotate the cylinder’s yoke to remove the cylinder. 2.Unplug the AGSS transfer tube connecting to the exhaust tube and refer to 6.2.8.
- Page 337 4.Unscrew the four screws on the upper rear panel (yoke cover) to remove it. 6.2.3.5 Remove the Expiration Valve Assembly 1.Remove the work surface cover plate . 2.Unplug the tubes from the expiration valve assembly. 3.Unscrew the four screws on the expiration valve assembly to remove the assembly. 6-18...
- Page 338 6.2.3.6 Remove the O2 Flush Assembly 1.Remove the work surface cover plate . 2.Remove the metal cover plate . 3.Unplug the tubes from the O2 flush assembly. 4.Unscrew the two screws on the bracket and remove it. 5.Remove the metal post on the right side of the O2 flush assembly. 6.Unscrew the five screws around the O2 flush assembly to remove it.
- Page 339 6.2.3.7 Remove the Touch Panel (A5 Only) 1.Remove the work surface cover plate. 2.Remove the metal cover plate. 3.Unplug the touch panel data cable. 4.Remove the six screws on the touch panel to remove the panel. 6.2.3.8 Remove the Common Gas Outlet Assembly 1.Remove the work surface cover plate.
- Page 340 6.2.3.9 Remove the Cylinder Bracket Assembly 1.Open the service door and refer to 6.2.1.1. 2.Remove the rear panel and refer to6.2.3.4. 3.Unplug the tubes from the cylinder bracket assembly. 4.Remove the copper pipe from cylinder bracket assembly. 5.Remove the four screws on the cylinder bracket to remove the assembly. 6.Unscrew the four screws on the cylinder bracket to remove O2, N2O and AIR cylinder bracket assemblies.
-
Page 341: Disassemble The Display
6.2.4 Disassemble the Display 1.Open the service door and refer to 6.2.1.1. 2.Remove the related cables and tubes from hardware box and remove the four mounting screws to remove the display. 6.2.4.1 Remove the Alarm Lamp Board 1.Remove the display assembly. 2.Unplug the related cables from the alarm lamp board. - Page 342 6.2.4.2 Remove the Display Adaptation Board 1.Remove display assembly and refer to 6.2.4. 2.Unscrew the five screws on the cover plate of the display mount. 3.Unplug the related cables from the display interface board. 4.Remove the four screws on the display interface board and remove the board. 6-23...
- Page 343 6.2.4.3 Remove the Touch Screen Control Board 1.Remove display assembly. 2.Remove the four screws and the cover plate of the touch screen control board. 3.Unplug the related cables from the touch screen control board. 4.Remove the two screws on the touch screen control board to remove the board. 6-24...
- Page 344 6.2.4.4 Remove the Backlight Inverter Board 1.Remove display assembly. 2.Remove the four screws and the cover plate of the backlight inverter board. 3.Unplug the related cables from the backlight inverter board. 4. Remove the two screws on the backlight inverter board to remove the board. 6-25...
- Page 345 6.2.4.5 Remove the Needle Valve Assemblies 1.Remove display assembly and refer to 6.2.4. 2.Loosen the two Allen set screws on the knob of needle valve to remove the knob. 3. Remove the two screws on the needle valve assembly to remove the assembly. 6.2.4.6 Remove the Touch Screen 1.Remove display assembly.
- Page 346 3. Remove the 11 screws around the display mount then remove the display front cover. 4.Slightly lift the touch screen off the display front cover to remove the touch screen. 6-27...
-
Page 347: Remove The Panel Of Pressure Gauges
6.2.4.7 Remove the Display Replacement Package 1.Remove the display interface board. 2.Remove the touch screen control board. 3.Remove the touch screen. 4.When the above mentioned assemblies are removed from the display, the remaining part is considered the display replacement package. 6.2.5 Remove the Panel of Pressure Gauges 1.Open the service door and refer to 6.2.1.1. - Page 348 5. Remove the four screws on the gauge panel to remove the panel. 6.2.5.1 Remove the Pressure Gauges 1.Remove the pressure gauge panel . 2.Unscrew the 12 screws on the pressure gauges to remove both the supply gas gauges and the high-pressure gauges.
- Page 349 6.2.5.2 Remove the Total Flowmeter 1.Remove the meter panel. 2. Remove the four screws on the total flowmeter and to remove it 6.2.5.3 Remove the System Switch 1.Remove the pressure gauge panel. 2. Remove the four screws on the system switch to remove the switch. 6.2.5.4 Remove the Indicator Light Board 1.Remove the pressure gauge panel.
-
Page 350: Remove The Auxiliary Gas Outlet Assembly
6.2.6 Remove the Auxiliary Gas Outlet Assembly 1.Open the service door and refer to 6.2.1.1. 2.Unplug the related tubes from auxiliary gas outlet assembly. 3. Remove the two screws on the auxiliary gas outlet assembly to remove the assembly. 6.2.7 Remove the Rotating Block of Breathing Circle 1.Remove the work surface cover plate and refer to 6.2.3.2. -
Page 351: Remove The Agss Assembly
2.Lift up the AGSS assembly along the fixed slide block to remove the assembly. 6.2.9 Disassemble the Base Assembly 6.2.9.1 Remove the Caster Assembly 1.Remove the breathing system and tilt the A5/A3 backward. 2. Remove the four screws and remove the caster assembly. 6-32... - Page 352 6.2.9.2 Remove the Brake Indicator Drive Plate I and II (A5 Only) 1.Tilt A5/A3 backward. 2.Unscrew the two screws on the brake indicator drive plate I to remove the plate. 3.Unscrew the one screw on the brake indicator drive plate II to remove the plate.
-
Page 353: Disassemble The Breathing System
1.Tilt A5/A3 backward. 2.Remove brake assembly. 3. Remove the six screws and remove the brake main axis. 6.2.9.5 Remove the Principal Axis of Brake (A5 Only) Tilt A5/A3 backward. Remove the brake indicator drive plate II. Unscrew the six screws on the brake rod to remove the rod. -
Page 354: Remove The Breathing Tubes
Turn the black plug counterclockwise to take it out of the housing.And then turn the O2 sensor counterclockwise to take it out of the threaded cup. 6.3.2 Remove the Breathing Tubes NOTE :When disassembling the breathing tube, hold the tube connectors at both ends of the tube to prevent damage to the tube. -
Page 355: Remove The Flow Sensor
6.3.3 Remove the Flow Sensor Turn the locking nuts counterclockwise. Pull out the inspiration and expiration connectors together with their locking nuts. And then pull out the flow sensors horizontally. 3.The following pictures show the appearance of inspiratory and expiratory flow sensor assemblies. -
Page 356: Remove The Manual Bag
6.3.4 Remove the Manual Bag Remove the manual bag from the connector on the breathing system as shown below. 6.3.5 Remove the Absorbent Canister 1. Hold and turn the rotary handle clockwise for 45 degrees. 2. Pull out the absorbent canister horizontally. WARNING :Sodalime is a caustic substance and is a strong irritant to eyes, skin and respiratory system. -
Page 357: Remove The Co2 Bypass Assembly
6.3.6 Remove the CO2 Bypass Assembly 1. Remove the absorbent canister as per section 6.3.5。 2. Press inward the fasteners on both sides and the CO2 bypass assembly will drop down for removal. 6.3.7 Remove the drain valve Remove the CO2 bypass assembly as per the section 6.3.6. Lift up and remove the CO2 Absorber Base. -
Page 358: Remove The Bypass Valve And The Trigger Board
Drain Valve Stem Drain Valve Body 6.3.8 Remove the Bypass Valve And the Trigger Board Remove the CO2 Bypass assembly as per section 6.3.6。 Remove the transfer tube. Unscrew the four screws as shown in the picture and remove the cover plate. 6-39... - Page 359 Unscrew the four screws as shown in the picture and remove the upper bypass cover. Unscrew the two screws as shown in the picture and remove the trigger board. CO2 Bypass Valve Trigger board Remove the cramp ring to take out the valve needle. Snap ring Valve Seal 6-40...
-
Page 360: Remove The Patient Circle Assembly
6.3.9 Remove the Patient Circle Assembly Remove the CO2 Bypass assembly as per section 6.3.6。 2. Pull the patient circle assembly away from the rotating block assembly. 6.3.10 Remove the Bellows Assembly 1. Turn the bellows dome counterclockwise and lift off to remove. 2. -
Page 361: Remove The Pop-Off Valve Assembly
6.3.11 Remove the Pop-off Valve Assembly Remove the bellows assembly as per section 6.3.10. Unscrew the four locking screws as shown in the picture . Hold and pull up the Pop-Off valve cover to remove it.。 3. Take out the rubber and metal Pop-Off valve. 6-42... -
Page 362: Remove The Water Collection Cup
6.3.12 Disassemble the Expiratory/Inspiratory Check Valve Assemblies 1. Turn the check valve cover counterclockwise to remove it. 2. Pull out the check valve as shown in the following picture. 6.3.13 Remove the Water Collection Cup 1. Hold the water collection cup and turn it counterclockwise to remove it. 6-43... -
Page 363: Remove The Airway Pressure Gauge
2. Remove the water collection cup. 6.3.14 Remove the Airway Pressure Gauge Lift the airway pressure gauge straight up to remove it. 6.3.15 Remove the Bag Arm 1. Unscrew the locking nut counterclockwise and lift straight up to remove bag arm. 6-44... -
Page 364: Remove The Back Upper Cover And Back Lower Cover Assemblies
2. Remove the bag arm from the bag arm mount. 6.3.16 Remove the Back Upper Cover and Back Lower Cover Assemblies 1. Remove the O2 sensor, breathing tubes, manual bag, patient circuit assembly, bellows assembly, water collection cup, airway pressure gauge and bag arm as per sections 、... -
Page 365: Remove The Front Upper Cover, Median Plate And Front Lower Cover Assemblies
4. Turn over the circle. Pull up to separate the back upper cover assembly. 5. Pull leftwards to take out the back lower cover assemblies. 6.3.17 Remove the Front Upper Cover, Median Plate and Front Lower Cover Assemblies 1. Remove the Back Upper Cover and Back Lower Cover Assemblies as per section 6.3.16. 2. - Page 366 3. Loosen the six screws on the upper cover. 4. Loosen the captive screws on the upper cover. 5. Hold the upper cover assembly tightly and pull it up to remove it. 6-47...
-
Page 367: Disassemble The Automatic/Manual Ventilation Switch Assembly
6. Remove the spring washer and plain washer (Note: pay special attention to the spring washer and plain washer when removing them because they easily get loose). 7. Pull up the median plate assembly to remove it. The Median Plate Assembly The Lower Cover Assembly... - Page 368 3. Unscrew the three screws as show in the picture. 4. Remove the O-Ring and pull out the axis pin. Take out the seal and pull out the axis pin Compression spring Axis 5. Remove the compression spring and replace the two seals ( 0030-10-13077) Seal 6-49...
-
Page 369: Remove The Apl Valve Assembly
6.3.19 Remove the APL Valve Assembly Turn the locking ring counterclockwise and pull the APL valve assembly straight up to remove it. 6-50... -
Page 370: Replacement Parts
Replacement Parts 7.1 Introduction The A5/A3 anesthesia system can be broken down into 18 big parts based on its structure and function. Each big part includes several replaceable parts. Tables 8-1 through 8-18 list the information about each replaceable part and Figures 8-1 through 8-14 indicate the position of each replaceable part on the A5/A3. -
Page 371: Diagrams And Tables
801-0631-00077-00 Total Flow meter 801-0631-00008-00 N2O Pressure Gauge Assembly (0~140psi) 801-0631-00011-00 Air Pressure Gauge Assembly (0~140psi) 801-0631-00010-00 System Switch Knob 801-0631-00012-00 O2 Pressure Gauge Assembly (0~140psi) 801-0631-00009-00 Storage Mount for Vaporizer (A5 only) (A3 optional) 801-0631-00076-00 Vaporizer Mounting Manifold 801-0631-00024-00... - Page 372 Rear Door 801-0631-00037-00 Oxygen Cylinder Yoke Assembly 801-0631-00048-00 Air Cylinder Yoke Assembly 801-0631-00049-00 Nitrous Oxide Yoke Assembly 801-0631-00050-00 Caster Assembly (right) (A5 only) 801-0631-00073-00 Caster Assembly (FRU) (A3 only) 801-0633-00001-00 Caster Assembly (left) (A5 only) 801-0631-00071-00 AGSS Transfer Tube 801-0631-00074-00...
-
Page 373: A5/A3 Upper Half
7.3.2 A5/A3 Upper Half FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Resister block assembly 801-0631-00119-00 ORC Assembly 801-0631-00041-00 Nitrous Oxide Inlet Assembly 801-0631-00034-00 Air Inlet Assembly 801-0631-00035-00 Oxygen Inlet Assembly 801-0631-00036-00 N2O Regulator Assembly 801-0631-00086-00 O2 & AIR Regulator Assembly 801-0631-00087-00 Oxygen System Switch... -
Page 374: A5/A3 Hardware Box
Speaker and Connecting Cable 801-0631-00038-00 Auxiliary AC Output Socket (NEMA 5-15) 801-0631-00032-00 Breaker (3.0A) 801-0631-00031-00 Breaker (10.0A) (A5 only) 801-0631-00030-00 Filter Power 250VAC 10A Panel Mount (A5 only) 801-0631-00029-00 Filter (0633) (FRU) (A3 only) 801-0633-00003-00 801-0631-00028-00 Power Board PCBA 801-0631-00025-00 Flow Channel 042-002414-00 Cell battery Lithium-ion 3V35mAh D12.5*2.0... -
Page 375: A5/A3 Work Surface
7.3.4 A5/A3 Work Surface FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION (English) PART NUMBER Docking Station Switch 801-0631-00101-00 Auto/Manual spring 801-0631-00114-00 Auto/Manual pin 801-0631-00113-00 Circuit Heater 801-0631-00069-00 Docking Station Cover 801-0631-00068-00 O2 Connector 801-0631-00067-00 O2 Flush Assembly 801-0631-00044-00 Common Gas Outlet 801-0631-00045-00 Track Pad (A5 only) -
Page 376: A5/A3 Patient Circuit Main Body
7.3.5 A5/A3 Patient Circuit Main Body FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Bellows Dome, A series 801-0631-00054-00 Bellows Assembly, A series 801-0631-00055-00 Airway pressure gauge, A series 801-0631-00064-00 Expiratory Flow Sensor Assembly, A series 801-0631-00056-00 Inspiratory / Expiratory Connector, A series 801-0631-00057-00... -
Page 377: A5/A3 Pre-Pak Absorber Canister Assembly
7.3.6 A5/A3 Pre-pak Absorber Canister Assembly FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER CO2 Absorber Hose, A series 801-0631-00092-00 CO2 Absorber Base Drain Valve, A series 801-0631-00112-00 CO2 Absorber Base, A series 801-0631-00100-00 CO2 Absorbent Canister, A series 801-0631-00066-00 CO2 Bypass Assembly, A series... -
Page 378: A5/A3 Valve Assembly
7.3.7 A5/A3 Valve assembly FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Check valve dome, A series 801-0631-00061-00 Valve cover 801-0631-00110-00 Disc 801-0631-00111-00... -
Page 379: A5/A3 O2 Cable Assembly
7.3.8 A5/A3 O2 Cable Assembly FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER O2 cell cover 801-0631-00090-00 Sensor Oxygen (O2 sensor) MedicelMOX-2 0611-10-45654 O2 Cell Cable 801-0631-00091-00 7-10... -
Page 380: A5/A3 Display Assembly
7.3.9 A5/A3 Display Assembly FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Needle Valve Assembly 801-0631-00020-00 Knob of N2O Needle Valve 801-0631-00021-00 Knob of Air Needle Valve 801-0631-00022-00 Knob of O2 Needle Valve 801-0631-00023-00 7-11... -
Page 381: A5/A3 Display Assembly Main Body
7.3.10 A5/A3 Display Assembly Main Body FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Warning Light Board PCBA 801-0631-00019-00 Touch Screen 801-0631-00014-00 Display Exchange Package 801-0631-00075-00 Touch Screen Control Board 801-0631-00018-00 Display Interface Board PCBA 801-0631-00017-00 7-12... -
Page 382: A5/A3 Vaporizer Mounting Minifold
7.3.11 A5/A3 Vaporizer Mounting Minifold FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Connector (Vaporizer Mount) 801-0631-00117-00 Valve of Vaporizer Mounting Manifold 801-0631-00106-00 Spring of Vaporizer Mounting Manifold 801-0631-00107-00 7-13... -
Page 383: A5/A3 Auxiliary Gas Outlet Assembly
7.3.12 A5/A3 Auxiliary Gas Outlet Assembly FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Aux Gas Supply Flow Meter Lighting Board PCBA 801-0631-00002-00 Auxiliary Gas Outlet Fittings(FRU) 801-0631-00122-00 7-14... -
Page 384: Base Assembly (A5)
7.3.13 Base Assembly (A5) FIG.NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Brake Assembly (A5 only) 801-0631-00094-00 Connector of Brake (A5 only) 801-0631-00095-00 Indicator Drive Plate (A5 only) 801-0631-00072-00 Principal Axis of Brake (A5 only) 801-0631-00096-00 Base of Chasis Assembly (A5 only) 801-0631-00097-00 7-15... -
Page 385: Other
PART NUMBER Waste Gas Hose for Gas module to Colder fitting 801-0631-00078-00 Gas Cylinder Wrench 801-0631-00079-00 A5/A3 Pre-Operation Checklist, English 801-0631-00081-00 A5/A3 Auxiliary O2/Air Reference Card 801-0631-00082-00 – Preventative Maintenance Kit (12 months) 801-0631-00084-00 – Preventative Maintenance Kit (36 months) -
Page 386: Tubes (A5/A3)
7.3.15 Tubes (A5/A3) DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER Tube.PU (polyether) 5.5mmX8mm green 082-000521-00 Tube.PU (polyether) 4mmX6mm green 082-000522-00 Tube.PU (polyether) 2.5mmX4mm green 082-000523-00 Tube.PU (polyether) 5.5mmX8mm orange 082-000517-00 Tube.PU (polyether) 2.5mmX4mm orange 082-000518-00 Tube.PU (polyether) 4mmX6mm orange 082-000520-00 Tube.PU (polyether) 2.5mmX4mm blue 082-000516-00 Tube.PU (polyether) 4mmX6mm blue... -
Page 387: O-Rings (A5/A3)
7.3.16 O-rings (A5/A3) DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER REMARK Seal,valve port 049-000140-00 for CO2 Bypass shaft Gaskte,CO2 bypass 049-000142-00 assembly Gasket,absorber canister 049-000143-00 exterior Gasket,absorber canister 049-000145-00 interior CO2 Absorber Hose 049-000146-00 Bellow check valve 049-000240-00 membrane Gasket, bellows canister 049-000243-00 base... -
Page 388: Yellow Number Rings (A5/A3)
7.3.17 Yellow Number Rings (A5/A3) DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER wire fixed.EC-2 char0 M6P-050037--- wire fixed.EC-2 char1 M6P-050038--- wire fixed.EC-2 char2 M6P-050039--- wire fixed.EC-2 char3 M6P-050040--- wire fixed.EC-2 char4 M6P-050041--- wire fixed.EC-2 char5 M6P-050042--- wire fixed.EC-2 char6 M6P-050043--- wire fixed.EC-2 char7 M6P-050044--- wire fixed.EC-2 char8... - Page 389 This page intentionally left blank. 7-20...
-
Page 390: Warranty
Mindray DS USA, Inc.’s option at the factory or at an authorized Distributor, any product which shall under normal use and service appear to the Company to have been defective in material or workmanship. -
Page 391: Disclaimers
A condition of this warranty is that this equipment or any accessories which are claimed to be defective be returned at Mindray DS USA, Inc.’s option to Mahwah, New Jersey or to an authorized Distributor, when authorized by Mindray DS USA, Inc., freight prepaid to the designated servicing location. - Page 392 This page intentionally left blank.
- Page 393 046-001141-00 Rev C October 10, 2011...
- Page 394 Hoevelaken • The Netherlands • Tel: +31 33 25 44 911 • Fax: +31 33 25 37 621 Mindray (UK) Limited • 3 Percy Road • St. John’s Park • Huntingdon • Cambridgeshire PE29 6SZ • United Kingdom • Tel: 01480 416840 • Fax: 01480 436588 Mindray Medical France SARL •...
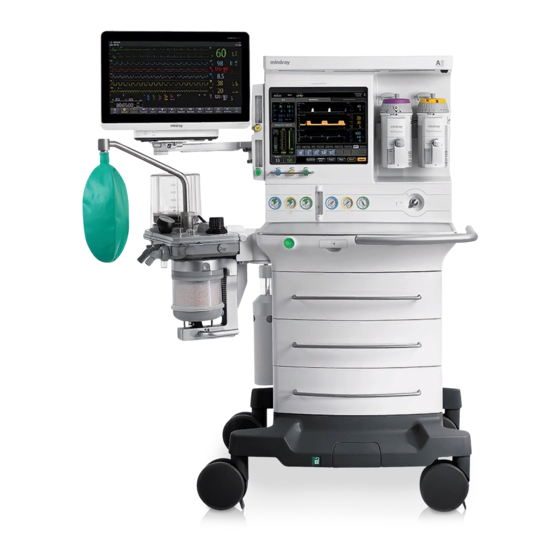














Need help?
Do you have a question about the A5 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers